Advertisement
Advertisement
Advertisement
Advertisement
Mumps is caused by a single-stranded, linear, negative-sense RNA Negative-sense RNA RNA viruses that have their genetic material encoded in the form of single-stranded, negative-sense RNA. Unlike retroviruses they do not employ DNA intermediates in their life-cycle. Respiratory Syncytial Virus virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology of the family Paramyxoviridae Paramyxoviridae A family of spherical viruses, of the order mononegavirales, somewhat larger than the orthomyxoviruses, and containing single-stranded RNA. Subfamilies include paramyxoviridae and pneumovirinae. Respiratory Syncytial Virus and the subfamily Rublavirinae. The mumps virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology is contagious and spreads only among humans by respiratory droplets Droplets Varicella-Zoster Virus/Chickenpox or direct contact transmission from an infected person or fomite. Mumps is typically a disease of childhood, which manifests initially with fever Fever Fever is defined as a measured body temperature of at least 38°C (100.4°F). Fever is caused by circulating endogenous and/or exogenous pyrogens that increase levels of prostaglandin E2 in the hypothalamus. Fever is commonly associated with chills, rigors, sweating, and flushing of the skin. Fever, muscle pain Muscle Pain Ion Channel Myopathy, headache Headache The symptom of pain in the cranial region. It may be an isolated benign occurrence or manifestation of a wide variety of headache disorders. Brain Abscess, poor appetite, and a general feeling of malaise Malaise Tick-borne Encephalitis Virus, and is classically followed by parotitis. Complications include meningitis Meningitis Meningitis is inflammation of the meninges, the protective membranes of the brain, and spinal cord. The causes of meningitis are varied, with the most common being bacterial or viral infection. The classic presentation of meningitis is a triad of fever, altered mental status, and nuchal rigidity. Meningitis, pancreatitis Pancreatitis Inflammation of the pancreas. Pancreatitis is classified as acute unless there are computed tomographic or endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatographic findings of chronic pancreatitis. The two most common forms of acute pancreatitis are alcoholic pancreatitis and gallstone pancreatitis. Acute Pancreatitis, permanent deafness, and testicular inflammation Inflammation Inflammation is a complex set of responses to infection and injury involving leukocytes as the principal cellular mediators in the body's defense against pathogenic organisms. Inflammation is also seen as a response to tissue injury in the process of wound healing. The 5 cardinal signs of inflammation are pain, heat, redness, swelling, and loss of function. Inflammation, which can result in infertility Infertility Infertility is the inability to conceive in the context of regular intercourse. The most common causes of infertility in women are related to ovulatory dysfunction or tubal obstruction, whereas, in men, abnormal sperm is a common cause. Infertility. Mumps is managed with supportive care and is preventable by vaccination Vaccination Vaccination is the administration of a substance to induce the immune system to develop protection against a disease. Unlike passive immunization, which involves the administration of pre-performed antibodies, active immunization constitutes the administration of a vaccine to stimulate the body to produce its own antibodies. Vaccination.
Last updated: Dec 17, 2024
Advertisement
Advertisement
Advertisement
Advertisement
Advertisement
Advertisement
Advertisement
Advertisement

RNA virus identification:
Viruses can be classified in many ways. Most viruses, however, will have a genome formed by either DNA or RNA. RNA genome viruses can be further characterized by either a single- or double-stranded RNA. “Enveloped” viruses are covered by a thin coat of cell membrane (usually taken from the host cell). If the coat is absent, the viruses are called “naked” viruses. Viruses with single-stranded genomes are “positive-sense” viruses if the genome is directly employed as messenger RNA (mRNA), which is translated into proteins. “Negative-sense,” single-stranded viruses employ RNA dependent RNA polymerase, a viral enzyme, to transcribe their genome into messenger RNA.
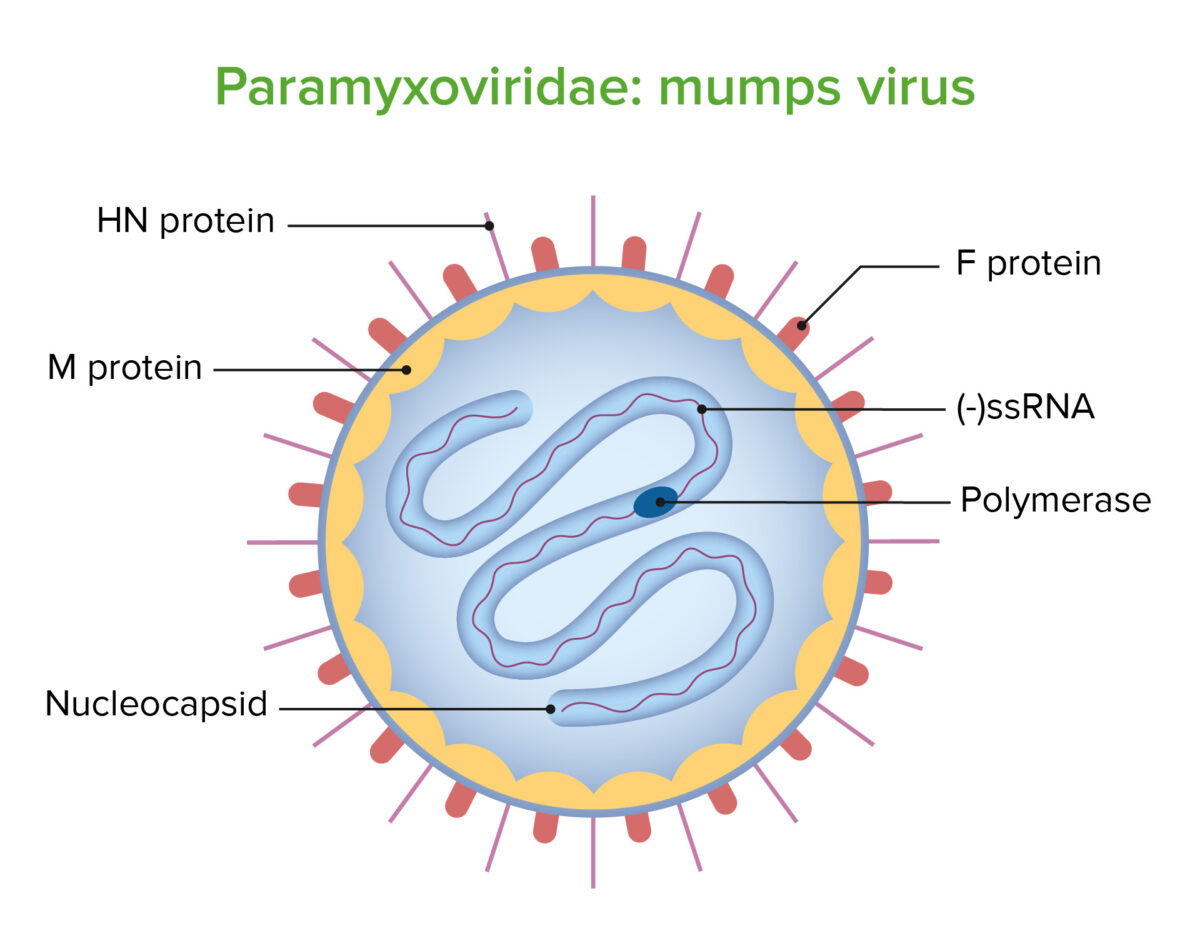
Structure of the mumps virus
Image by Lecturio. License: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0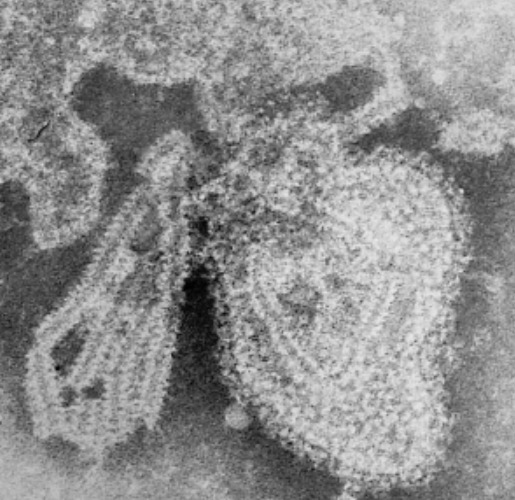
Transmission electron microscopy of mumps virus
Image: “TEM micrograph of a mumps virus particle” by CDC/ Dr. F. A. Murphy. License: Public DomainThe incubation Incubation The amount time between exposure to an infectious agent and becoming symptomatic. Rabies Virus period is 2–3 weeks.
After the incubation Incubation The amount time between exposure to an infectious agent and becoming symptomatic. Rabies Virus period, prodromal symptoms occur for 3–5 days, including:
After the prodromal period, the patient may present asymptomatically (20% of cases) or develop symptoms depending on the affected organ:
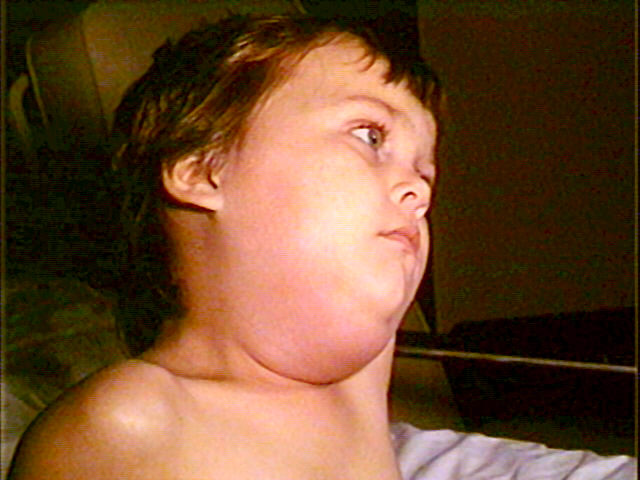
Pediatric patient with mumps presenting with swelling of the submandibular gland
Image: “Child with mumps” by CDC/NIP/Barbara Rice. License: Public DomainMumps is usually diagnosed on clinical grounds and no confirmatory laboratory testing is needed.