Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Hydrophilic vs. Hydrophobic – Absorption and Distribution | Pharmacokinetics (PK)
-
Slides Hydrophilic Hydrophobic Absorption Distribution PK.pdf
-
Reference List Pharmacology.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
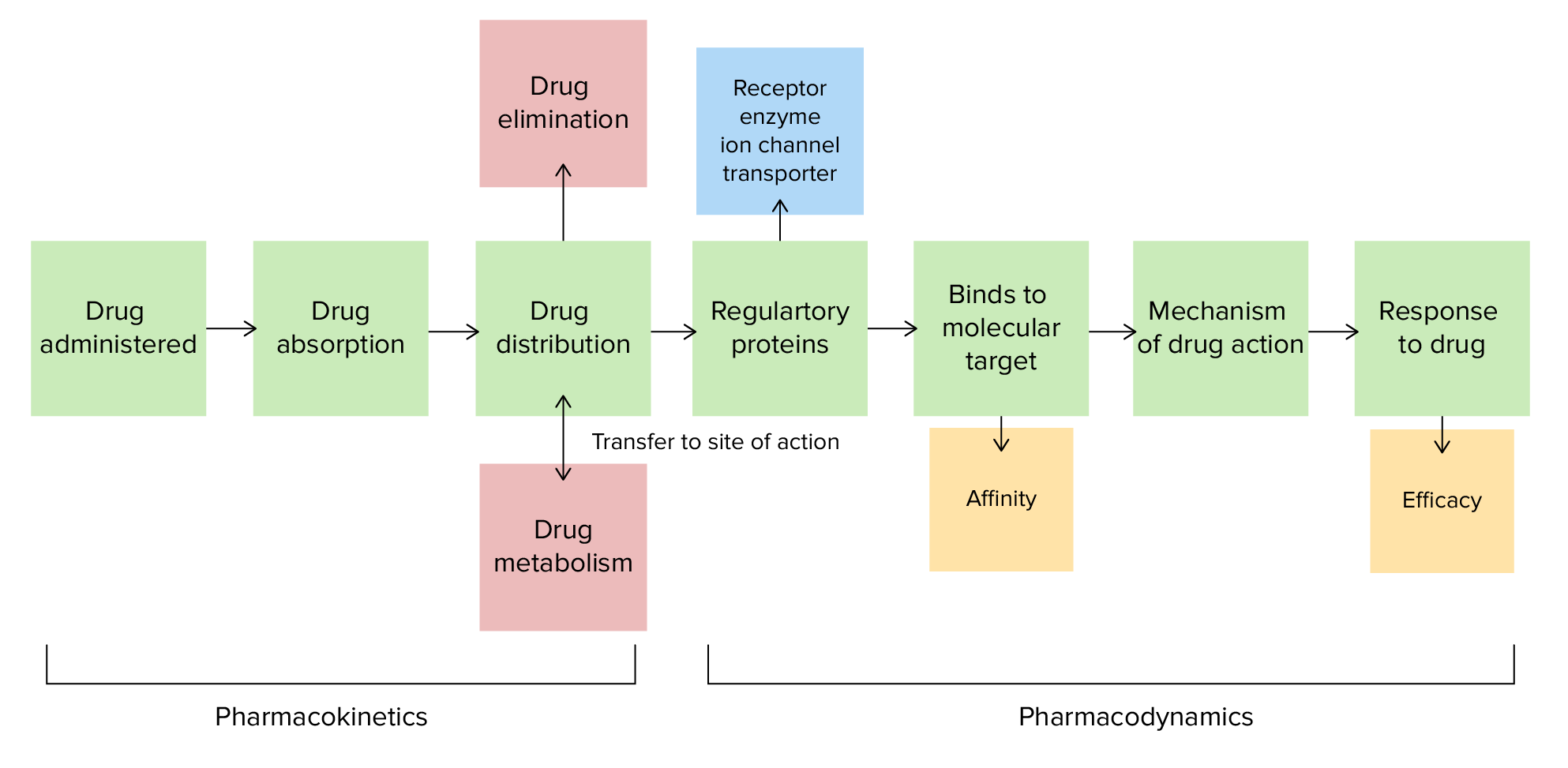
00:01 Now why do we talk about hydrophilic and hydrophobic drugs. Hydrophilic drugs or lipophobic drugs are are drugs that love waters. So hydro means water, philic means love. Now any drug that loves water is going to hate oil. So lipophobic and hydrophilic are the same thing. Hydrophilic drugs are usually polar. Hydrophobic drugs are usually not polar. Hydrophilic drugs dissolve in water so it's aqueous diffusion. Hydrophobic drugs dissolve in lipid or oil so they have lipid diffusion. Hydrophilic drugs need a pore or a transporter to get across that lipid bilayer. 00:44 Hydrophobic drugs or lipophilic drugs often can cross barriers without the need of pores or transporters. 00:52 This is an important distinguishing feature between these two types of drug. Hydrophilic drugs, because they can't cross that cell membrane usually don't cross the blood brain barrier or the blood uterine barrier. So generally speaking, which is'nt always true, hydrophilic drugs don't affect cerebral function and usually are safer in pregnancy. 01:16 Hydrophobic drugs or lipophilic drugs are almost always drugs that have some kind of a central effect and almost always have some kind of a fetal effect. Now when we talk about aqueous diffusion, we are talking about molecule movement through water, and lipid diffusion is through oil. Aqueous diffusion is always dependant on the passages of water between cells or the passage of water through pore. It is a passive process when you have aqueous diffusion and similarly with lipid diffusion you have movement through membranes and it is also a passive process. 01:56 All of the passive processes are governed by Fick's Law. Now before we get too bogged down on the equation, let's just remember that it is propertional to the diffusion constant of the drug, the surface area of the membrane, the thickness of the membrane and the concentration difference between the inside of the cell and the outside of the cell. Usually the outside being C1. So, let's apply this information that we just learned to drugs. 02:27 Choose the best answer. A drug that is hydrophilic... A, can permeate a cell without pores or transporters. B, will cross the blood brain barrier. C, is always non-polar. D, will always affect the fetus in a pregnant patient. And E, will passively permeate into a cell by Fick's Law. Which one is correct? So the answer is E. 02:54 All of the other ones are wrong. All of the other ones describe a lipophilic drug. So a lipophilic drug permeates a cell without pores or transporters. A lipophilic drug will cross the brain barrier and will often affect a fetus because it crosses the blood uterine barrier and it's almost always non-polar. All drugs generally will passively permeate into a cell by Fick's Law whether it's through an open channel or through the membrane in the case of a lipophilic drug. It's a hard question and i'll tell you why people get this question wrong. Because people assume that just because you are hydrophilic, you can't permeate into a cell. That's not true. Hydrophilic drug can passively permeate into a cell. It does'nt always need an active transporter. And the reason why it can passively permeate is because it can go through that cell pore that we had talked about earlier.
About the Lecture
The lecture Hydrophilic vs. Hydrophobic – Absorption and Distribution | Pharmacokinetics (PK) by Pravin Shukle, MD is from the course Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics. It contains the following chapters:
- Hydrophilic vs. Hydrophobic
- Quiz: Characteristics of Hydrophilic Drugs
Included Quiz Questions
Which statement regarding lipophilic drugs is most accurate?
- They are typically nonpolarized.
- They cannot cross the blood-brain barrier.
- They act similarly to hydrophilic drugs.
- They typically cross cell membranes through protein channels.
- They do not cross the placenta.
According to Fick’s law, what will increase passive diffusion into a cell?
- Increased surface area
- Increased membrane thickness
- Low diffusion constant of the drug
- Decrease in surface area to membrane thickness ratio
- Decreased concentration gradient
Which statement regarding hydrophilic drugs is most accurate?
- They generally require a protein channel to cross cell membranes.
- They are more likely to cross the placenta than lipophilic drugs.
- They are generally more likely to have cerebral effects than lipophilic drugs.
- They are essentially nonpolar molecules.
- They cross the blood-brain barrier.
Customer reviews
4,7 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
2 |
| 4 Stars |
|
1 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |
very clear and visual, good speed, nice images and accessible vocabulary
I really wanted to give it 5 stars specially because of the question pertaining to Fick' s law that was included, however the fact that Sir didn' t mention that all forms of diffusion are passive and the word Diffusion itself means being randomised made me give this 4 stars only.
good good good pronunciation good good good pronunciation good good good pronunciation