A diabetes Diabetes Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia and dysfunction of the regulation of glucose metabolism by insulin. Type 1 DM is diagnosed mostly in children and young adults as the result of autoimmune destruction of β cells in the pancreas and the resulting lack of insulin. Type 2 DM has a significant association with obesity and is characterized by insulin resistance. Diabetes Mellitus mellitus ( DM DM Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia and dysfunction of the regulation of glucose metabolism by insulin. Type 1 DM is diagnosed mostly in children and young adults as the result of autoimmune destruction of β cells in the pancreas and the resulting lack of insulin. Type 2 DM has a significant association with obesity and is characterized by insulin resistance. Diabetes Mellitus) é uma doença metabólica crónica caracterizada por hiperglicemia persistente em consequência do défice de secreção de insulina ( DM DM Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia and dysfunction of the regulation of glucose metabolism by insulin. Type 1 DM is diagnosed mostly in children and young adults as the result of autoimmune destruction of β cells in the pancreas and the resulting lack of insulin. Type 2 DM has a significant association with obesity and is characterized by insulin resistance. Diabetes Mellitus tipo 1), resistência à insulina ( DM DM Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia and dysfunction of the regulation of glucose metabolism by insulin. Type 1 DM is diagnosed mostly in children and young adults as the result of autoimmune destruction of β cells in the pancreas and the resulting lack of insulin. Type 2 DM has a significant association with obesity and is characterized by insulin resistance. Diabetes Mellitus tipo 2) ou ambos (latent autoimmune diabetes Diabetes Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia and dysfunction of the regulation of glucose metabolism by insulin. Type 1 DM is diagnosed mostly in children and young adults as the result of autoimmune destruction of β cells in the pancreas and the resulting lack of insulin. Type 2 DM has a significant association with obesity and is characterized by insulin resistance. Diabetes Mellitus in adults ( LADA LADA Autoimmune diabetes in adults with slowly progressive pancreatic beta cell failure and the presence of circulating autoantibodies to pancreatic islets cell antigens. Diabetes Mellitus)). O objetivo do tratamento é prevenir o desenvolvimento de complicações crónicas graves e potencialmente incapacitantes provocadas por danos em vários órgãos. O controlo glicémico adequado a longo prazo é crucial na prevenção de complicações. As complicações macrovasculares incluem doença cardíaca, AVC e doença vascular periférica. A doença microvascular podem causar retinopatia, neuropatia, nefropatia ou doença cardíaca sintomática, que não são observadas durante teste de stress ou angiografia, utilizados para diagnosticar doença de grandes vasos.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
A diabetes Diabetes Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia and dysfunction of the regulation of glucose metabolism by insulin. Type 1 DM is diagnosed mostly in children and young adults as the result of autoimmune destruction of β cells in the pancreas and the resulting lack of insulin. Type 2 DM has a significant association with obesity and is characterized by insulin resistance. Diabetes Mellitus mellitus ( DM DM Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia and dysfunction of the regulation of glucose metabolism by insulin. Type 1 DM is diagnosed mostly in children and young adults as the result of autoimmune destruction of β cells in the pancreas and the resulting lack of insulin. Type 2 DM has a significant association with obesity and is characterized by insulin resistance. Diabetes Mellitus) é uma doença comum que pode provocar múltiplas complicações graves. O controlo glicémico a longo prazo é crucial para prevenir o desenvolvimento destas complicações.
As complicações crónicas da diabetes Diabetes Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia and dysfunction of the regulation of glucose metabolism by insulin. Type 1 DM is diagnosed mostly in children and young adults as the result of autoimmune destruction of β cells in the pancreas and the resulting lack of insulin. Type 2 DM has a significant association with obesity and is characterized by insulin resistance. Diabetes Mellitus apresentam processos fisiopatológicos únicos e dependem do sistema orgânico atingido.
Existem várias formas de doença renal na diabetes Diabetes Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia and dysfunction of the regulation of glucose metabolism by insulin. Type 1 DM is diagnosed mostly in children and young adults as the result of autoimmune destruction of β cells in the pancreas and the resulting lack of insulin. Type 2 DM has a significant association with obesity and is characterized by insulin resistance. Diabetes Mellitus, incluindo lesões glomerulares não clássicas e doença tubulointersticial.
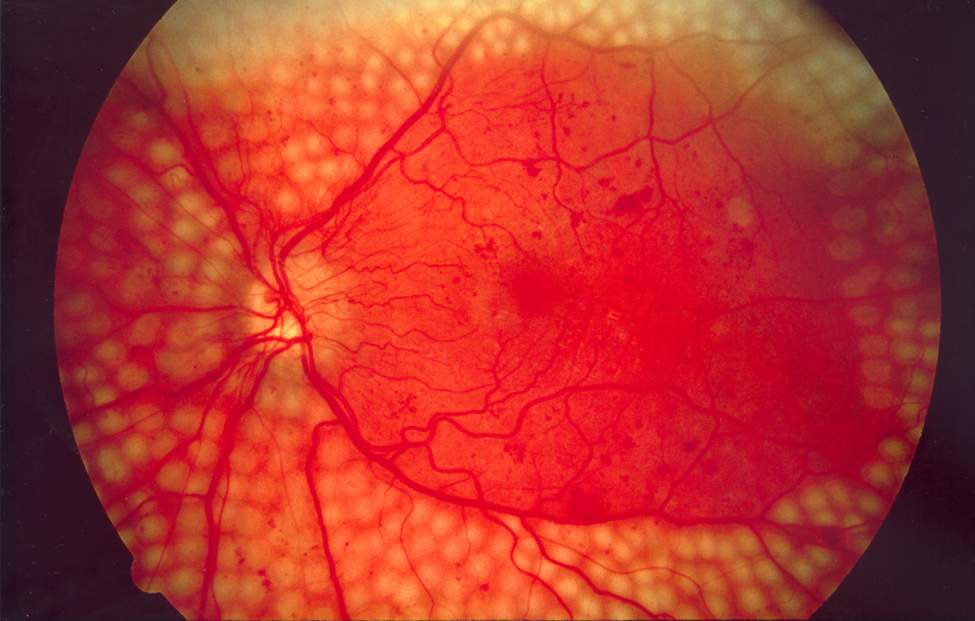
Imagem do fundo ocular de cirurgia a laser de dispersão para retinopatia diabética
Imagem: “Fundus photo showing scatter laser surgery for diabetic retinopathy” por National Eye Institute, National Institutes of Health. Licença: Domínio Público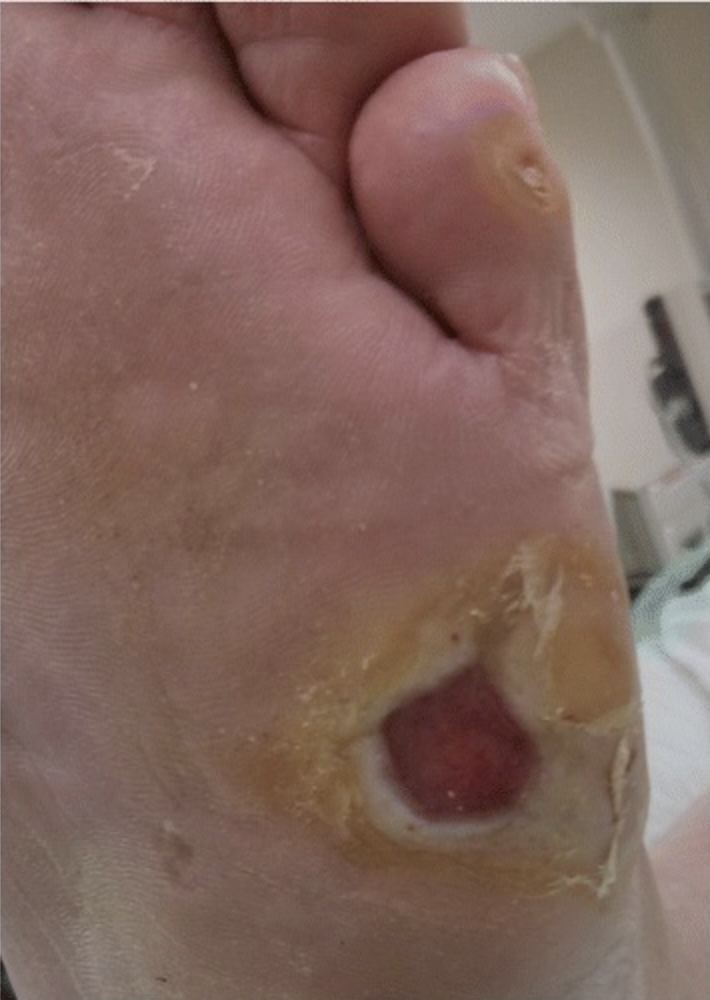
Lesão do pé em indivíduo com neuropatia periférica:
Os indivíduos com neuropatia periférica não conseguem sentir pequenas lesões nas extremidades. Assim, muitas vezes, estas lesões não são tratadas. Em combinação com a redução do fluxo sanguíneo para as extremidades, estas lesões podem condicionar a formação de úlceras crónicas nos pés que podem necessitar de desbridamento cirúrgico em indivíduos com diabetes.
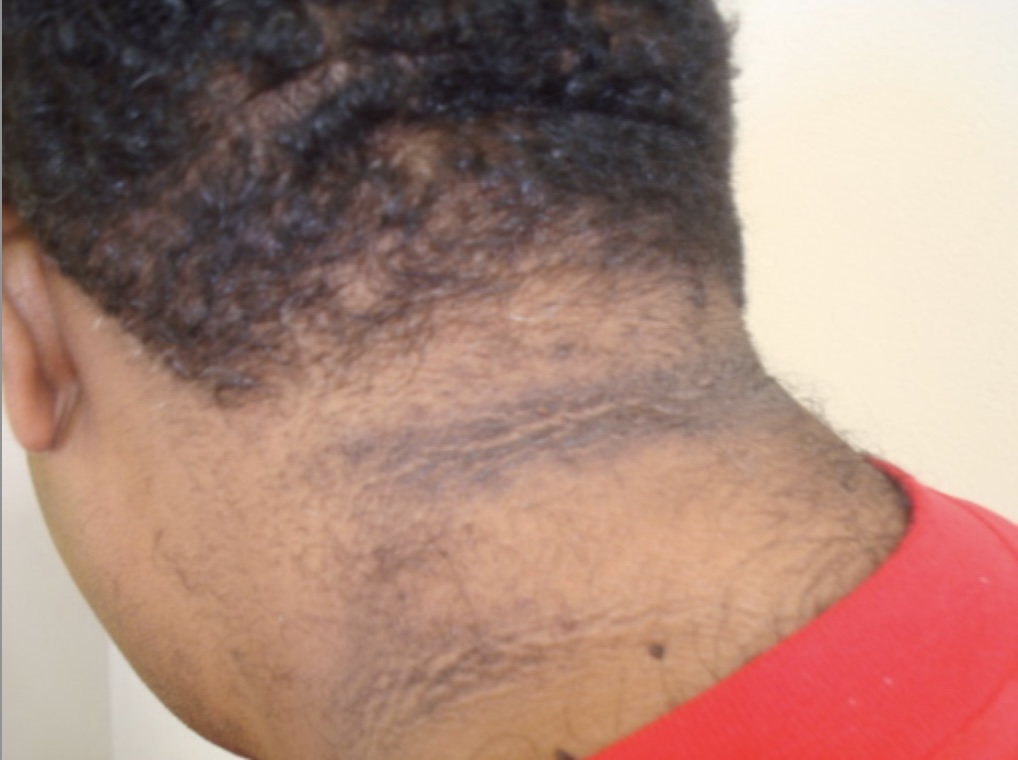
Acantose nigricans: um achado comum em indivíduos com resistência à insulina (como na diabetes). A acantose nigricans caracteriza-se por áreas aveludadas, espessadas e escurecidas da pele, frequentemente observadas na região da posterior do pescoço.
Imagem: “Acanthosis nigricans Grade 1” por Department of Clinical Medical Sciences, The University of West Indies, St Augustine, Trinidad & Tobago, Licença: CC BY 2.0Doença arterial coronária:
Doença arterial periférica:
Estenose carotídea: ecografia para avaliar a extensão da doença oclusiva
Geralmente a nefropatia diabética é diagnosticada durante uma análise de urina anual para rastreio de microalbuminúria.
Diagnosticada durante rastreio anual com exames oftalmológicos (oftalmologista ou optometrista)
Em todas as complicações associadas à diabetes Diabetes Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia and dysfunction of the regulation of glucose metabolism by insulin. Type 1 DM is diagnosed mostly in children and young adults as the result of autoimmune destruction of β cells in the pancreas and the resulting lack of insulin. Type 2 DM has a significant association with obesity and is characterized by insulin resistance. Diabetes Mellitus, a prevenção é fundamental e o controlo glicémico é a principal prioridade.