What is diabetes mellitus?
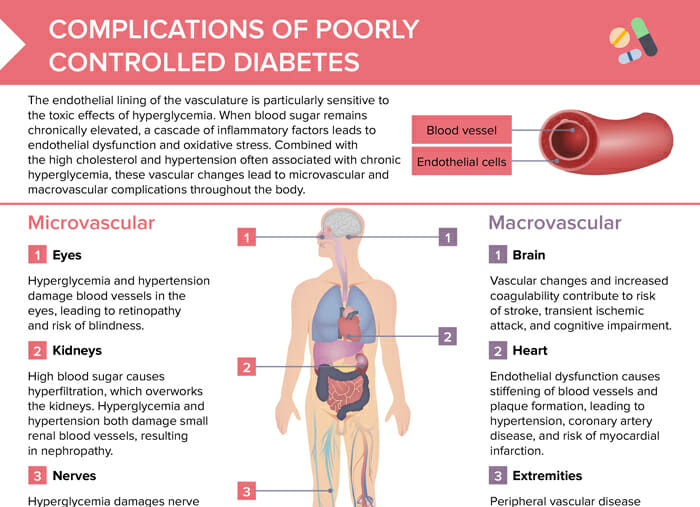
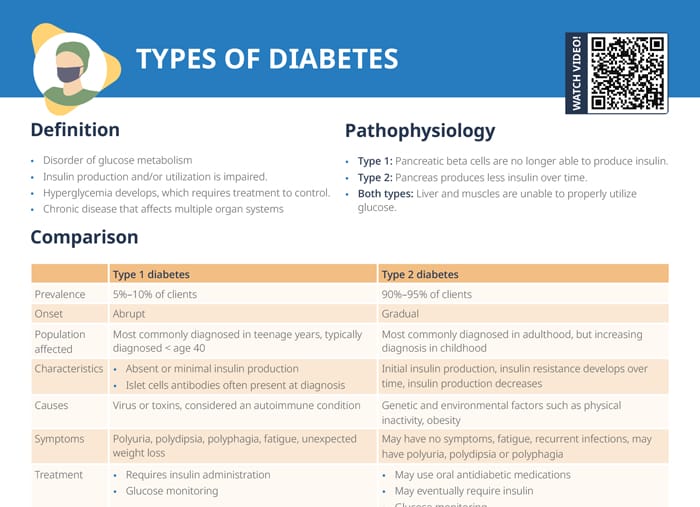
Diabetes mellitus is a disorder of glucose metabolism where the production and/or utilization of insulin is impaired and the liver and muscles are unable to properly utilize glucose. As a consequence, hyperglycemia develops, which requires treatment to control. Diabetes is a chronic disease affecting multiple organ systems.
How many types of diabetes are there?
The main two types of diabetes mellitus are type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Other types are gestational diabetes (occuring during pregnancy), monogenic diabetes (caused by genetic mutations), and secondary diabetes (caused by other medical conditions).
What are the types of diabetes?
Type 1 diabetes mellitus
In type 1 diabetes, the pancreatic beta cells are no longer able to produce insulin. Only 5%–10% of clients affected by diabetes have type 1. The onset is abrupt, typically at teenage age. In this condition, insulin production is absent or minimal. Often, islet cells antibodies are present at diagnosis.
Type 2 diabetes mellitus
In type 2 diabetes, the pancreas produces less insulin over time. 90%–95% of diabetes patients are affected by this type. The onset is gradual, most commonly diagnosed in adulthood. In this condition, insulin is initially produced; insulin resistance develops over time, and insulin production gradually decreases.
Diabetes insipidus
It is important to differentiate the types of diabetes mellitus from diabetes insipidus. In this condition, the kidneys are unable to concentrate urine.
What causes type 1 vs type 2 diabetes?
While type 2 diabetes mellitus is caused by genetic and environmental factors (physical inactivity, obesity), type 1 diabetes is considered an autoimmune condition, caused by virus or toxins.
How to diagnose type 1 vs type 2 diabetes
Type 1 diabetes symptoms
Symptoms of type 1 diabetes include:
- Polyuria
- Polydipsia
- Polyphagia
- Fatigue
- Unexpected weight loss
Type 2 diabetes symptoms
Symptoms of type 2 diabetes can include:
- May have no symptoms
- Fatigue
- Recurrent infections
- Polyuria
- Polydipsia
- Polyphagia
- Blurred vision (many times first symptom)
Lab diagnosis of diabetes
The following lab tests can confirm the diagnosis of diabetes:
- HbA1c ≥ 6.5 %
- Fasting plasma glucose ≥ 126 mg/dL
- Two-hour plasma glucose ≥ 200 mg/dL
- Symptoms with a random plasma glucose ≥ 200 mg/dL
Treatment of type 1 vs type 2 diabetes
Type 1 diabetes is treated via insulin administration and glucose monitoring. In type 2, oral antidiabetic medications can be used, but insulin administration may eventually be required. Glucose monitoring and lifestyle changes are the other measures of treatment of type 2.
Client education for diabetes patients
- Teach clients how and when to monitor glucose levels at home.
- Provide education on the role of diet and exercise in diabetes management.
- Teach clients how to use prescribed medications and about potential side effects.
- Educate clients on when to call their provider and when to seek emergency care
Signs of a diabetic emergency
Watch out for these signs in your diabetes patients, type 1 as well as type 2:
- Hunger
- Clammy skin
- Profuse sweating
- Drowsiness or confusion
- Feeling faint
- Sudden loss of responsiveness
- Weak and rapid pulse
- Nausea/vomiting
- Seizures
- Temporary paralysis