What is a transdermal medication patch?
A transdermal medication patch is an adhesive patch that is applied to a client’s skin, where it continuously administers medication through the skin into the bloodstream. This method provides a controlled, steady dose of medication, often over the course of hours or days.
Nursing tip: Medication patches need to be monitored for skin damage and correct position daily.
Nursing tip: Do not apply transdermal patch to non-intact skin, unless specifically ordered by provider.
What are the advantages of transdermal medication administration?
When applied transdermally, medication diffuses through skin layers into the systemic circulation, allowing slow absorption of medication over time. This is advantageous for a number of medications and uses, including:
- Nicotine patches for smoking cessation
- Pain relief (e.g., fentanyl patch, lidocaine patch, buprenorphine patch, CBD patch)
- Hormone replacement therapy (e.g., transdermal estrogen patch)
- Birth control (contraceptive patch)
- Transdermal patch for nausea (sea sickness patch)
- Angina treatment (nitroglycerin patch)
Nicotine patch
Image by RegBarc. License: CC BY-SA 3.0Summary of the benefits of the transdermal route:
- Uniform release of medication avoids peaks, reducing risk of side effects and toxicity.
- Less invasive than parenteral route
- Alternative when parenteral access is limited in ‘hard–stick’ clients and those with needle phobia
- Reduced dosing frequency can improve compliance.
- Alternative to PO in clients who are unconscious or vomiting
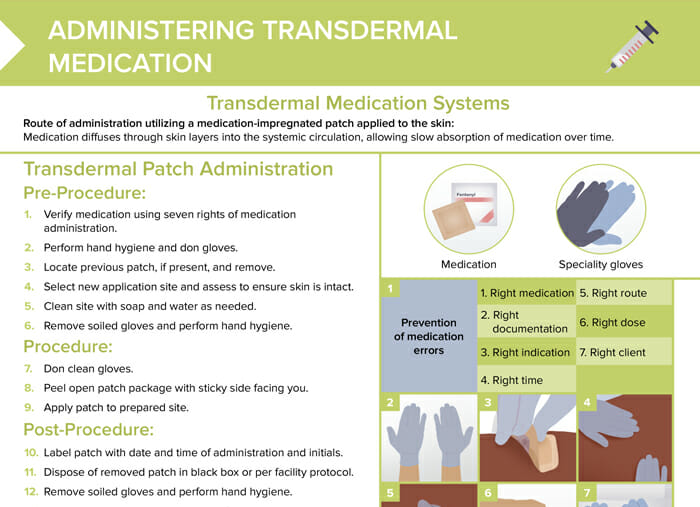
How to apply a transdermal patch
Pre-procedure: how to prepare administration of a transdermal medication patch
- Verify medication using seven rights of medication administration.
- Perform hand hygiene and don gloves.
- Locate previous patch, if present, and remove.
- Select new application site and assess to ensure skin is intact.
- Clean site with soap and water as needed.
- Remove soiled gloves and perform hand hygiene.
Procedure
- Don clean gloves.
- Peel open patch package with sticky side facing you.
- Apply patch to prepared site.
Post-procedure
- Label patch with date and time of administration and initials.
- Dispose of removed patch in black box/biohazard box or per facility protocol.
- Remove soiled gloves and perform hand hygiene.
- Document date, time, and location of patch clearly in client chart.
Types of transdermal patches
Types of transdermal patches include:
- Drug-in-adhesive: Medication is contained within/mixed with the adhesive, in one or multiple layers.
- Reservoir: Medication is stored in a reservoir that is separated from the skin with a rate-controlling membrane.
- Matrix system: Medication is embedded in a polymer matrix.