Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Summary – Back Muscles
-
Slides 03 Abdominal Wall Canby.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
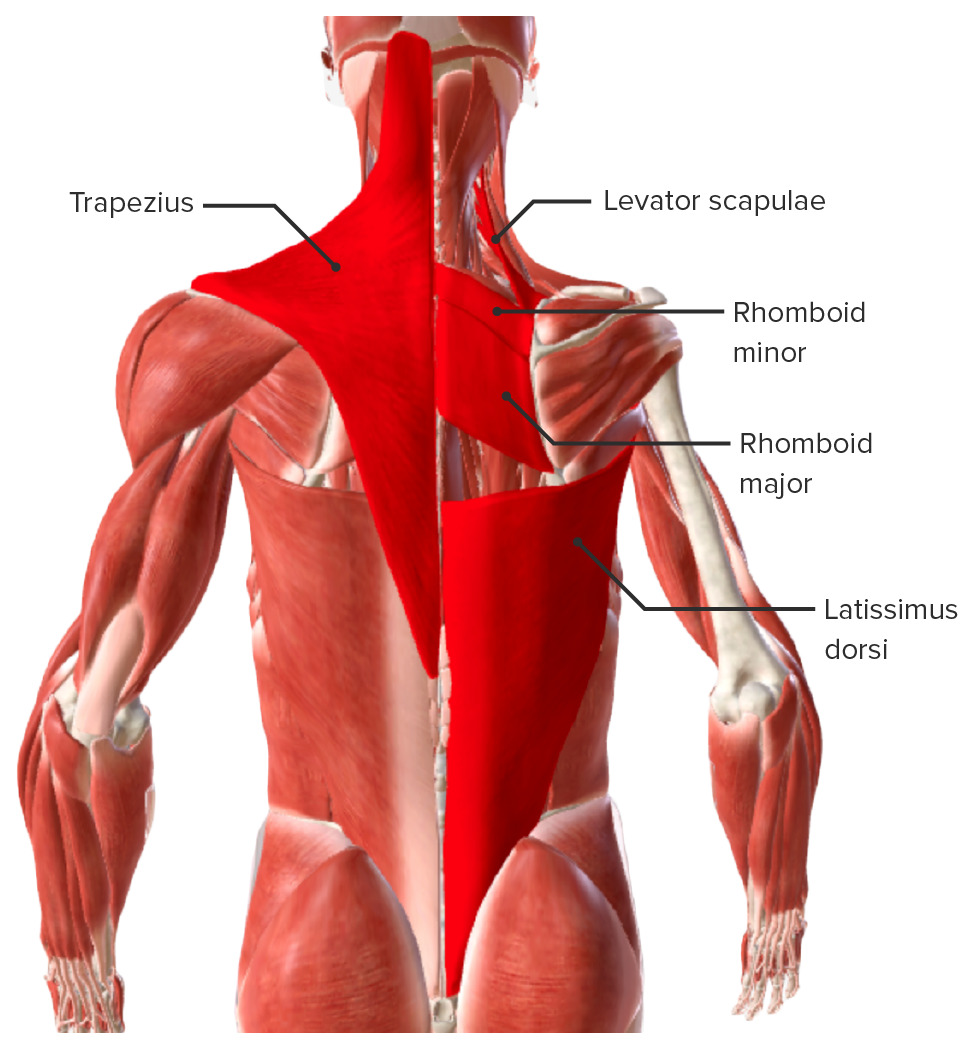
00:00 Now, that brings us to the key take-home messages from this presentation. 00:05 First, skin, fascia, three layers of muscles - superficial, intermediate and deep, neurovascular structures, ribs, vertebral column and spinal cord with its attendant meninges constitute the back. 00:23 Back muscles principally attach to the skull, vertebral column, the scapula region and the humerus. 00:29 Back muscles are arranged in three layers - superficial, intermediate and deep. 00:35 Superficial and intermediate muscles are innvervated by named anterior rami of spinal nerves with the exception of trapezius which is a cranial nerve. 00:44 Deep muscles are innervated by unnamed, usually, posterior rami of spinal nerves, certainly an exception was the suboccipital nerve that was named. 00:57 Four muscles constitute the suboccipital group. We have two recti - major, minor and two obliques - superior and inferior. 01:06 The rectus major and both obliques form the borders of the suboccipital triangle and for most part the innervation and blood supply to the muscles of the back is segmental. 01:21 Thank you for following along throughout this course. We have had great opportunities to explore the complexity, the beauty and all of human anatomy. We have looked at osteology, we have looked at musculature and we have looked at various neurovascular components that collectively form and construct what we know as a human being. The best way to learn anatomy is to kind of break it down into its components, understand the concepts and once you have a firm mastery of the concepts then you can start to build on layers of detail. 02:02 And certainly, we did not have time within the scope of this course to get into a lot of detail, but hopefully, I have prompted your curiosity, your intellectual curiosity and you will want to search out some of this detail once you have a nice grasp of the the concepts. 02:20 Thank you again and best wishes to you.
About the Lecture
The lecture Summary – Back Muscles by Craig Canby, PhD is from the course Abdominal Wall with Dr. Canby.
Included Quiz Questions
What muscle has its most superior attachments to the spinous process of the 2nd cervical vertebra and rotates the neck and head to the opposite side when it contracts?
- Semispinalis cervicis
- Semispinalis capitis
- Splenius cervicis
- Longissimus
- Platysma
What is the innervation of the muscles of the suboccipital region?
- Posterior ramus of C1
- Anterior ramus of C1
- Posterior ramus of C2
- Anterior ramus of C2
- Greater occipital nerve
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |