What is erectile dysfunction?
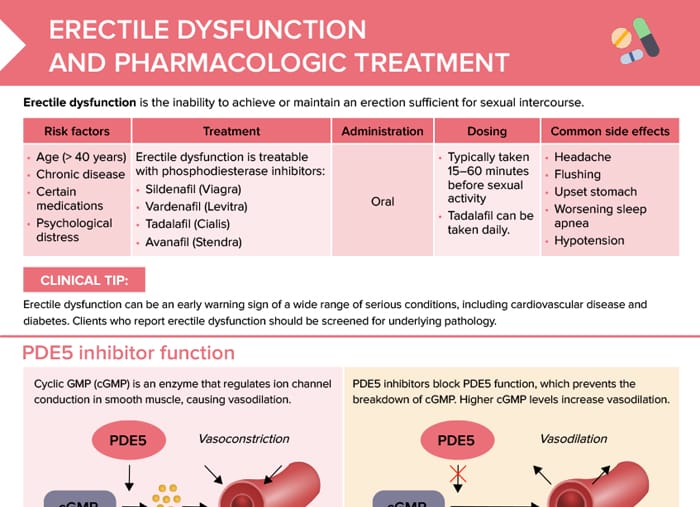
Erectile dysfunction (ED) is the inability to achieve or maintain an erection sufficient for sexual intercourse.
Risk factors for ED include:
- Age > 40 years
- Chronic disease
- Certain medications
- Psychological distress
Clinical tip: Erectile dysfunction can be an early warning sign of a wide range of serious conditions, including cardiovascular disease and diabetes. Clients who report erectile dysfunction should be screened for underlying pathology.
Pharmacological treatment of erectile dysfunction
Erectile dysfunction is treatable with phosphodiesterase inhibitors:
- Sildenafil (Viagra)
- Vardenafil (Levitra)
- Tadalafil (Cialis)
- Avanafil (Stendra)
All of those medications are administered orally and are typically taken 15–60 minutes before sexual activity. Tadalafil can be taken daily.
Phosphodiesterase inhibitors: mechanism of action
Cyclic GMP (cGMP) is an enzyme that regulates ion channel conduction in smooth muscle, causing vasodilation. Phosphodiesterase 5 (PDE5) is an enzyme that breaks down cGMP, leading to vasoconstriction.
PDE5 inhibitors block PDE5 function, which prevents the breakdown of cGMP. Higher cGMP levels increase vasodilation. Increased vasodilation facilitates penile engorgement and sustained erectile function.
Side effects of Viagra, Levitra, Cialis, and Stendra
Common side effects occurring with ED drugs include:
- Headache
- Flushing
- Upset stomach
- Worsening sleep apnea
- Hypotension
Precautions:
- Coronary heart disease
- CV event in previous 6 months (MI, stroke, serious dysrhythmia)
- Preexisting low or high BP
- Heart failure
- Unstable angina
Client education about ED medications
- Never combine PDE5 inhibitors and nitroglycerine. Can be fatal!
- Caution when combining PDE5 inhibitors and other vasodilators due to hypotension risk.
- Priapism is a painful erection; seek medical intervention if priapism lasts > 4 hours. Can cause permanent damage.
- Avoid grapefruit and large, fatty meals, which can delay onset of medication.
Tadalafil vs sildenafil vs vardenafil vs avanafil
Table: Comparison of erectile dysfunction drugs
| Sildenafil (Viagra) | Tadalafil (Cialis) | Vardenafil (Levitra) | Avanafil (Stendra) | |
| Onset | 30–60 minutes | 30–45 minutes (sometimes sooner) | 30–60 minutes | Quickest; 15–30 minutes |
| Duration of action | 4–6 hours | Up to 36 hours | 4–6 hours | 6–12 hours |
| Food interactions | High-fat meal can slow absorption. | Not significantly impacted | High-fat meal can slow absorption. | Not significantly impacted |
A notable difference between the well-known drugs sildenafil (Viagra) and tadalafil (Cialis) is the duration of action: While sildenafil works for about 4–6 hours, tadalafil can have an effect for up to 36 hours, allowing for more spontaneity and earning the medication the nickname “weekend pill.”