What is tuberculosis?
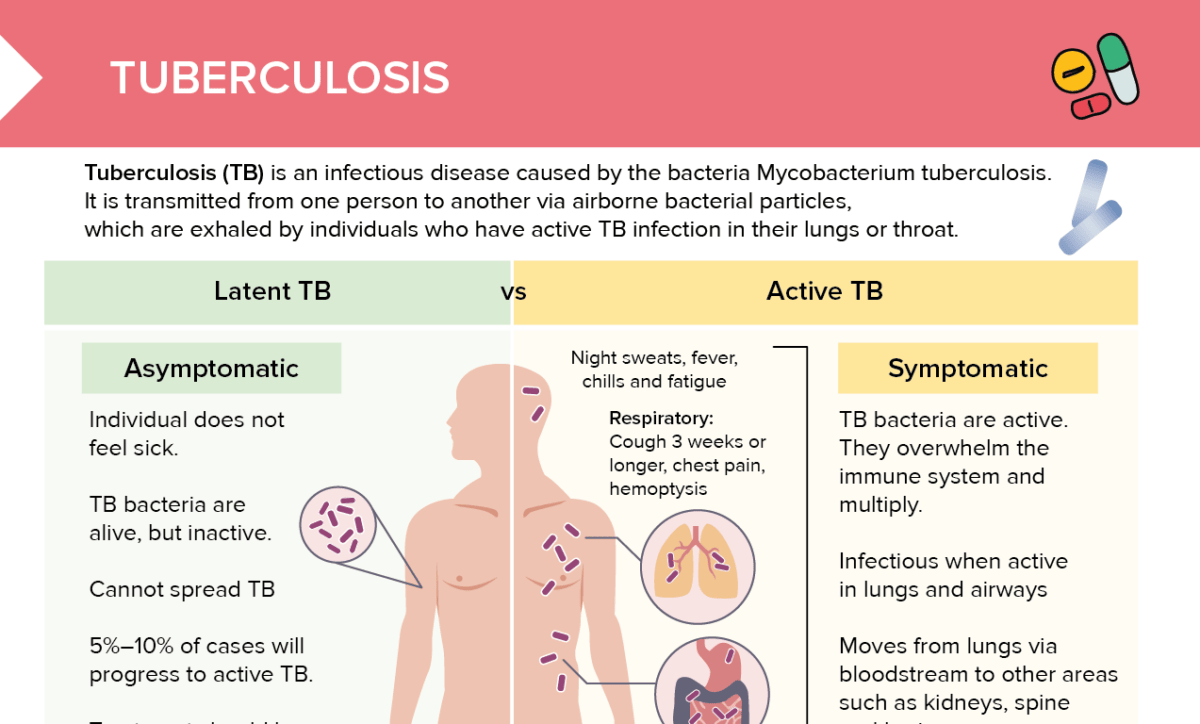
Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It is transmitted from one person to another via airborne bacterial particles, which are exhaled by individuals who have active TB infection in the lungs or throat.
Latent vs active tuberculosis
Latent and active tuberculosis represent different stages of tuberculosis infection.
Latent tuberculosis (asymptomatic)
This is when a person is infected with the Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacterium, but does not feel sick and does not show any signs or symptoms of the disease. This happens because the immune system is able to keep the bacteria under control, preventing them from multiplying. People with latent tuberculosis cannot spread the disease. However, if the immune system weakens, latent tuberculosis can become active, which happens in about 5–10% of cases.
Treatment should be offered. If declined, follow with annual symptom assessment and periodic chest X-ray.
Active tuberculosis (symptomatic)
In this stage, the tuberculosis bacteria are active and multiply, overwhelming the immune system. The disease becomes infectious when it is active in the lungs and airways, and will move from there via the bloodstream to other areas, such as the kidneys, spine, and brain. Active tuberculosis requires prompt medical treatment with a combination of antibiotics over several months to prevent complications and transmission to others.
Related videos
How can tuberculosis be transmitted?
While individuals with latent tuberculosis are not contagious, people with active tuberculosis are infectious and can spread the bacteria to others through airborne droplets when they cough, sneeze, or talk.
What are the symptoms of tuberculosis?
In the latent stage, tuberculosis is asymptomatic.
In the active stage, symptoms include:
- Night sweats
- Fever
- Chills
- Fatigue
- Respiratory:
- Cough 3 weeks or longer
- Chest pain
- Hemoptysis
- GI-related:
- Loss of appetite
- Unexplained weight loss
Methods of tuberculosis screening
Note that positive screening indicates exposure to Mycobacterium tuberculosis, but not if the infection is latent, active, or if the result is due to previous BCG vaccine (skin test only). Physical exam and further testing is required.
Tuberculin skin test
This involves injecting a small amount of tuberculin (a protein derivative of TB bacteria) into the skin of the forearm. A healthcare provider will check the injection site 48–72 hours later for redness and/or a hard, raised bump (induration), which may indicate infection.
Tip: When assessing skin test, measure only the area of induration (not redness).
Interferon gamma release assays (IGRAs)
These are blood tests that measure how the immune system reacts to tuberculosis bacteria.
How is tuberculosis diagnosed?
If the skin or blood screening test is positive, take these next steps:
- Review exposure risk.
- Assess for symptoms.
- Chest X-ray (may show lesions or cavitation)
- Sputum analysis