As imunoglobulinas ( Igs Igs Immunoglobulins (Igs), also known as antibodies, are glycoprotein molecules produced by plasma cells that act in immune responses by recognizing and binding particular antigens. The various ig classes are IgG (the most abundant), IgM, IgE, IgD, and IgA, which differ in their biologic features, structure, target specificity, and distribution. Immunoglobulins: Types and Functions), também conhecidas como anticorpos, são moléculas de glicoproteínas produzidas por células plasmáticas que atuam nas respostas imunes reconhecendo e ligando-se a antigénios específicos. Os anticorpos passam por processos que aperfeiçoam a afinidade do antigénio e fornecem uma defesa adequada através da troca de classe. As várias classes de Ig Ig X-linked Agammaglobulinemia são a IgG IgG The major immunoglobulin isotype class in normal human serum. There are several isotype subclasses of igg, for example, igg1, igg2a, and igg2b. Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis (a classe mais MAIS Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome abundante), IgM IgM A class of immunoglobulin bearing mu chains (immunoglobulin mu-chains). Igm can fix complement. The name comes from its high molecular weight and originally being called a macroglobulin. Immunoglobulins: Types and Functions, IgE IgE An immunoglobulin associated with mast cells. Overexpression has been associated with allergic hypersensitivity. Immunoglobulins: Types and Functions, IgD IgD An immunoglobulin which accounts for less than 1% of plasma immunoglobulin. It is found on the membrane of many circulating B lymphocytes. Immunoglobulins: Types and Functions e IgA IgA Represents 15-20% of the human serum immunoglobulins, mostly as the 4-chain polymer in humans or dimer in other mammals. Secretory iga is the main immunoglobulin in secretions. Immunoglobulins: Types and Functions, que diferem nas suas características biológicas, estrutura, especificidade do alvo e distribuição. As principais funções incluem opsonização, neutralização da infeciosidade dos agentes patogénicos, citotoxicidade e ativação do complemento. As classes específicas apresentam mecanismos defensivos únicos.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
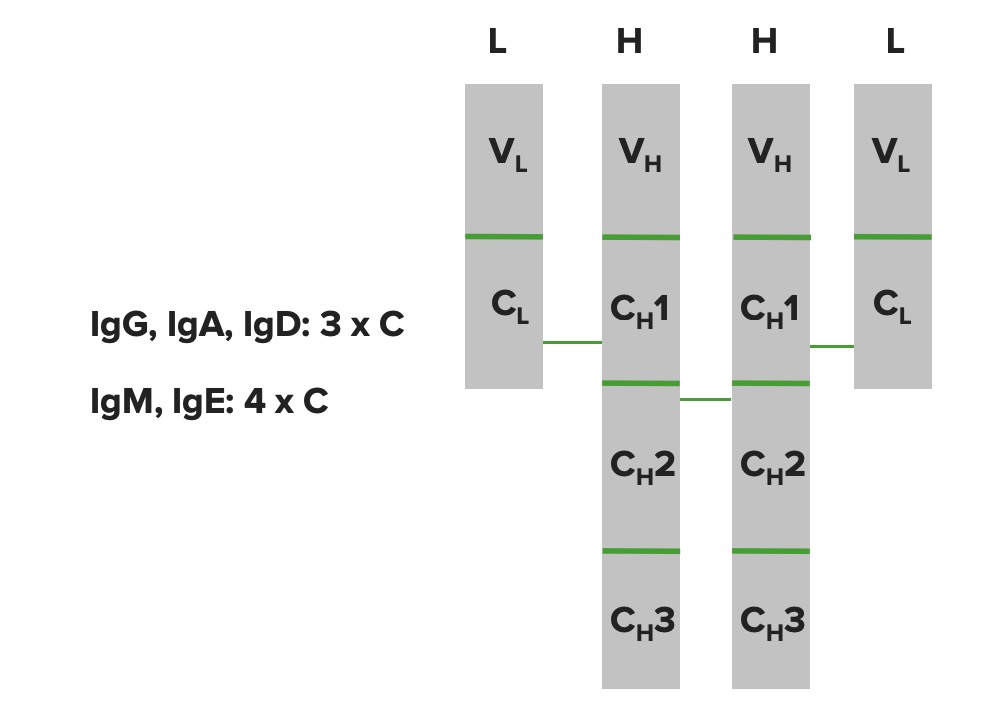
Domínios de imunoglobulinas:
As cadeias pesadas e cadeias leves são dobradas em estruturas chamadas domínios. A cadeia leve possui 1 domínio variável e 1 domínio constante. A cadeia pesada possui 1 domínio variável, mas dependendo da molécula de Ig pode possuir domínios constantes diferentes (IgG, IgA e IgD têm 3 domínios constantes, enquanto IgM e IgE têm 4 domínios constantes).
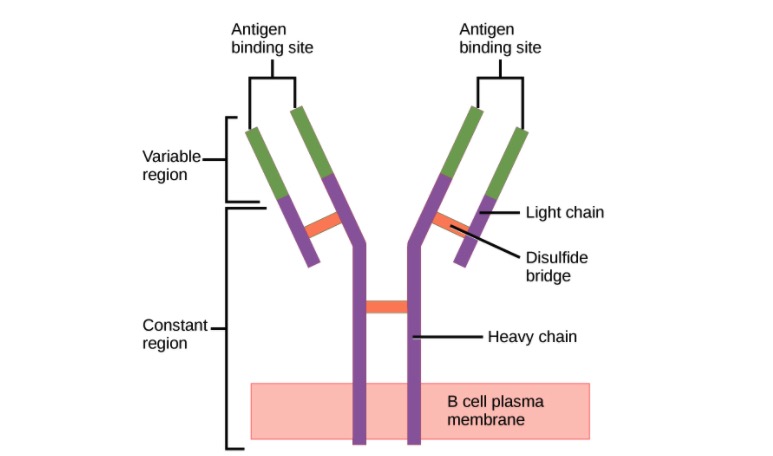
Estrutura do anticorpo (regiões):
Um anticorpo possui uma região variável única (formada por cadeias pesadas e leves) capaz de se ligar a um antigénio diferente e uma região constante (formada por cadeias pesadas).
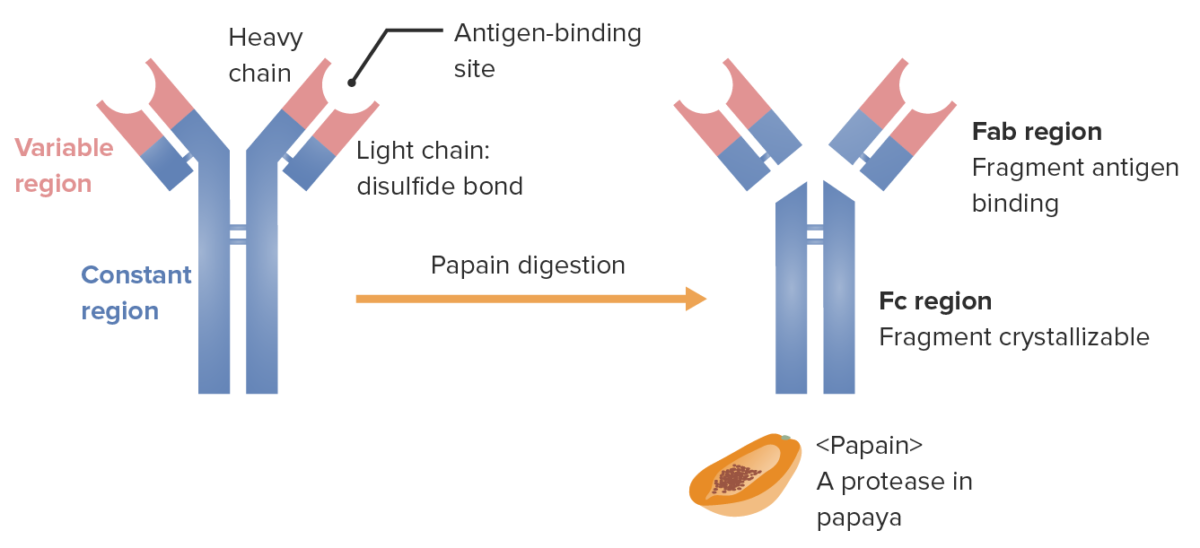
Fragmentos da imunoglobulina (determinada pelo local onde a enzima papaína divide a Ig):
A região Fab (fragmento de ligação ao antigénio) contém as regiões variáveis (a vermelho) e partes da região constante (a azul) das cadeias pesada e leve. A região Fc (fragmento cristalizável) contém a parte restante (cauda) do anticorpo (região constante apenas da cadeia pesada).
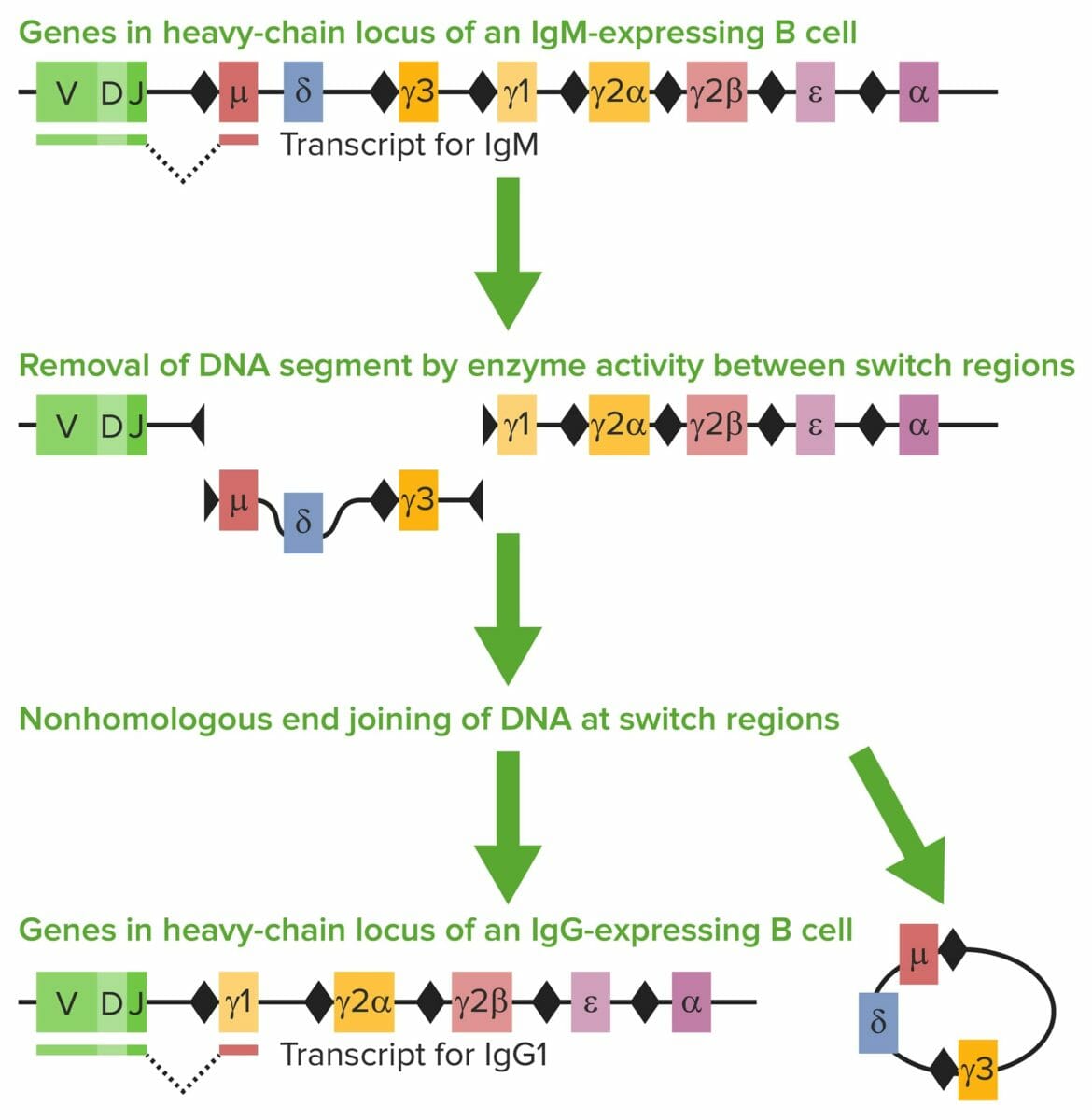
Recombinação de troca de classe (CSR):
A cadeia pesada possui diferentes segmentos de genes: região variável (V), região de diversidade (D), região de junção (J) e região constante (C).
A região C da cadeia pesada determina a classe/isótipo de Ig. Quando os antigénios são encontrados, as células B maduras IgM-positivas sofrem CSR. Os exões que codificam o segmento de gene de codificação constante (Cμ) da IgH são excisados. As áreas repetitivas de DNA, também conhecidas como regiões de troca (losangos negros) estão presentes.
As regiões de comutação guiam as enzimas, como a citidina desaminase induzida por ativação (AICDA), relativamente aos locais de rutura da cadeia dupla de DNA (DSBs) e onde o segmento VDJ e a nova região constante são unidos por uma enzima de reparação. O Cμ é substituído por um segmento novo de gene constante (por exemplo, Cγ, Cε ou Cα). Na imagem, Cγ1 é anexado ao segmento VDJ, formando IgG1.
Os anticorpos criados possuem propriedades importantes (diversidade e especificidade) e essenciais na resposta imune.
Existem mecanismos específicos, que originam a grande diversidade de anticorpos existentes, tais como:
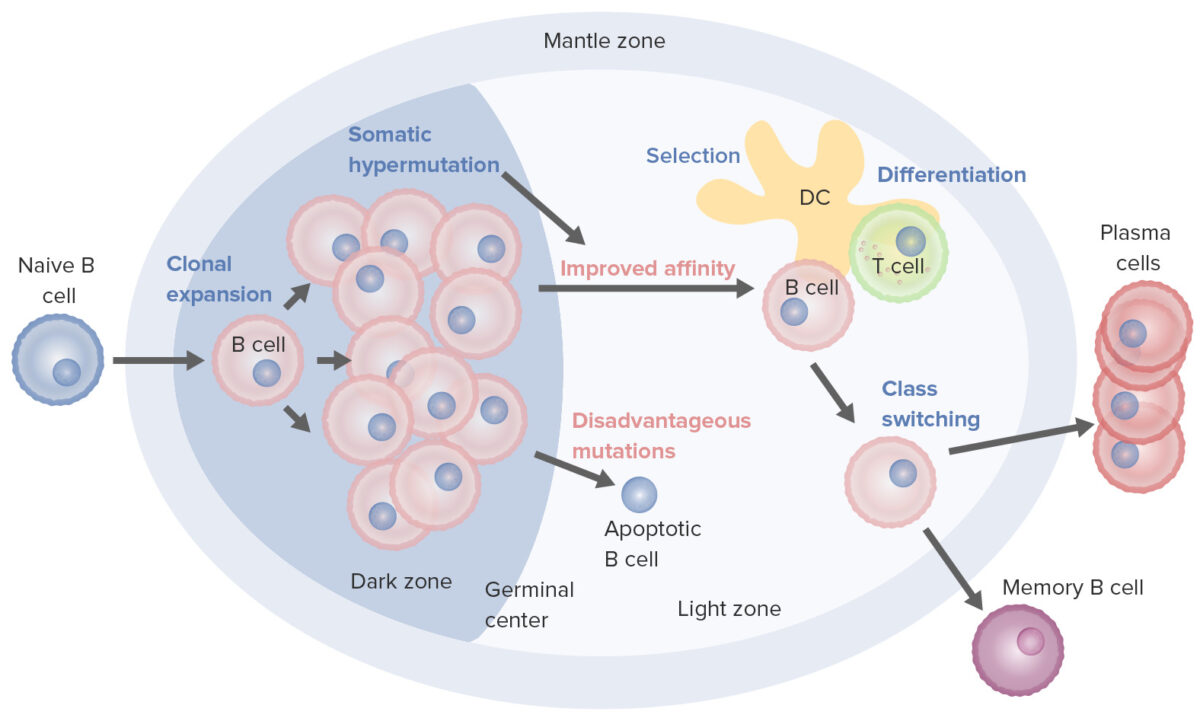
Processos de ativação e maturação de células B que ocorrem no centro germinativo:
Na fase de ativação, a célula B desloca-se da zona do manto e entra no centro germinativo. Ocorre a proliferação de células B (expansão clonal) e a afinidade do anticorpo para o antigénio é aperfeiçoada através do processo de hipermutação somática. Os ciclos repetidos de proliferação e hipermutação ajustam o recetor de células B. No entanto, nem todas as células B se diferenciam, sobretudo se a afinidade for fraca. Se a ligação antigénio-anticorpo não for otimizada ocorre apoptose celular. As células B com forte afinidade sobrevivem (seleção), com a ajuda de sinais de sobrevivência de células dendríticas foliculares e células T. As células B selecionadas avançam para a mudança de classe e diferenciação em células plasmáticas ou células de memória.
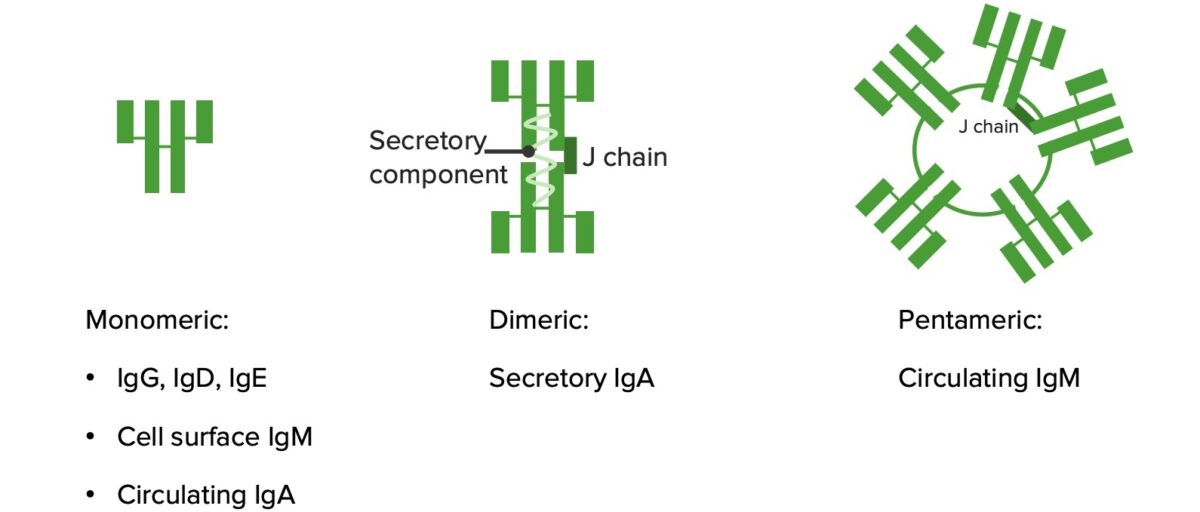
Monômeros e Polímeros:
As imunoglobulinas IgA, IgD e IgE são monómeros (estrutura ilustrada na imagem mais à esquerda). A IgA torna-se um dímero nas secreções mucosas. A IgM forma um pentâmero.
Imagem por Lecturio.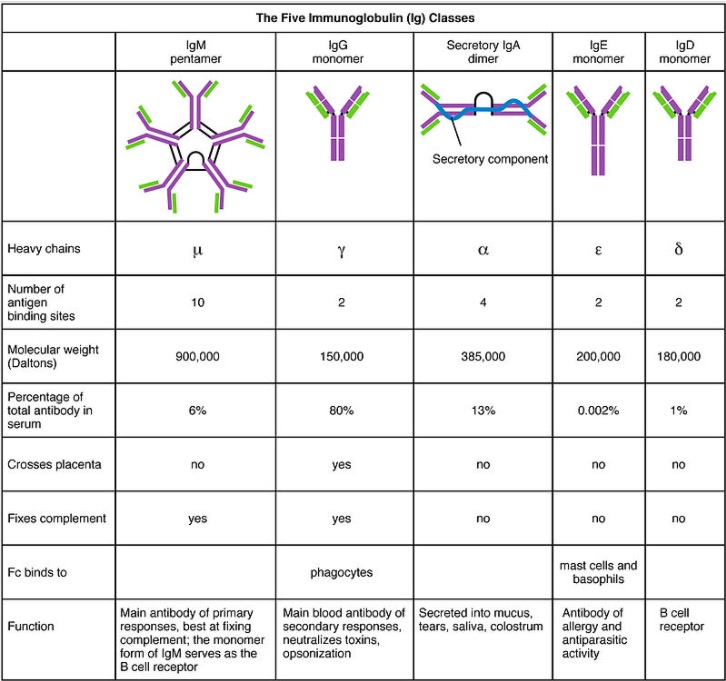
As 5 classes de Ig: estrutura e principais características
Imagem: “The five classes of immunoglobulins” por OpenStax College. Licença: CC BY 3.0