Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Obesity: Medications and Bariatric Surgery
-
Slides Obesity ChronicCare.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
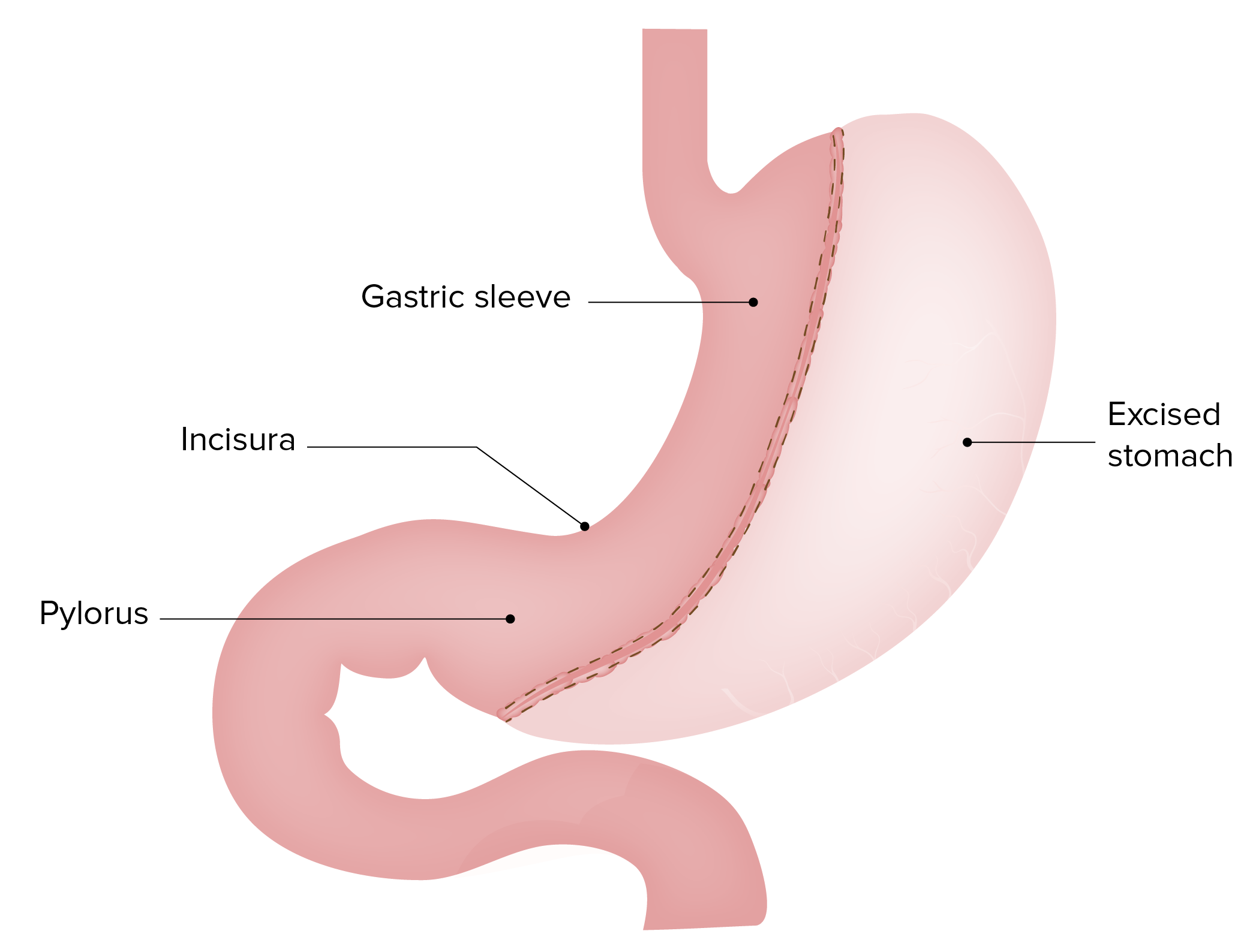
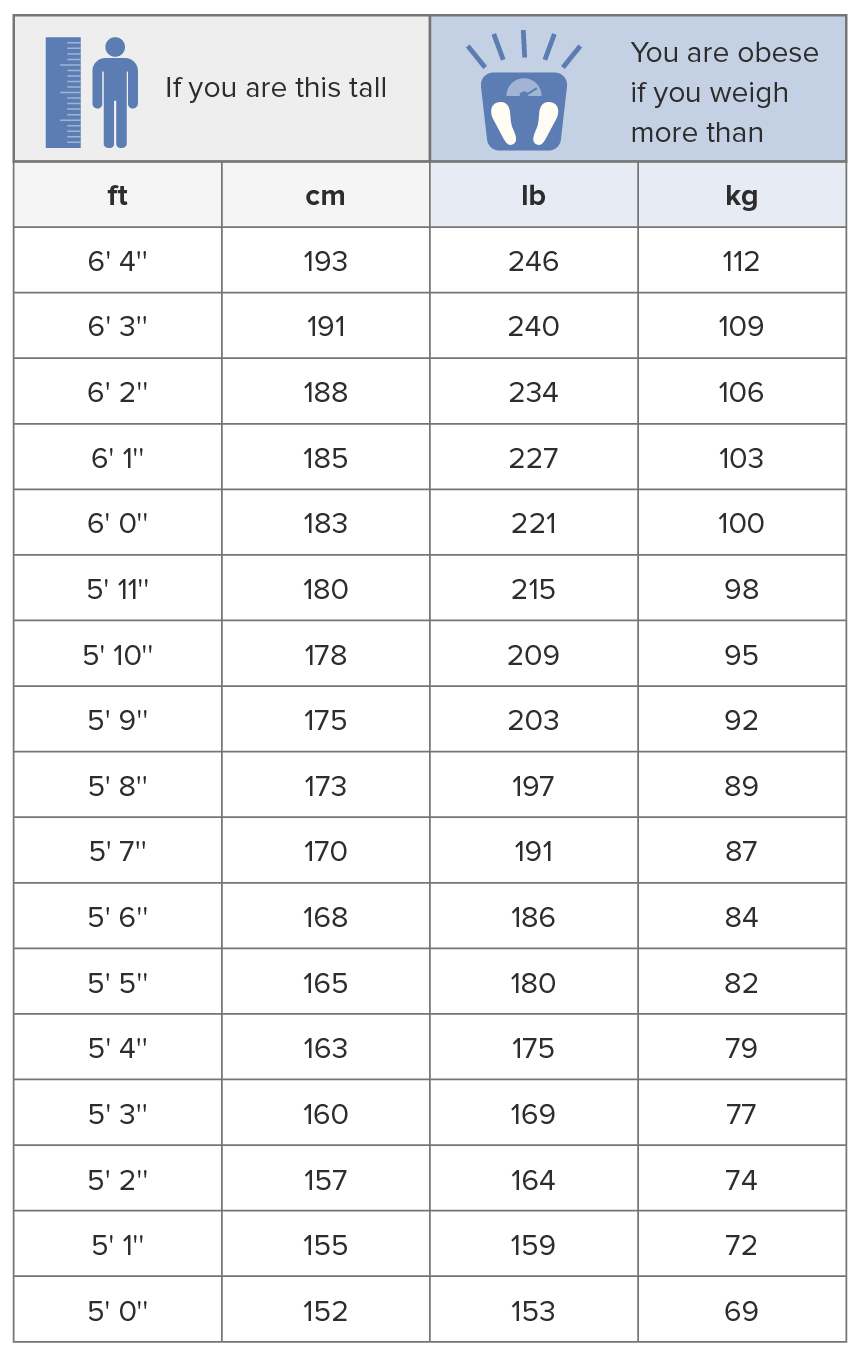
00:01 Failing that, failing diet and beyond exercise, of course, those are always going to be foundational. 00:06 We’re going to recommend those throughout. 00:08 There are several effective medication available in the United States for the treatment of obesity. 00:13 And they do work. 00:15 In clinical trials, more than half of individuals treated with these medications lost at least 5% of their body weight. 00:21 So, again, these are significant weight loss. 00:24 We’re talking along the lines of 6 kg, 8 kg, 9 kg. 00:29 Glucagon-like peptide 1 agonists, dual GLP-1/glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide receptor agonists and phentermine topiramate generally have been associated with the largest amounts of weight loss in these clinical trials. 00:44 GLP-1 agonists were originally utilized to treat diabetes, with the added benefit of weight loss. 00:51 However, since incretin-based therapies are so effective for weight loss and come with a potential cardiovascular benefit (particularly semaglutide), they are also useful for patients without diabetes, as well. Nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea are common side effects with this group of drugs. Phentermine, a sympathomimetic drug often combined with topiramate, is reasonable for patients without a history of uncontrolled hypertension or cardiovascular disease. 01:21 One thing with taking any drug with topiramate in it is it can make patients feel a little bit hazy or foggy, with some difficulty in concentration. 01:29 So, that's one thing to watch and can be managed by cutting the dose. 01:34 Naltrexone-bupropion also is effective, another combination agent. 01:39 Bupropion, we have to watch out for its effects in patients with seizures because it lowers the seizure threshold, can have some effects on sleep as well, but generally pretty well tolerated. 01:51 And orlistat, a lipase inhibitor, is generally reserved for patients who cannot use any of the other options. 01:58 But say the patient is failing their diet, exercise, medications and still has some indications for bariatric surgery, that's the time to think about maybe doing surgery for these patients. 02:10 So, bariatric surgery, the general indications, the things you should know for the exam, body mass index of 35 kg/m² or more or at least 30 kg/m² with complications of obesity, primarily hypertension, diabetes. 02:27 Now, these treatments really do work. 02:29 It's possible to lose 50% of the excess body weight or more. 02:34 So, the improvements can be dramatic. 02:36 It's really the only thing that cures diabetes, for example. 02:42 And one thing we do understand is that now gastric volume procedures, either the Roux-en-Y gastric bypass or the gastric sleeve have become more popular than the banding procedure or laparoscopic band because those procedures, the gastric volume procedures definitely promote greater weight loss. 03:04 So, if you want to lose a few pounds, the band procedures are okay. 03:07 But if you really want to make a difference in disease outcomes, like hypertension and diabetes, gastric volume procedures are definitely more effective. 03:16 And now the gastric sleeve is the most popular form of bariatric surgery in the United States. 03:21 As I mentioned, it can be highly effective in reducing the risk of diabetes, it can reduce the risk of incident hypertension and it also greatly improves pre-existing diabetes and hypertension as well. 03:35 It’s associated – there is an associated risk of complications. 03:39 3 to 5% of these gastric volume procedures, whether we’re talking about the Roux-en-Y bypass or the other sleeve can have leaks after surgery. 03:49 There is about a 1% perioperative risk of serious adverse events, which isn’t different than some other procedures like an open cholecystectomy, but still something to consider as patients elect to have these procedures. 04:07 However, in the long term, and particularly as patients get good counseling and good follow-up, so they understand what the procedure entails and what their life will be like after the procedure in terms of early satiety and having to be evaluated for potential nutritional deficiencies and having to titrate their diet accordingly, those patients I think who are prepped appropriately and followed appropriately have a lifestyle that’s actually improved after surgery versus not. 04:35 And I can say from personal experience, those patients who have unreasonable expectations and don't get the kinds of follow-up that they need have oftentimes more side effects, more symptoms and a worse lifestyle afterwards. 04:50 So, we discussed the epidemiology of obesity. 04:54 Diet and exercise are the cornerstone. 04:56 Really try to focus on those lower carbohydrate diets. 05:00 Those seem to be the ones that work best. 05:03 And you can work to that goal gradually with the patients’ values in mind. 05:07 It is perfectly reasonable. 05:09 Medications can certainly help and they might stimulate patients to lose a little bit more weight. 05:15 How long you continue those drugs is a matter of controversy. 05:18 And for patients who fail diet and exercise conservative therapy and really are suffering with obesity and its complications, bariatric surgery is an option. 05:30 Hope you found that helpful. 05:31 Thanks very much for your attention.
About the Lecture
The lecture Obesity: Medications and Bariatric Surgery by Charles Vega, MD is from the course Chronic Care.
Included Quiz Questions
In the management of obesity, health benefits have been reported with a minimum weight loss of what percent?
- 5
- 50
- 25
- 1
- 10
Which of the following is a common side effect of phentermine/topiramate therapy for weight loss?
- Dry mouth
- Nocturia
- Fatty diarrhea
- Hypoglycemia
- Skin rash
Which of the following is the most appropriate initial therapy for a patient with a body mass index of 35 kg/m2?
- Diet and exercise
- Gastric banding
- Gastric sleeve
- Phentermine/topiramate
- Naltrexone/bupropion
Which of the following is a contraindication for naltrexone/bupropion in the treatment of obesity?
- Seizure disorder
- Diabetes mellitus
- History of malignancy
- Prior stroke
- Coronary artery disease
Which of the following is the most appropriate indication for bariatric surgery?
- BMI ≥40 kg/m2, or a BMI of 35 to 39.9 kg/m2 with at least one serious comorbidity, who have not met weight loss goals with diet, exercise, and drug therapy
- BMI ≥40 kg/m2, or a BMI of 35 to 39.9 kg/m2 with at least one serious comorbidity
- BMI ≥40 kg/m2
- BMI ≥40 kg/m2 with at least one serious comorbidity
- BMI ≥40 kg/m2 with at least one serious comorbidity, who have not met weight loss goals with diet, exercise, and drug therapy
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
1 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |
Excellent presentation, He made it clear which is the cornerstone of management, advantages and disadvantages of management. Greetings from Mexico