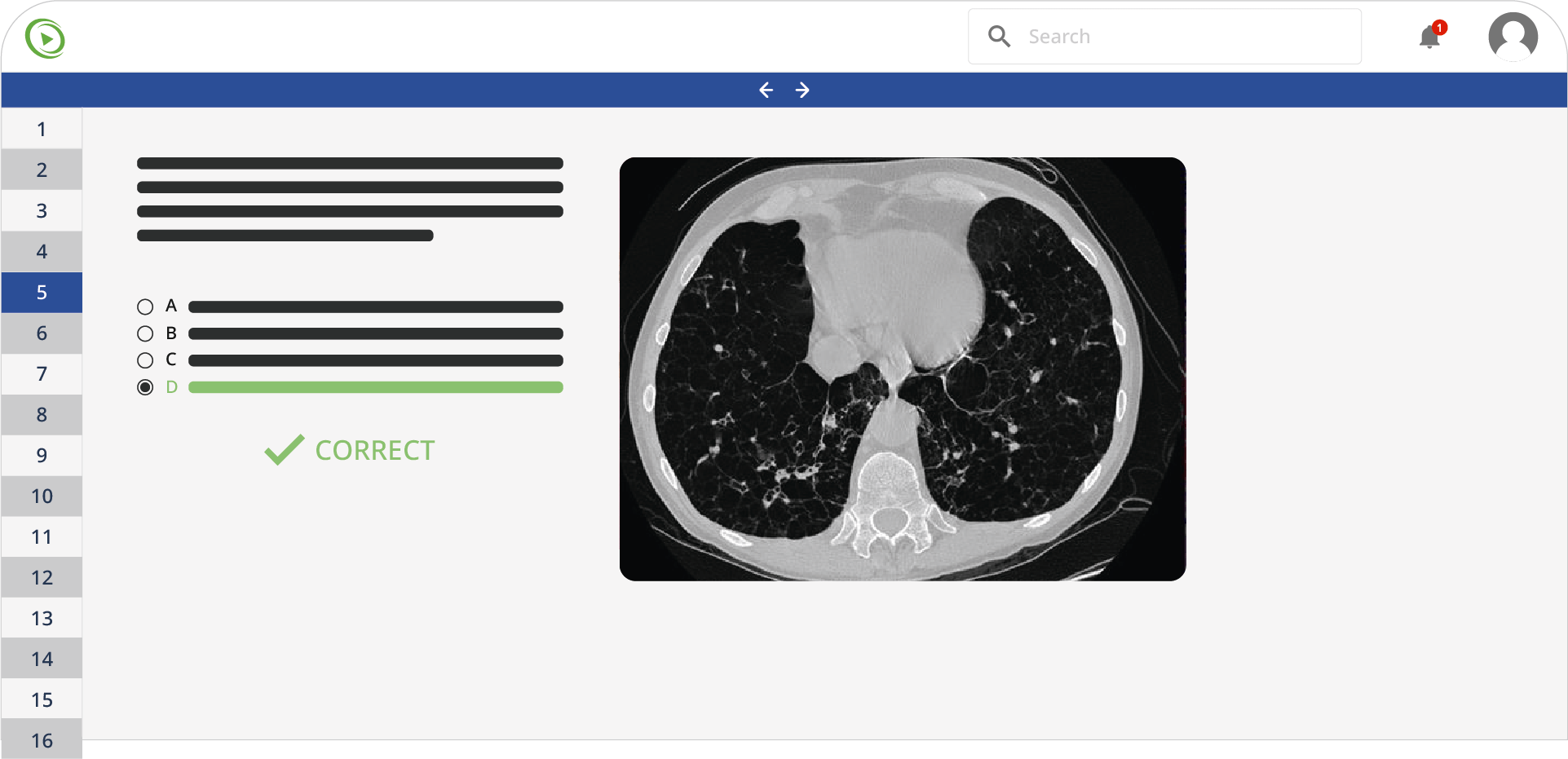
A 32-year-old G1P0 woman at 35 weeks gestation presents to the emergency department for a 2-hour history of left calf swelling and redness. The pain has progressively worsened since its onset. Her pregnancy has been uneventful. She denies a history of insect bites or trauma. She does not use alcohol, tobacco, or illicit drugs. She does not take any medications, other than prenatal vitamins. Her temperature is 36.8°C (98.2°F), blood pressure is 105/60 mm Hg, pulse is 110/min, and respirations are 15/min. The left calf is edematous with overlying erythema. The skin feels warm and pain is elicited with passive dorsiflexion of the foot. The femoral, popliteal, and pedal pulses are palpable bilaterally. Abdominal exam reveals a fundal height consistent with gestational age. The lungs are clear to auscultation bilaterally. Which of the following hormones is most likely related to the development of this patient’s condition?
A. Estriol
B. Progesterone
C. Human chorionic gonadotropin
D. Human placental lactogen
E. Prolactin
A 24-year-old G2P0 woman presents to her physician at 15 weeks gestation to discuss the results of recent screening tests. She has no complaints and the current pregnancy has been uncomplicated. Her previous pregnancy terminated with spontaneous abortion in the first trimester. Her immunizations are up to date. Vital signs include: blood pressure 110/60 mm Hg, heart rate 78/min, respiratory rate 14/min, and temperature 36.8℃ (98.2℉). The physical exam is unremarkable. Laboratory studies show:
| HBsAg | negative |
| HBcAg | negative |
| Anti-HBsAg | positive |
| HIV 1/2 AB | negative |
| VDRL | positive |
Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
A. PCR for HBV DNA
B. T. pallidum hemagglutination assay
C. Prescription of benzylpenicillin
D. HBV vaccination
E. Full serum panel for HBV
A 32-year-old G2P0 woman presents at 37 weeks gestation with a watery vaginal discharge. Her current pregnancy included an abnormal ultrasound finding at 20 weeks gestation. Vital signs include: blood pressure 110/80 mm Hg, heart rate 91/min, respiratory rate 13/min, and temperature 36.4℃ (97.5℉). The fetal heart rate is 141/min. On speculum examination, there are no vaginal or cervical lesions, but there is a continuous watery vaginal discharge with traces of blood. The discharge is fern- and nitrite-positive. Soon after the initial examination, the bleeding increases. Fetal monitoring shows a heart rate of 103/min with late decelerations. Which of the following was most likely seen on ultrasound?
A. Loss of the normal retroplacental hyperechogenic region
B. Velamentous cord insertion
C. Retroplacental hematoma
D. Subchorionic cyst
E. Placental edge-internal os distance of 3 cm
A 29-year-old G3P2 woman undergoes a cesarean section at 38 weeks gestation and delivers a boy weighing 4570 g with Apgar scores of 5 and 8 at 1 and 5 minutes, respectively. The pregnancy was complicated by gestational diabetes with poor glycemic control. The newborn’s heart rate is 122/min, respiratory rate is 31/min, and temperature is 36.4℃ (97.5℉). On examination, the newborn is pale, lethargic, diaphoretic, and has poor muscular tone. The liver is 2 cm below the right costal margin. Which of the following is the most likely cause of the newborn’s condition?
A. Microangiopathy
B. Hyperinsulinemia
C. Hyperglycemia
D. Hyperbilirubinemia
E. Polycythemia
A 32-year-old G2P2 woman presents for a routine gynecologic evaluation. She is feeling well, but has noticed small amounts of vaginal bleeding in the middle of her menstrual cycles over the past 6 months. Her last pregnancy was 3 years ago. Subsequent menstrual cycles have been regular, lasting about 2–3 days. She is up to date with recommended cervical cancer screening. She denies any recent travel or history of trauma. She is sexually active with her husband and they use condoms consistently. She drinks alcohol occasionally, but does not smoke or use illicit drugs. The physical exam is unremarkable. Ultrasound reveals a fleshy mass with a pedunculated stalk deep in the cervical canal. The uterine lining is 5-mm thick and homogeneous. Multiple small leiomyomas are observed. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
A. No further intervention with follow-up in 6 months
B. Electrocautery and cryofreezing
C. Cervical brush biopsy
D. Removal of the lesion with a ring forceps
E. Administration of antibiotics
A 26-year-old woman, G1 P0, at 30 weeks of pregnancy presents to the office for a well-woman checkup. Up until now, her pregnancy has progressed without any problems, but she says that last week a couple of painful ulcers appeared on her vulva. When questioned about her sexual relationships, she says she has not been with anyone but her husband, but she had refrained from sex up until last month because she was afraid for her baby’s safety. Physical examination shows no other abnormalities. Tzanck testing is performed with positive results. The patient asks if this will affect her delivery because she wants a “natural” delivery. Which of the following options is most appropriate in this patient?
A. Cesarean delivery is the best option
B. If there are no lesions during labor, vaginal delivery will be possible
C. She should have an abortion
D. This disease will be cured with acyclovir therapy
E. Vaginal delivery is the best option
A 24-year-old pregnant woman with a 37-week pregnancy presents to the office for a scheduled check-up. She is HIV positive and is currently taking an abacavir/lamivudine-dolutegravir regimen. Aside from that, the patient is completely healthy, and she and her fetus show no abnormalities. Her laboratory results from today showed the following:
- Viral load: 278 copies/mL
- CD4: 772/mm3
Which of the following is correct regarding immediate postpartum management for the newborn?
A. Combination prophylaxis for the newborn
B. Continue baseline ART regimen with single regimen prophylaxis for the newborn
C. Induce labor
D. Intrapartum intravenous abacavir
E. Scheduled cesarean delivery at 38 weeks
A 27-year-old gravida 2, para 2 woman presents to her OB/GYN’s office concerned that she may be pregnant. She and her husband use condoms for contraception. The night before, the condom broke during intercourse. She has 2 children under the age of 3 and does not want another child at this time. She says she cannot take “the pill” because she had a blood clot in her leg after her last cesarean section successfully treated with 6 months of anticoagulation. She smokes cigarettes and drinks alcohol regularly. Which of the following would be the most appropriate recommendation for this patient?
A. Reassure her that she is likely not pregnant
B. Refer her to an abortion clinic
C. Recommend etonogestrel implant
D. Recommend copper IUD
E. Recommend levonorgestrel IUD
A 36-year-old woman, gravida 3, para 3, presents to the postpartum clinic complaining of left breast pain. She gave birth 3 weeks ago, and the breast pain started yesterday. She has exclusively breastfed her infant since birth. She says she hasn’t been feeling well for the past 2 days and has experienced fatigue and muscle soreness. Her temperature is 38.3°C (101°F). Physical examination shows the lateral side of her left breast to be erythematous and warm. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
A. Arrange for hospital admission
B. Prescribe an antibiotic and tell her she must stop breastfeeding until her symptoms resolve
C. Prescribe an antibiotic and tell her she should continue breastfeeding
D. Reassure her that these infections usually resolve on their own within a few days, and recommend that she continue breastfeeding
E. Reassure her that these infections usually resolve on their own within a few days, and recommend that she stop breastfeeding until her symptoms resolve
A 32-year-old woman presented for her annual physical examination. She mentioned that her family history had changed since her last visit: her mother was recently diagnosed with breast cancer and her sister tested positive for the BRCA2 mutation. The patient, therefore, requested testing as well. If the patient tests positive for the BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutation, which of the following is the best screening approach?
A. Annual clinical breast exams, annual mammography, and monthly self-breast exams
B. Twice-yearly clinical breast exams, annual mammography, annual breast MRI, and breast self-exams
C. Annual ultrasound, annual mammography, and monthly self-breast exams
D. Order magnetic resonance imaging of the breast
E. Refer to radiation therapy
Do you want to practice more OBGYN questions?
Create a free Lecturio account and you’ll have access to the Lecturio question bank with more than 1,200 USMLE Step 2 CK practice questions.