Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Chromosomal Abnormalities: Turner Syndrome, Klinefelter Syndrome, Trisomy X and XYY, Mosaics, Chimeras and Structural Defects
-
Slides 09-57 Chromosomal Abnormalities.pdf
-
Reference List Embryology.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
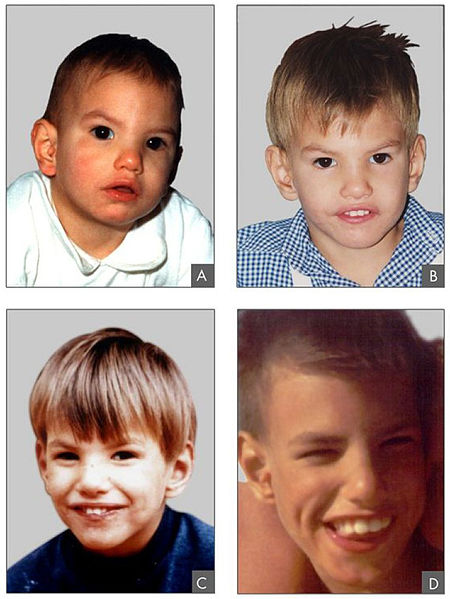
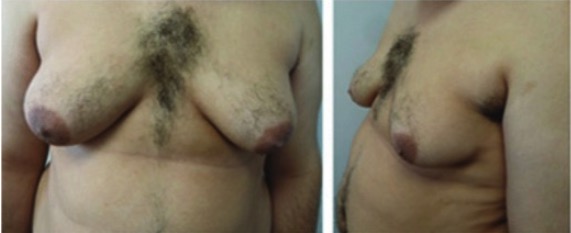
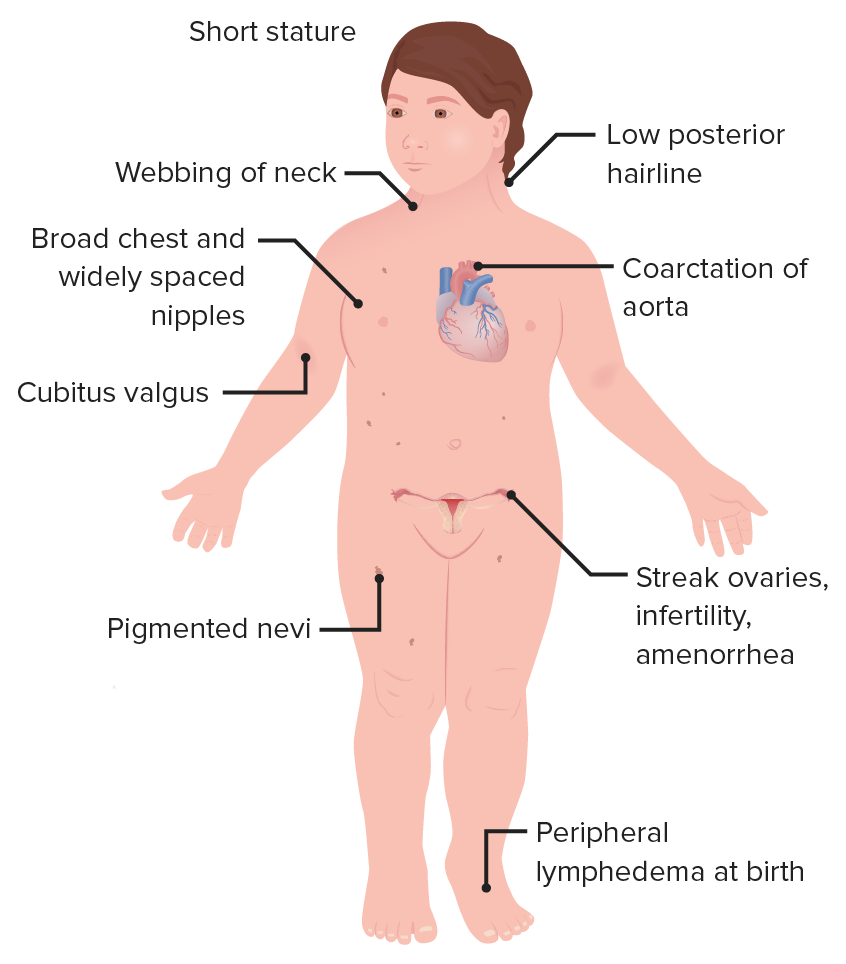
00:01 The only viable monosomy is known as Turner syndrome and it occurs in females who instead of two X chromosomes, have one X chromosome. 00:09 It can occur if portions of one X chromosome are significantly deleted so that only one functional one remains. 00:15 The vast majority of major chromosomal abnormalities do not make it to term and as I mentioned before, Turner syndrome is the only monosomy with any degree of survival after birth. 00:27 Individuals with Turner syndrome typically have short stature and a webbed neck extending from the base of the skull and ears down to points of the shoulders, lymphedema in the limbs, swelling and then a wide chest with widely spaced nipples. 00:41 There are also absences of ovaries and frequently you see amenorrhea or failure of the menstrual periods to occur. 00:48 The ovaries are often fibrous called streak ovaries that are present or all together absent ovaries. 00:56 Typically, these people have no major intellectual disability and hormonal treatments or surgical treatments can deal with the other sequelae of Turner syndrome, giving normalcy and functionality to people with this condition. 01:09 Klinefelter syndrome is a trisomy wherein the affected individual is XXY. 01:14 Because a Y chromosome is present, these individuals develop as male and typically they only see problems develop around puberty as masculine secondary sexual characteristics do not develop to the degree that would normally be expected. 01:28 People with XXY are typically not mentally retarded or having any developmental delays or associated with it but the more copies of an X chromosome someone has due to very early nondisjunction events, the more likely developmental delays are going to be encountered. 01:45 People with Klinefelter syndrome will be sterile because the testes and the seminiferous tubules within them will atrophy and fail to get a lumen that can transport spermatozoa. 01:55 They will frequently have gynecomastia or breast tissue develops in males, less body hair, decreased muscle growth and increased height. 02:04 Cognitive impairment may occur, but as I mentioned before, doesn't intend to be strictly associated with Klinefelter syndrome. 02:11 Trisomy X or women who are born with three copies of an X chromosome tend to develop very typically of females and may be completely asymptomatic. 02:21 Only karyotyping will eventually show that these people have three copies of the X chromosome. 02:27 In terms of commonalities, they often are taller than average, have wide set eyes and epicanthal folds, fold over on the top of the eyelid, and there are usually no intellectual or developmental deficits associated with this condition and may be clinically unknown unless the person has genetic testing done. 02:47 Jacob syndrome is another trisomy wherein the affected person is XYY. 02:52 Because the Y chromosome is present, these people develop in a typically male pattern and they're often asymptomatic, much as people with triple X syndrome. 03:02 These boys will eventually develop increased height, but otherwise will develop normally and there may be minor cognitive delays but there's no consensus on whether that is linked to a Jacob syndrome or not. 03:13 XYY people have traditionally been described as aggressive, developmentally delayed and more likely to wind up in jail than others, but subsequent research are shown that this is really not a compelling link and there may be not be any sort of aggressive behavior caused by XYY trisomy. 03:32 In addition to nondisjunction events during meiosis that cause problems in the germ cells, there can sometimes be nondisjunction events during mitosis. 03:44 If this occurs while an embryo is growing, we can wind up with nondisjunction event creating two separate genetic lineages within a single embryo, meaning part of the body will develop in one way with a separate genetic blueprint than another part of the body. 04:01 This is known as mosaicisim. 04:03 It's very different from something called chimerism, although the two may manifest similarly with genetically distinct lineages appearing in different parts of the body. 04:13 A chimera is when two blastocysts that would otherwise develop as completely distinct individuals fuse during very early development to create a single organism but with cells from two separate sources. 04:28 In addition to nondisjunction during mitosis or meiosis, portions of chromosomes can also be damaged, they can be struck off or otherwise badly damaged or fragile leading to spontaneous abortion and occasionally to a viable offspring. 04:46 In the case of Cri du chat or cry of the cat syndrome, there's a deletion on chromosome 5. 04:52 This is sometimes been described as a partial monosomy because it leaves a single, truly functional version of chromosome 5. 04:59 Children with this condition tend to have smaller facial characteristics and you can see in the image that's associated with this, he has a very small mouth so microstomia is present. 05:10 And the reason this syndrome has the name that it does is that children with this condition, even immediately after birth, tend to cry in the way that is reminiscent of a kitten, so cry of the cat syndrome is because of this distinctive yell that these children give very soon after they're born. 05:29 Fragile X syndrome occurs because of genetic problem within the X chromosome. 05:34 An excessive number of nucleotide repeats CGG over and over and over creates a very fragile portion of the X chromosome. 05:44 The gene which this occurs is one that's involved with allowing neurons to connect with other neurons effectively and therefore, the problems that manifest generally manifest to in their neurologic ways. 05:55 Affects males more often than females because males have one and only one copy of the X chromosome available, although females can be carriers and occasionally symptomatic for fragile X syndrome. 06:07 These children typically have protruding ears, a relatively elongated face, hypermobile digits and cognitively, there's gonna be some issues involved with processing of information and sometimes these are going to appear autistic and these children may need to have very specific testing done to distinguish whether or not it's true autism or a result of a defect in the X chromosome that's causing these connections in the brain to be a little bit nonfunctional. 06:36 Early intervention can help get these children more functional and lead to better outcomes throughout the rest of their life. 06:43 Rett syndrome is in fact very similar in effect to fragile X syndrome, but it's due to a mutation of the MECP2 gene that is also in the X chromosome. 06:55 In this case, only females are affected because this mutation is invariably fatal in males who have one copy of X chromosome and cannot live without a functional copy. 07:07 It's not typically inherited but it's going to occur as an acquired mutation after the child has already been conceived or in the germ cell line. 07:16 Affected infants are gonna develop normally but regress at roughly 6 months of age and in fact sometimes it become microcephalic as the brain fails to grow and continue pushing the skull outward. 07:28 Symptoms are gonna manifest again at 6 months of age, language and motor delays are most commonly described, as well as seizures, breathing abnormalities and sometimes autistic-like behavior occurring in children with Rett syndrome. 07:44 Thank you very much and I'll see you for our next talk.
About the Lecture
The lecture Chromosomal Abnormalities: Turner Syndrome, Klinefelter Syndrome, Trisomy X and XYY, Mosaics, Chimeras and Structural Defects by Peter Ward, PhD is from the course Conception, Implantation and Fetal Development. It contains the following chapters:
- Turner Syndrome (X)
- Klinefelter Syndrome (XXY)
- Trisomy X and XYY
- Mosaics and Chimeras
- Cri du chat Syndrome
- Rett Syndrome
Included Quiz Questions
Which of the following is not typically a characteristic of Turner syndrome?
- Intellectual disability
- 'Webbed' neck
- Lymphedema in limbs
- Absence of ovaries and amenorrhea
- Wide chest with widely-spaced nipples
Why is trisomy X typically asymptomatic?
- The additional X chromosomes are inactivated, existing as Barr bodies.
- The additional genetic material in the X chromosome is evolutionarily favorable.
- Trisomy X is incompatible with life.
- Trisomy X more often than not is quite symptomatic.
- The nondisjunction event carries over only non-coding genetic material.
The fusion of two blastocysts creating a single organism containing cells with two separate genetic lineages is known as what?
- Chimerism
- Mosaicism
- Omphalopagus
- Conjoined twins
- Duplex syndrome
Rett syndrome is typically a fatal mutation in males, but it could be compatible with life in a population with which of the following conditions?
- Klinefelter syndrome
- Jacobs syndrome
- Cri du chat
- Fragile X
- Trisomy 18
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
1 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |
this app is amazing thank you doctor, for helping me