Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Intravenous Anesthetics – Anesthetic Drugs
-
Slides Intravenous Anesthetics Anesthetic Drugs.pdf
-
Reference List Pharmacology.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
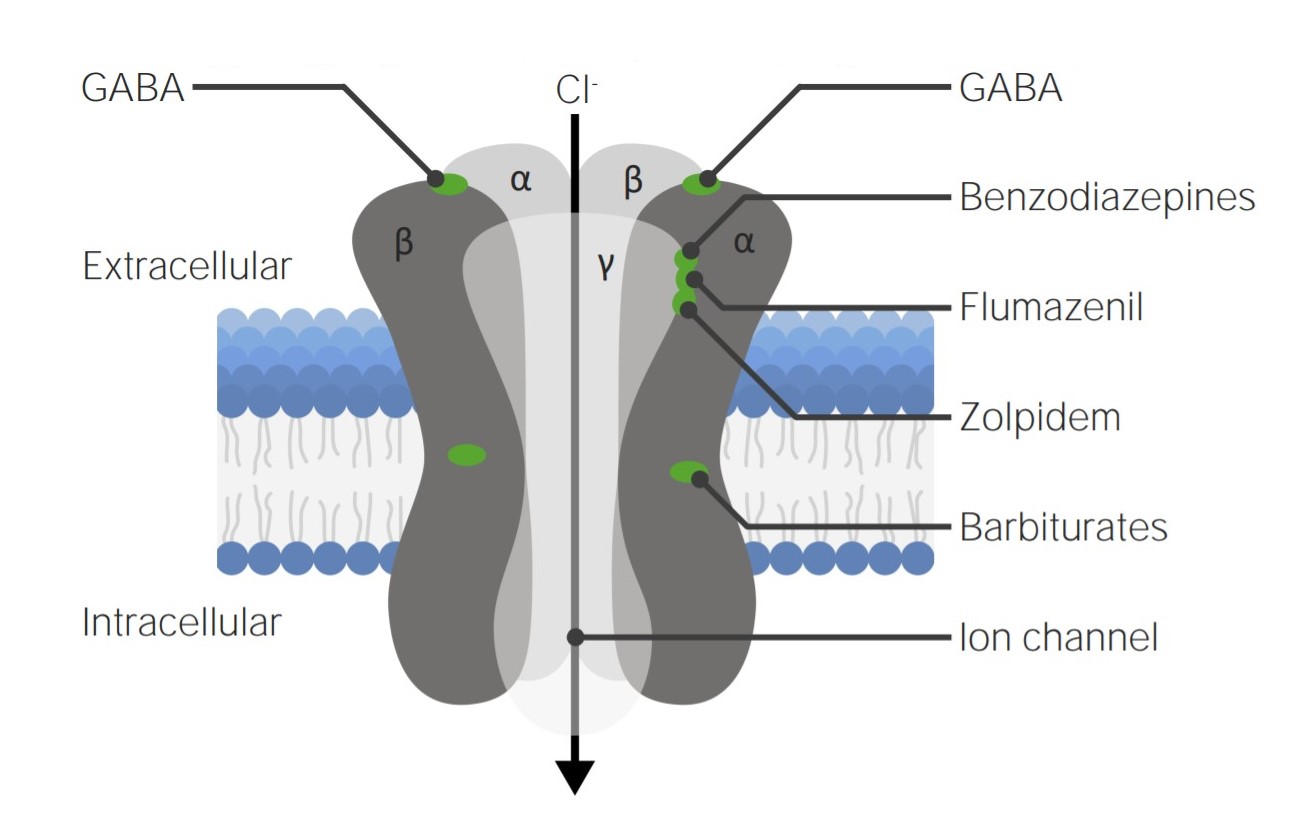
00:01 Treatment strategies. We talked about the gases and the volatile liquids, let's now move on to the intravenous agents. 00:12 We have barbiturates like thiopental, and dissociatives. We have opioids and benzodiazepines. 00:18 And we have the miscellaneous agents. 00:21 Let's talk about barbiturates. So, barbiturates include thiopental and others. 00:27 They are highly lipid soluble. They enter the brain very quickly. And they act through the GABA A receptor. 00:34 It may decrease circulatory blood flow as well. So that is nice because you can decrease intracranial pressures. 00:41 So, in cases of head injury or where you're worried about high intracranial pressures, this is a good choice of medication. 00:50 You can see here how quickly this drug is moving from each of the different tissue compartments. 00:59 Remember that benzodiazepines and barbiturates work through the GABA A receptor, I keep showing this to you all the time because it's such a beautiful illustration. Midazolam is one of the most commonly used benzodiazepine. 01:12 It has a slower onset than thiopental. Flumazenil may be used to reverse excess sedation or dosing due to the benzodiazepine. 01:21 Remember that flumazenil does not reverse barbiturates. The next category of drugs are the dissociatives drugs. 01:31 Dissociative anesthesia generally involves a conscious patient. It causes marked analgesia and amnesia. 01:40 These are actually quite fun to view in the operating room because you can have some great conversations with your patients as you're going through surgery. Ketamine is the prototypical agent. 01:51 It is a cardiovascular stimulant and it may increase intracranial pressure so there are some select patients that we don't want to use this medication on. 02:00 It is associated with some very interesting postoperative emergence issues, patient are often quite disoriented. 02:07 They can be quite excitable and they can have hallucinations. Once again, the nurses love these patients because of some really great conversations. It is similar to PCP, which is a street hallucinogen, and I do cover this in our toxicology lecture. 02:27 Propofol is as rapid as the barbiturates. Recovery is very rapid. 02:32 There are some antiemetic actions so it doesn't cause a lot of nausea. And it may cause a slight drop in blood pressure. 02:39 when you use it for induction. I use this drug all the time in the intensive care unit. 02:45 It gives great sedation and I know that some of my colleagues in anesthesia use it in the operating room as well. 02:52 It is also used in dental anesthesia and it gained notoriety because the dentists were the first ones to use it, and then they ended up getting accused of sexual harassment while their patients were under. 03:05 It came out later that propofol actually causes quite erotic dreams, and so it become the drug of choice in people who have had multiple surgeries because they love the dreams that they've had. 03:17 This is also a famous drug because this is the drug that Michael Jackson's doctor was administering to Michael Jackson.
About the Lecture
The lecture Intravenous Anesthetics – Anesthetic Drugs by Pravin Shukle, MD is from the course CNS - Pharmacology. It contains the following chapters:
- Barbiturates
- Benzodiazepenes
- Dissassociatives
- Propofol
Included Quiz Questions
Which of the following statements about the reversal agent for excess sedation or dosing due to benzodiazepines is accurate?
- Flumazenil is effective in reversing the effects of midazolam.
- Flumazenil can reverse the effects of barbiturates.
- Flumazenil acts on the NMDA receptor.
- Flumazenil is commonly used to reverse the effects of ketamine.
- Flumazenil has a faster onset than benzodiazepines.
What is NOT a side effect of ketamine when used as a general anesthetic?
- Priapism
- Hallucination
- Disorientation
- Vomiting
- Abnormal heart rhythm
What is a common sedative medication in the ICU?
- Propofol
- Ketamine
- Phenobarbital
- Diazepam
- Flumazenil
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |