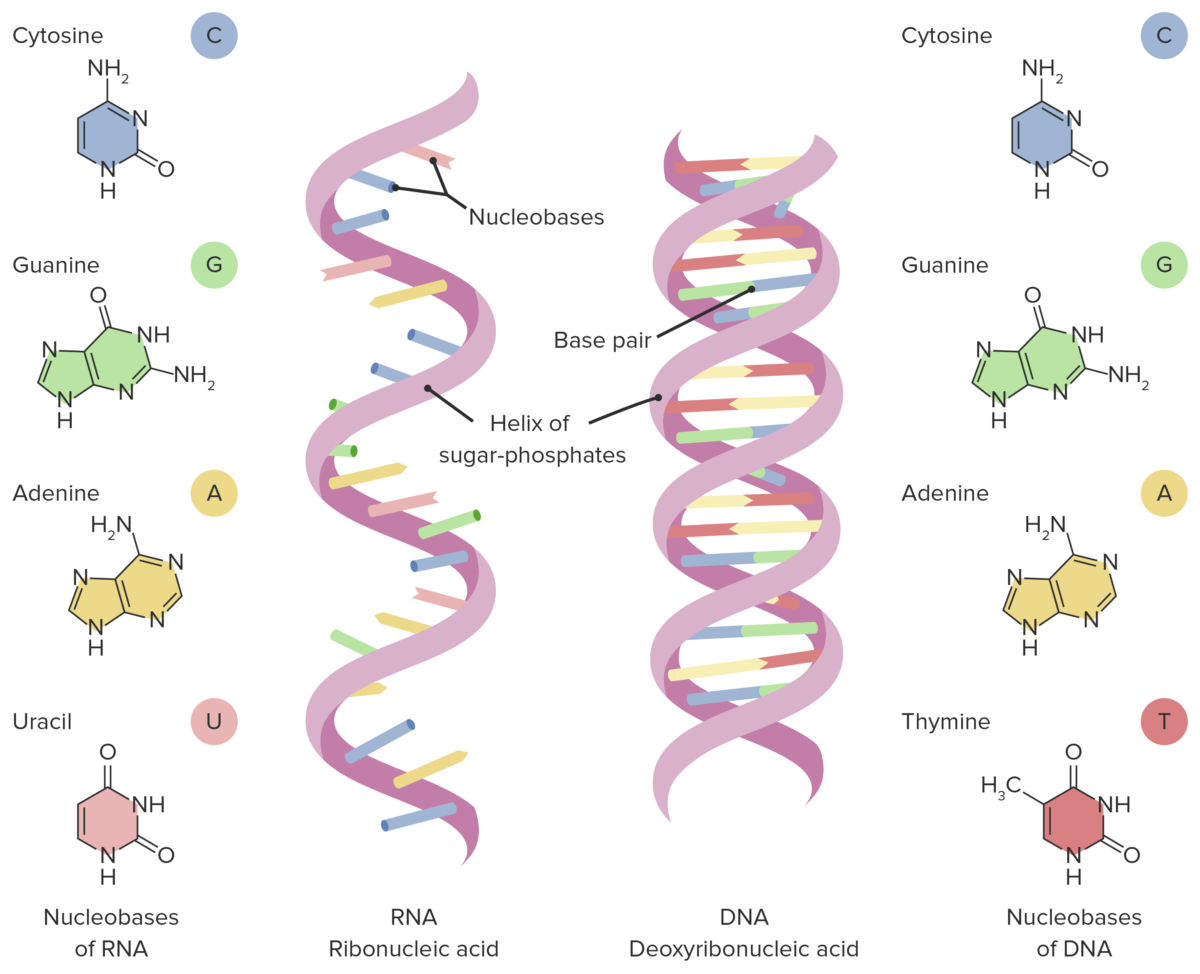
O ácido ribonucleico ( RNA RNA A polynucleotide consisting essentially of chains with a repeating backbone of phosphate and ribose units to which nitrogenous bases are attached. RNA is unique among biological macromolecules in that it can encode genetic information, serve as an abundant structural component of cells, and also possesses catalytic activity. RNA Types and Structure), tal TAL Renal Sodium and Water Regulation como o ácido desoxirribonucleico ( DNA DNA A deoxyribonucleotide polymer that is the primary genetic material of all cells. Eukaryotic and prokaryotic organisms normally contain DNA in a double-stranded state, yet several important biological processes transiently involve single-stranded regions. DNA, which consists of a polysugar-phosphate backbone possessing projections of purines (adenine and guanine) and pyrimidines (thymine and cytosine), forms a double helix that is held together by hydrogen bonds between these purines and pyrimidines (adenine to thymine and guanine to cytosine). DNA Types and Structure), é um polímero de nucleótidos essencial para a síntese de proteínas celulares. Ao contrário do DNA DNA A deoxyribonucleotide polymer that is the primary genetic material of all cells. Eukaryotic and prokaryotic organisms normally contain DNA in a double-stranded state, yet several important biological processes transiently involve single-stranded regions. DNA, which consists of a polysugar-phosphate backbone possessing projections of purines (adenine and guanine) and pyrimidines (thymine and cytosine), forms a double helix that is held together by hydrogen bonds between these purines and pyrimidines (adenine to thymine and guanine to cytosine). DNA Types and Structure, o RNA RNA A polynucleotide consisting essentially of chains with a repeating backbone of phosphate and ribose units to which nitrogenous bases are attached. RNA is unique among biological macromolecules in that it can encode genetic information, serve as an abundant structural component of cells, and also possesses catalytic activity. RNA Types and Structure é uma estrutura de cadeia simples contendo a ribose Ribose A pentose active in biological systems usually in its d-form. Nucleic Acids como fração de açúcar (em vez de desoxirribose) e uracilo (em vez de timina). Enquanto o DNA DNA A deoxyribonucleotide polymer that is the primary genetic material of all cells. Eukaryotic and prokaryotic organisms normally contain DNA in a double-stranded state, yet several important biological processes transiently involve single-stranded regions. DNA, which consists of a polysugar-phosphate backbone possessing projections of purines (adenine and guanine) and pyrimidines (thymine and cytosine), forms a double helix that is held together by hydrogen bonds between these purines and pyrimidines (adenine to thymine and guanine to cytosine). DNA Types and Structure armazena a informação genética, o RNA RNA A polynucleotide consisting essentially of chains with a repeating backbone of phosphate and ribose units to which nitrogenous bases are attached. RNA is unique among biological macromolecules in that it can encode genetic information, serve as an abundant structural component of cells, and also possesses catalytic activity. RNA Types and Structure geralmente executa as instruções codificadas no DNA DNA A deoxyribonucleotide polymer that is the primary genetic material of all cells. Eukaryotic and prokaryotic organisms normally contain DNA in a double-stranded state, yet several important biological processes transiently involve single-stranded regions. DNA, which consists of a polysugar-phosphate backbone possessing projections of purines (adenine and guanine) and pyrimidines (thymine and cytosine), forms a double helix that is held together by hydrogen bonds between these purines and pyrimidines (adenine to thymine and guanine to cytosine). DNA Types and Structure, mas o RNA RNA A polynucleotide consisting essentially of chains with a repeating backbone of phosphate and ribose units to which nitrogenous bases are attached. RNA is unique among biological macromolecules in that it can encode genetic information, serve as an abundant structural component of cells, and also possesses catalytic activity. RNA Types and Structure também executa diversas funções não codificantes. Existem 3 tipos principais de RNA RNA A polynucleotide consisting essentially of chains with a repeating backbone of phosphate and ribose units to which nitrogenous bases are attached. RNA is unique among biological macromolecules in that it can encode genetic information, serve as an abundant structural component of cells, and also possesses catalytic activity. RNA Types and Structure que desempenham papéis diferentes, mas colaborativos, na síntese de proteínas: RNA RNA A polynucleotide consisting essentially of chains with a repeating backbone of phosphate and ribose units to which nitrogenous bases are attached. RNA is unique among biological macromolecules in that it can encode genetic information, serve as an abundant structural component of cells, and also possesses catalytic activity. RNA Types and Structure mensageiro ( mRNA mRNA RNA sequences that serve as templates for protein synthesis. Bacterial mRNAs are generally primary transcripts in that they do not require post-transcriptional processing. Eukaryotic mRNA is synthesized in the nucleus and must be exported to the cytoplasm for translation. Most eukaryotic mRNAs have a sequence of polyadenylic acid at the 3' end, referred to as the poly(a) tail. The function of this tail is not known for certain, but it may play a role in the export of mature mRNA from the nucleus as well as in helping stabilize some mRNA molecules by retarding their degradation in the cytoplasm. RNA Types and Structure), RNA RNA A polynucleotide consisting essentially of chains with a repeating backbone of phosphate and ribose units to which nitrogenous bases are attached. RNA is unique among biological macromolecules in that it can encode genetic information, serve as an abundant structural component of cells, and also possesses catalytic activity. RNA Types and Structure de transferência ( tRNA tRNA The small RNA molecules, 73-80 nucleotides long, that function during translation (translation, genetic) to align amino acids at the ribosomes in a sequence determined by the mRNA (RNA, messenger). There are about 30 different transfer rnas. Each recognizes a specific codon set on the mRNA through its own anticodon and as aminoacyl trnas (RNA, transfer, amino Acyl), each carries a specific amino acid to the ribosome to add to the elongating peptide chains. RNA Types and Structure) e RNA RNA A polynucleotide consisting essentially of chains with a repeating backbone of phosphate and ribose units to which nitrogenous bases are attached. RNA is unique among biological macromolecules in that it can encode genetic information, serve as an abundant structural component of cells, and also possesses catalytic activity. RNA Types and Structure ribossomal ( rRNA rRNA The most abundant form of RNA. Together with proteins, it forms the ribosomes, playing a structural role and also a role in ribosomal binding of mRNA and tRNAs. Individual chains are conventionally designated by their sedimentation coefficients. In eukaryotes, four large chains exist, synthesized in the nucleolus and constituting about 50% of the ribosome. RNA Types and Structure). Durante a transcrição, o RNA RNA A polynucleotide consisting essentially of chains with a repeating backbone of phosphate and ribose units to which nitrogenous bases are attached. RNA is unique among biological macromolecules in that it can encode genetic information, serve as an abundant structural component of cells, and also possesses catalytic activity. RNA Types and Structure é sintetizado a partir do DNA DNA A deoxyribonucleotide polymer that is the primary genetic material of all cells. Eukaryotic and prokaryotic organisms normally contain DNA in a double-stranded state, yet several important biological processes transiently involve single-stranded regions. DNA, which consists of a polysugar-phosphate backbone possessing projections of purines (adenine and guanine) and pyrimidines (thymine and cytosine), forms a double helix that is held together by hydrogen bonds between these purines and pyrimidines (adenine to thymine and guanine to cytosine). DNA Types and Structure através de uma série de etapas catalisadas pela enzima RNA RNA A polynucleotide consisting essentially of chains with a repeating backbone of phosphate and ribose units to which nitrogenous bases are attached. RNA is unique among biological macromolecules in that it can encode genetic information, serve as an abundant structural component of cells, and also possesses catalytic activity. RNA Types and Structure polimerase. O mRNA mRNA RNA sequences that serve as templates for protein synthesis. Bacterial mRNAs are generally primary transcripts in that they do not require post-transcriptional processing. Eukaryotic mRNA is synthesized in the nucleus and must be exported to the cytoplasm for translation. Most eukaryotic mRNAs have a sequence of polyadenylic acid at the 3' end, referred to as the poly(a) tail. The function of this tail is not known for certain, but it may play a role in the export of mature mRNA from the nucleus as well as in helping stabilize some mRNA molecules by retarding their degradation in the cytoplasm. RNA Types and Structure formado servirá como um modelo aminoacídico para a síntese de proteínas. A tradução prossegue com o tRNA tRNA The small RNA molecules, 73-80 nucleotides long, that function during translation (translation, genetic) to align amino acids at the ribosomes in a sequence determined by the mRNA (RNA, messenger). There are about 30 different transfer rnas. Each recognizes a specific codon set on the mRNA through its own anticodon and as aminoacyl trnas (RNA, transfer, amino Acyl), each carries a specific amino acid to the ribosome to add to the elongating peptide chains. RNA Types and Structure a transportar o aminoácido correspondente, com base na sequência de nucleótidos decifrada (codão) no mRNA mRNA RNA sequences that serve as templates for protein synthesis. Bacterial mRNAs are generally primary transcripts in that they do not require post-transcriptional processing. Eukaryotic mRNA is synthesized in the nucleus and must be exported to the cytoplasm for translation. Most eukaryotic mRNAs have a sequence of polyadenylic acid at the 3' end, referred to as the poly(a) tail. The function of this tail is not known for certain, but it may play a role in the export of mature mRNA from the nucleus as well as in helping stabilize some mRNA molecules by retarding their degradation in the cytoplasm. RNA Types and Structure. Os ribossomas, que são compostos por rRNA rRNA The most abundant form of RNA. Together with proteins, it forms the ribosomes, playing a structural role and also a role in ribosomal binding of mRNA and tRNAs. Individual chains are conventionally designated by their sedimentation coefficients. In eukaryotes, four large chains exist, synthesized in the nucleolus and constituting about 50% of the ribosome. RNA Types and Structure, facilitam então a montagem de aminoácidos num polipéptido. Estes componentes trabalham em conjunto para converter o modelo de mRNA mRNA RNA sequences that serve as templates for protein synthesis. Bacterial mRNAs are generally primary transcripts in that they do not require post-transcriptional processing. Eukaryotic mRNA is synthesized in the nucleus and must be exported to the cytoplasm for translation. Most eukaryotic mRNAs have a sequence of polyadenylic acid at the 3' end, referred to as the poly(a) tail. The function of this tail is not known for certain, but it may play a role in the export of mature mRNA from the nucleus as well as in helping stabilize some mRNA molecules by retarding their degradation in the cytoplasm. RNA Types and Structure obtido a partir do DNA DNA A deoxyribonucleotide polymer that is the primary genetic material of all cells. Eukaryotic and prokaryotic organisms normally contain DNA in a double-stranded state, yet several important biological processes transiently involve single-stranded regions. DNA, which consists of a polysugar-phosphate backbone possessing projections of purines (adenine and guanine) and pyrimidines (thymine and cytosine), forms a double helix that is held together by hydrogen bonds between these purines and pyrimidines (adenine to thymine and guanine to cytosine). DNA Types and Structure na proteína desejada.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
O ácido ribonucleico ( RNA RNA A polynucleotide consisting essentially of chains with a repeating backbone of phosphate and ribose units to which nitrogenous bases are attached. RNA is unique among biological macromolecules in that it can encode genetic information, serve as an abundant structural component of cells, and also possesses catalytic activity. RNA Types and Structure) é um polímero de nucleótidos de cadeia única ligado através de ligações fosfodiéster 3’–5′.
Os nucleótidos são a unidade básica de qualquer ácido nucleico. Os nucleótidos do RNA RNA A polynucleotide consisting essentially of chains with a repeating backbone of phosphate and ribose units to which nitrogenous bases are attached. RNA is unique among biological macromolecules in that it can encode genetic information, serve as an abundant structural component of cells, and also possesses catalytic activity. RNA Types and Structure são formados pelas seguintes partes:
Componentes de ácido nucleico:
| RNA RNA A polynucleotide consisting essentially of chains with a repeating backbone of phosphate and ribose units to which nitrogenous bases are attached. RNA is unique among biological macromolecules in that it can encode genetic information, serve as an abundant structural component of cells, and also possesses catalytic activity. RNA Types and Structure | DNA DNA A deoxyribonucleotide polymer that is the primary genetic material of all cells. Eukaryotic and prokaryotic organisms normally contain DNA in a double-stranded state, yet several important biological processes transiently involve single-stranded regions. DNA, which consists of a polysugar-phosphate backbone possessing projections of purines (adenine and guanine) and pyrimidines (thymine and cytosine), forms a double helix that is held together by hydrogen bonds between these purines and pyrimidines (adenine to thymine and guanine to cytosine). DNA Types and Structure | |
|---|---|---|
| Fração de açúcar | Ribose Ribose A pentose active in biological systems usually in its d-form. Nucleic Acids | Desoxirribose |
| Bases Bases Usually a hydroxide of lithium, sodium, potassium, rubidium or cesium, but also the carbonates of these metals, ammonia, and the amines. Acid-Base Balance azotadas |
|
|
| Estrutura base | Cadeia simples | Cadeia dupla |
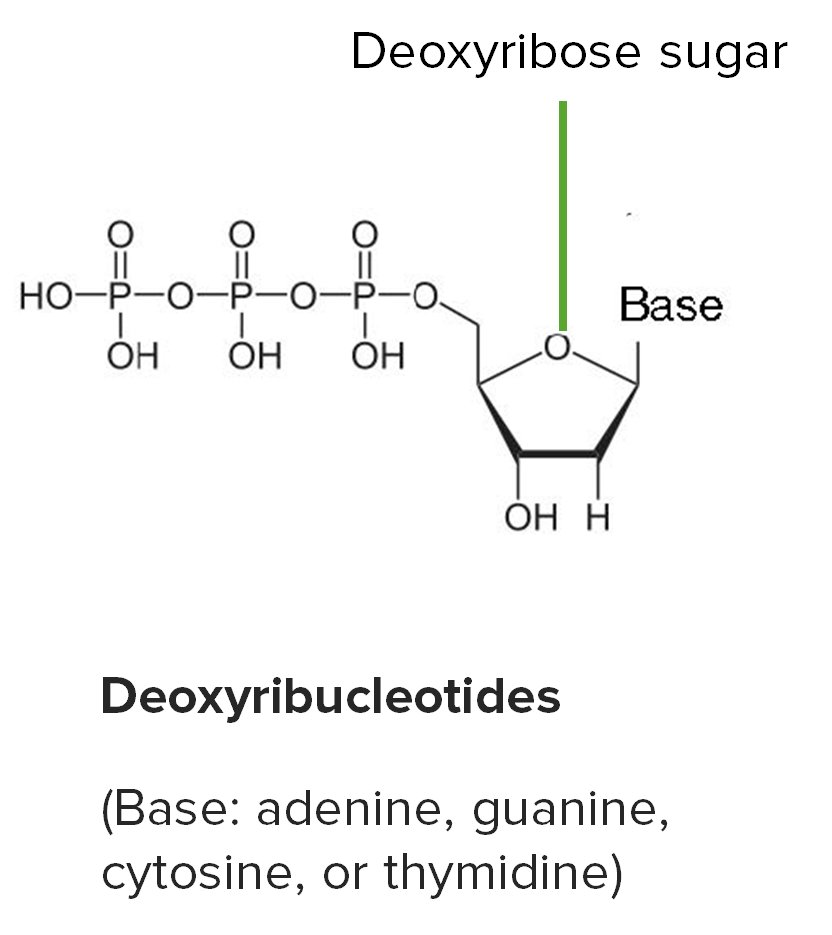
Estrutura básica dos ribonucleótidos: o carbono 2′ está ligado ao hidroxil (OH) no RNA.
Imagem por Lecturio.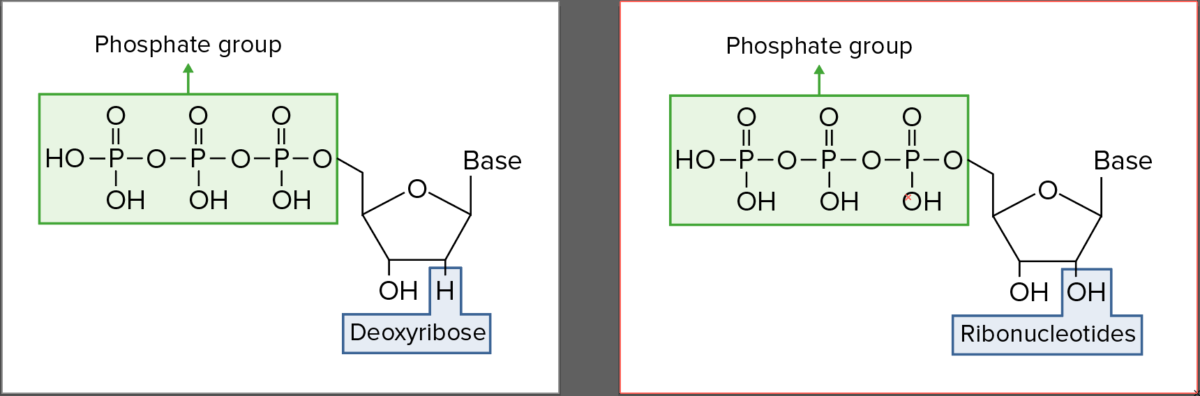
Estruturas de cada ribonucleótido
Desoxirribonucleótidos:
1. Grupo fosfato
2. Deoxirribose (Nota: Carbono 2′ está ligado ao H.)
3. Base azotada (adenina, timina, guanina, citosina)
Ribonucleótidos:
1. Grupo fosfato
2. Ribose (Nota: Carbono 2′ está ligado ao OH.)
3. Base azotada (adenina, timina, guanina, citosina)
Diferenças entre a estrutura do DNA e do RNA. Nota: O RNA é uma estrutura de cadeia simples e tem como base o uracilo (em vez da timina).
Imagem por Lecturio.RNA RNA A polynucleotide consisting essentially of chains with a repeating backbone of phosphate and ribose units to which nitrogenous bases are attached. RNA is unique among biological macromolecules in that it can encode genetic information, serve as an abundant structural component of cells, and also possesses catalytic activity. RNA Types and Structure codificante versus RNA RNA A polynucleotide consisting essentially of chains with a repeating backbone of phosphate and ribose units to which nitrogenous bases are attached. RNA is unique among biological macromolecules in that it can encode genetic information, serve as an abundant structural component of cells, and also possesses catalytic activity. RNA Types and Structure não codificante
Mnemónica
Para lembrar os codões de iniciação de mRNA mRNA RNA sequences that serve as templates for protein synthesis. Bacterial mRNAs are generally primary transcripts in that they do not require post-transcriptional processing. Eukaryotic mRNA is synthesized in the nucleus and must be exported to the cytoplasm for translation. Most eukaryotic mRNAs have a sequence of polyadenylic acid at the 3′ end, referred to as the poly(a) tail. The function of this tail is not known for certain, but it may play a role in the export of mature mRNA from the nucleus as well as in helping stabilize some mRNA molecules by retarding their degradation in the cytoplasm. RNA Types and Structure, use a mnemónica AUG (em inglês):
Para lembrar os codões de finalização de mRNA mRNA RNA sequences that serve as templates for protein synthesis. Bacterial mRNAs are generally primary transcripts in that they do not require post-transcriptional processing. Eukaryotic mRNA is synthesized in the nucleus and must be exported to the cytoplasm for translation. Most eukaryotic mRNAs have a sequence of polyadenylic acid at the 3′ end, referred to as the poly(a) tail. The function of this tail is not known for certain, but it may play a role in the export of mature mRNA from the nucleus as well as in helping stabilize some mRNA molecules by retarding their degradation in the cytoplasm. RNA Types and Structure, use as mnemónicas UGA, UAA, e UAG:
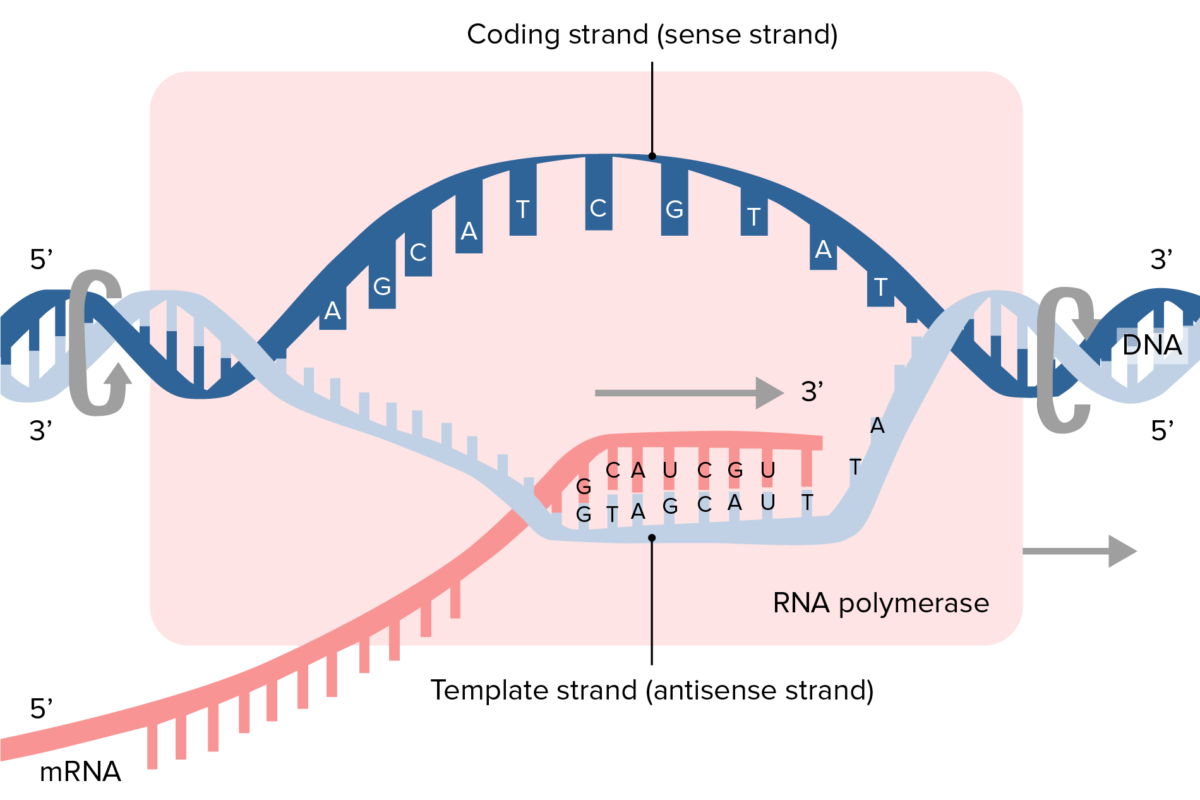
Ilustração do processo de transcrição e síntese de mRNA
Imagem por Lecturio.O RNA RNA A polynucleotide consisting essentially of chains with a repeating backbone of phosphate and ribose units to which nitrogenous bases are attached. RNA is unique among biological macromolecules in that it can encode genetic information, serve as an abundant structural component of cells, and also possesses catalytic activity. RNA Types and Structure mensageiro ( mRNA mRNA RNA sequences that serve as templates for protein synthesis. Bacterial mRNAs are generally primary transcripts in that they do not require post-transcriptional processing. Eukaryotic mRNA is synthesized in the nucleus and must be exported to the cytoplasm for translation. Most eukaryotic mRNAs have a sequence of polyadenylic acid at the 3′ end, referred to as the poly(a) tail. The function of this tail is not known for certain, but it may play a role in the export of mature mRNA from the nucleus as well as in helping stabilize some mRNA molecules by retarding their degradation in the cytoplasm. RNA Types and Structure) serve como um modelo aminoacídico para a síntese de proteínas.
mRNA mRNA RNA sequences that serve as templates for protein synthesis. Bacterial mRNAs are generally primary transcripts in that they do not require post-transcriptional processing. Eukaryotic mRNA is synthesized in the nucleus and must be exported to the cytoplasm for translation. Most eukaryotic mRNAs have a sequence of polyadenylic acid at the 3′ end, referred to as the poly(a) tail. The function of this tail is not known for certain, but it may play a role in the export of mature mRNA from the nucleus as well as in helping stabilize some mRNA molecules by retarding their degradation in the cytoplasm. RNA Types and Structure procariótico
mRNA mRNA RNA sequences that serve as templates for protein synthesis. Bacterial mRNAs are generally primary transcripts in that they do not require post-transcriptional processing. Eukaryotic mRNA is synthesized in the nucleus and must be exported to the cytoplasm for translation. Most eukaryotic mRNAs have a sequence of polyadenylic acid at the 3′ end, referred to as the poly(a) tail. The function of this tail is not known for certain, but it may play a role in the export of mature mRNA from the nucleus as well as in helping stabilize some mRNA molecules by retarding their degradation in the cytoplasm. RNA Types and Structure eucariótico
Existe uma crença antiga de que aos procariontes não têm a cap 5′. Recentemente, no entanto, descobriu-se que algumas bactérias têm uma cap 5′ de nicotinamida adenina dinucleotídeo ( NAD NAD+ A coenzyme composed of ribosylnicotinamide 5′-diphosphate coupled to adenosine 5′-phosphate by pyrophosphate linkage. It is found widely in nature and is involved in numerous enzymatic reactions in which it serves as an electron carrier by being alternately oxidized (NAD+) and reduced (NADH). Pentose Phosphate Pathway) :
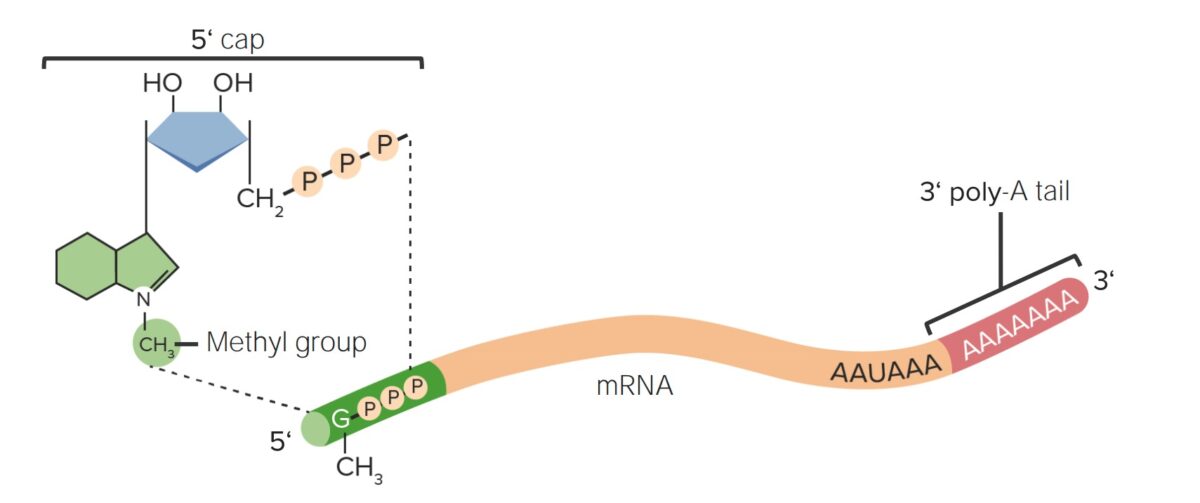
Visão geral dos segmentos de RNA mensageiro (mRNA): inclusão da cap 5′ e da cauda 3′ de poli-A
Imagem por Lecturio.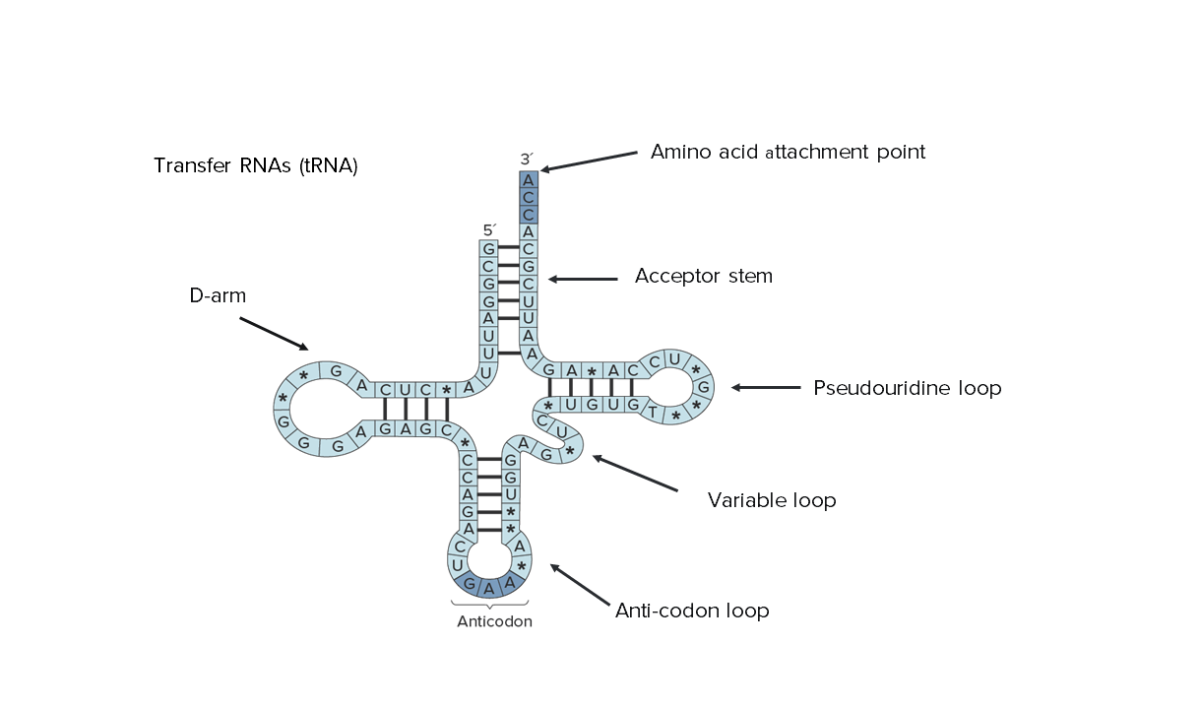
Estrutura secundária de RNA de transferência (tRNA): Repare que toda a sua sequência pode ser vista, indicando o tamanho reduzido.
Imagem por Lecturio.O RNA RNA A polynucleotide consisting essentially of chains with a repeating backbone of phosphate and ribose units to which nitrogenous bases are attached. RNA is unique among biological macromolecules in that it can encode genetic information, serve as an abundant structural component of cells, and also possesses catalytic activity. RNA Types and Structure de transferência transporta aminoácidos para ribossomas para montagem em proteínas. Este processo é conduzido por estas 2 ações principais:
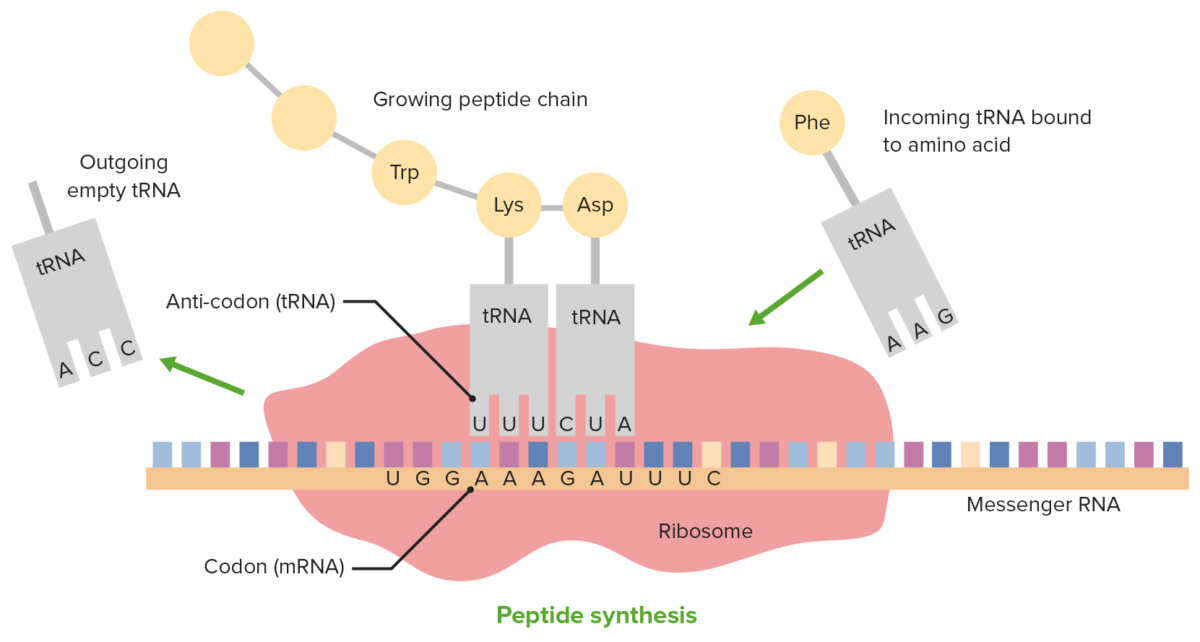
A tradução e o papel do tRNA
Imagem por Lecturio.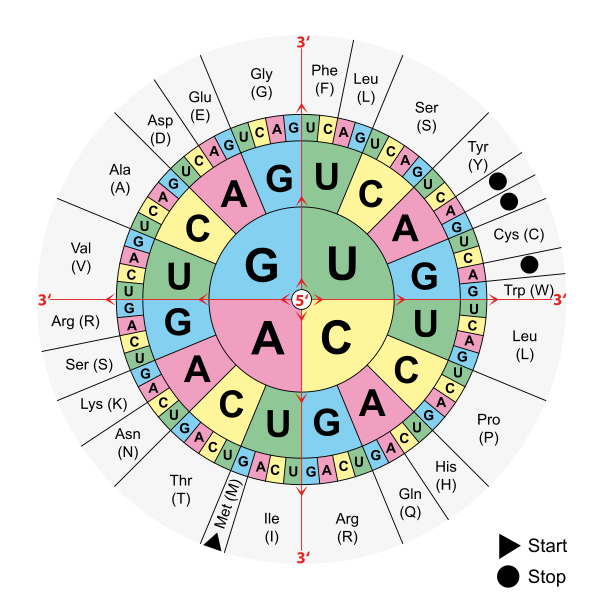
A degeneração do código genético, como mostra esta roda de codões. Note que muitos aminoácidos são codificados por mais de uma combinação de bases.
Imagem: “Aminoacids table” por Mouagip. Licença: Public DomainOs ribossomas consistem em 2 subunidades de rRNA de tamanho desigual, e as dimensões são medidas em termos de um valor “S” (Svedberg ou unidade de sedimentação):
| Subunidades | rRNA rRNA The most abundant form of RNA. Together with proteins, it forms the ribosomes, playing a structural role and also a role in ribosomal binding of mRNA and tRNAs. Individual chains are conventionally designated by their sedimentation coefficients. In eukaryotes, four large chains exist, synthesized in the nucleolus and constituting about 50% of the ribosome. RNA Types and Structure | Função |
|---|---|---|
| 50S | 5S | Transmite e coordena centros funcionais do ribossoma |
| 23S | Peptidil transferase: formação de ligações peptídicas | |
| 30S | 16S | Liga o codão de iniciação; esqueleto ribossomal |
| Subunidades | rRNA rRNA The most abundant form of RNA. Together with proteins, it forms the ribosomes, playing a structural role and also a role in ribosomal binding of mRNA and tRNAs. Individual chains are conventionally designated by their sedimentation coefficients. In eukaryotes, four large chains exist, synthesized in the nucleolus and constituting about 50% of the ribosome. RNA Types and Structure | Função |
|---|---|---|
| 60S | 5S | Apoio estrutural |
| 5.8S | Tradução | |
| 28S | Peptidil transferase: formação de ligações peptídicas | |
| 40S | 18S | Tradução |
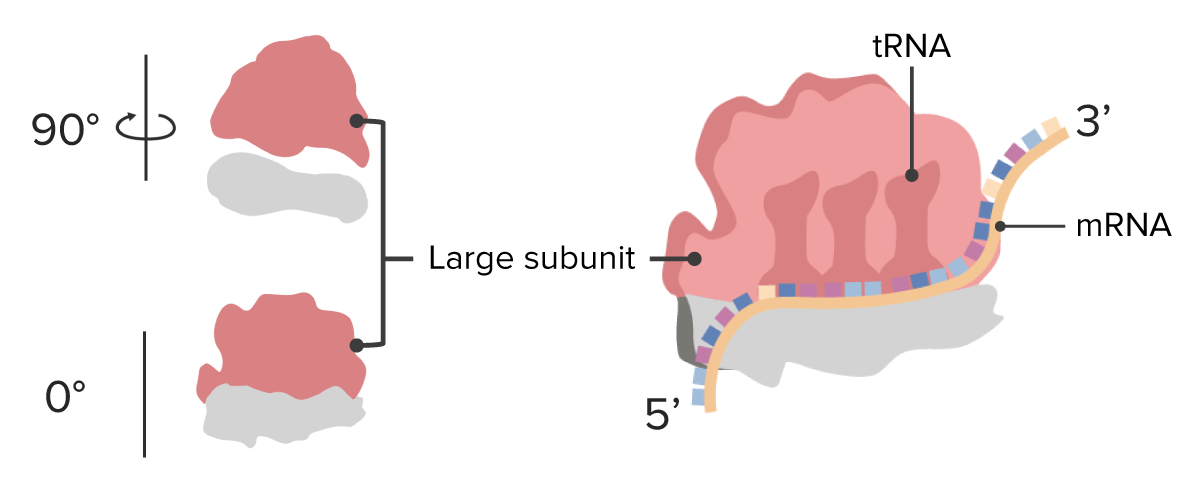
Ribossoma: subunidades grandes
Imagem por Lecturio.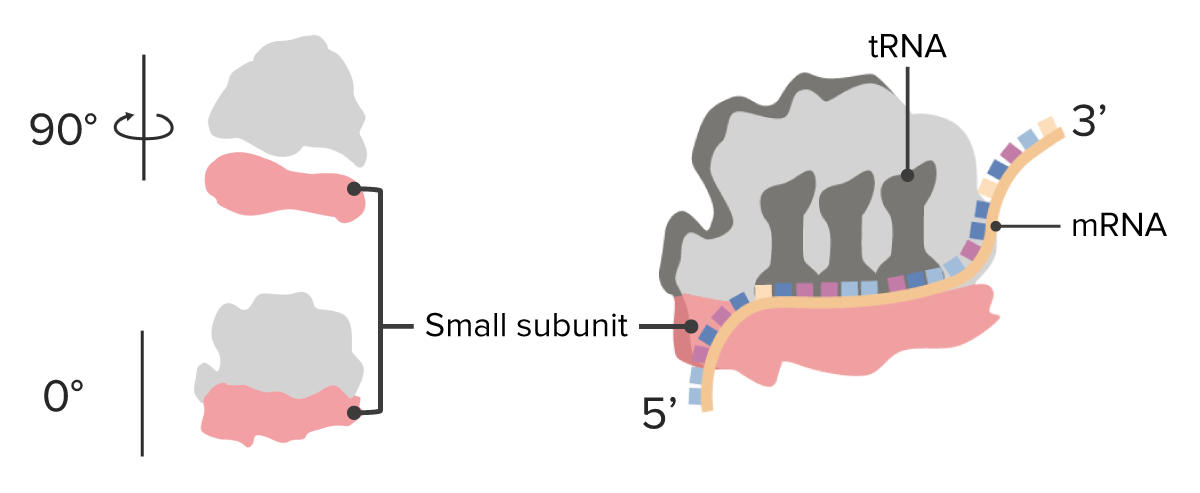
Ribossoma: subunidades pequenas
Imagem por Lecturio.Pequeno RNA RNA A polynucleotide consisting essentially of chains with a repeating backbone of phosphate and ribose units to which nitrogenous bases are attached. RNA is unique among biological macromolecules in that it can encode genetic information, serve as an abundant structural component of cells, and also possesses catalytic activity. RNA Types and Structure nuclear:
Pequeno RNA RNA A polynucleotide consisting essentially of chains with a repeating backbone of phosphate and ribose units to which nitrogenous bases are attached. RNA is unique among biological macromolecules in that it can encode genetic information, serve as an abundant structural component of cells, and also possesses catalytic activity. RNA Types and Structure nucleolar:
Micro RNA Micro RNA Small double-stranded, non-protein coding RNAs, 21-25 nucleotides in length generated from single-stranded microRNA gene transcripts by the same ribonuclease III, dicer, that produces small interfering RNAs (small interfering RNA). They become part of the RNA-induced silencing complex and repress the translation of target RNA by binding to homologous 3’utr region as an imperfect match. The small temporal RNAs (stRNAs), let-7 and lin-4, from c. Elegans, are the first 2 miRNAs discovered, and are from a class of miRNAs involved in developmental timing. RNA Types and Structure:
Pequeno RNA RNA A polynucleotide consisting essentially of chains with a repeating backbone of phosphate and ribose units to which nitrogenous bases are attached. RNA is unique among biological macromolecules in that it can encode genetic information, serve as an abundant structural component of cells, and also possesses catalytic activity. RNA Types and Structure regulatório:
6sRNA 6sRNA RNA Types and Structure:
Pequeno RNA RNA A polynucleotide consisting essentially of chains with a repeating backbone of phosphate and ribose units to which nitrogenous bases are attached. RNA is unique among biological macromolecules in that it can encode genetic information, serve as an abundant structural component of cells, and also possesses catalytic activity. RNA Types and Structure de interferência:
RNA RNA A polynucleotide consisting essentially of chains with a repeating backbone of phosphate and ribose units to which nitrogenous bases are attached. RNA is unique among biological macromolecules in that it can encode genetic information, serve as an abundant structural component of cells, and also possesses catalytic activity. RNA Types and Structure de interação PIWI:
CRISPR CRISPR Repetitive nucleic acid sequences that are principal components of the archaeal and bacterial CRISPR-CAS systems, which function as adaptive antiviral defense systems. RNA Types and Structure ( crRNA crRNA Repetitive nucleic acid sequences that are principal components of the archaeal and bacterial CRISPR-CAS system, which function as adaptive antiviral defense systems. RNA Types and Structure):
Ribonuclease Ribonuclease Enzymes that catalyze the hydrolysis of ester bonds within RNA. Interferons P (RNAse P):
Intrões “self-splicing”:
Viroide: