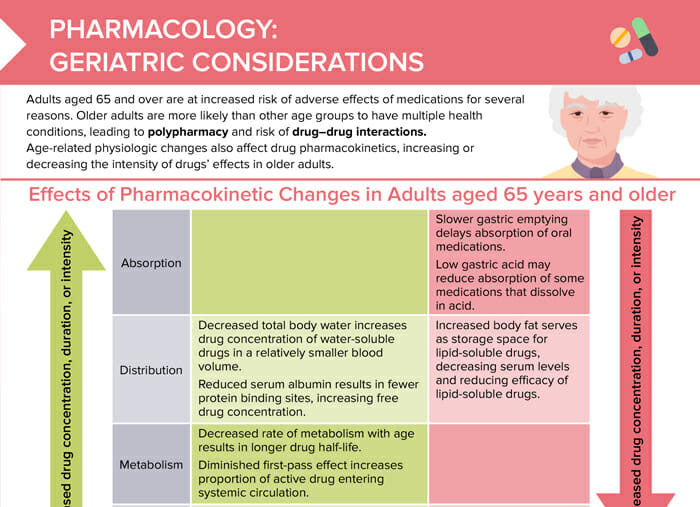
What is dementia?
Dementia is a general term for chronic impairment of brain function that affects thinking. It is not one specific disease, and is not part of the normal aging process.
Dementia occurs in:
- 5%–10% of adults aged 65–80
- 20% older than 80
- Close to 50% of adults 85 years and older
What is the difference between dementia and Alzheimer’s?
While dementia is an umbrella term used to describe the group of symptoms, Alzheimer’s disease is a specific type of dementia.
What are the different types of dementia?
How many types of dementia are there?
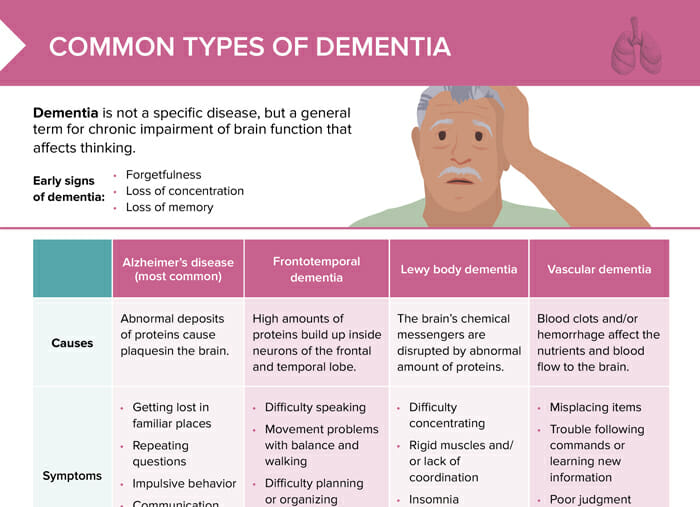
There are four main types of dementia: Alzheimer’s disease, frontotemporal dementia, Lewy body dementia, and vascular dementia.
What are the most common types of dementia?
The most common manifestation of dementia is Alzheimer’s disease, accounting for 60%–80% of dementia cases.
What is Alzheimer’s disease?
Alzheimer’s disease is caused by abnormal deposits of proteins causing plaques in the brain. Symptoms include:
- Getting lost in familiar places
- Repeating questions
- Impulsive behavior
- Communication problems
Symptoms typically onset in the mid-60s (early-onset Alzheimer’s may be seen as early as the 30s).
Note: All Alzheimer’s is dementia, but not all dementia is Alzheimer’s.
What is frontotemporal dementia?
Frontotemporal dementia is caused by high amounts of proteins building up inside neurons of the frontal and temporal lobe. Symptoms include:
- Difficulty speaking
- Movement problems with balance and walking
- Difficulty planning and organizing
- Changes in emotional pattern
Symptoms typically onset between 45 and 64 years old.
What is Lewy body dementia?
Lewy body dementia is caused by the brain’s chemical messengers being disrupted by abnormal amounts of proteins. Symptoms include:
- Difficulty concentrating
- Rigid muscles and/or lack of coordination
- Insomnia
- Daytime sleepiness
- Hallucinations
Symptoms typically onset at age 50 or older.
What is vascular dementia?
Vascular dementia is caused by blood clots and/or hemorrhage affecting the nutrients and blood flow to the brain. Symptoms include:
- Misplacing items
- Trouble following commands or learning new information
- Poor judgment
Symptoms typically onset over the age of 65.
What is childhood dementia?
Childhood dementia is an umbrella term describing a group of conditions that affect cognitive abilities in children and adolescents. These conditions are rare and often genetically driven, and they can manifest as problems with memory, learning, attention, and problem-solving abilities.
What causes dementia?
Dementia is caused by damage to brain cells which interferes with the ability to communicate with each other, affecting thinking, behavior, and feelings. Different types of dementia are associated with particular kinds of brain cell damage in specific regions of the brain.
While the exact cause may not be known, certain risk factors like age, family history, and lifestyle habits are commonly associated with increased risk of dementia.
How to prevent dementia
Due to dementia being associated with genetic predispositions, there is no fail-safe way to prevent dementia. However, certain lifestyle changes are thought to reduce the risk of dementia, including:
- Physical activity and controlling cardiovascular risk factors
- Healthy diet
- Active social life and mental stimulation
- Minimizing alcohol intake and smoking
- Good sleeping habits
What are the early signs of dementia?
The earliest symptoms affected people may notice include:
- Forgetfulness
- Loss of concentration
- Loss of memory
What are the stages of dementia?
Dementia typically progresses through several stages, though the timing and symptoms can vary significantly. The stages often referenced are:
- No impairment
- Very mild cognitive decline to mild cognitive decline:
- Minor memory problems, losing things around the house; may still seem normal
- Friends and family or doctors (with standardized tests) may begin to notice cognitive problems.
- Moderate cognitive decline: clear-cut symptoms present
- Moderately severe cognitive decline:
- Major gaps in memory and cognitive function
- May need assistance with ADLs
- Severe cognitive decline (middle dementia):
- Memory continues to worsen
- Personality changes
- Extensive help with ADLs needed
- Very severe cognitive decline (late dementia):
- Loss of ability to respond to and interact with environment
- Loss of control of movement
What is sundowning?
Sundowning or “sundown syndrome” describes a state of increased confusion and agitation that typically occurs in the late afternoon or evening in people with dementia. Nurses can help manage sundowning by taking measures such as maintaining a regular sleep schedule, providing adequate lighting, and reducing evening noise and activity.
Nursing interventions for dementia
Nursing interventions for dementia patients focus on maintaining quality of life, managing symptoms, promoting safety, and supporting the individual and their family. Key nursing interventions include:
- Promote orientation (with clocks, calendars, signs, reminders)
- Encourage independence while creating a safe environment (prevent falls/injuries)
- Social interaction and communication (boost mood and cognitive function with activities while using clear language and non-verbal cues and treating the client with respect)
- Promote good sleep hygiene and nutrition (assistance with feeding, regular sleep patterns)
- Medication management
- Assisting family and caregivers emotionally and with education