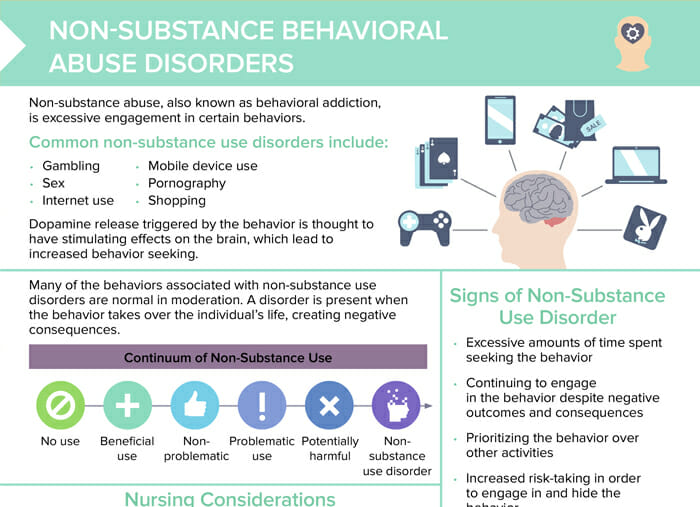
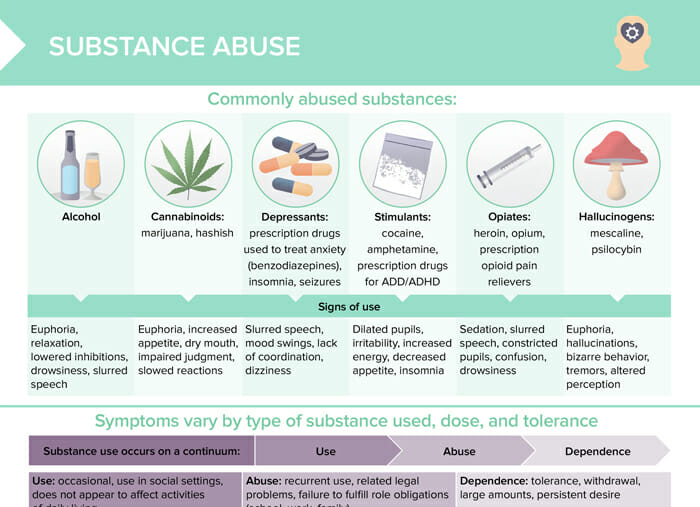
What is substance use disorder?
Substance Use Disorder (SUD) is a medical condition characterized by the recurrent use of drugs or alcohol that causes significant clinical and functional impairment. This includes health problems, disability, and failure to meet major responsibilities at work, school, or home. It is diagnosed based on evidence of impaired control, social impairment, risky use, and pharmacological criteria like tolerance and withdrawal symptoms.
Substance use disorders are chronic, but treatable medical conditions.
What are the most commonly abused substances?
The most commonly abused substances include:
- Stimulants (cocaine, amphetamine, prescription drugs for ADD/ADHD)
- Depressants (prescription drugs to treat anxiety (like benzodiazepines), insomnia, seizures)
- Opiates (heroin, opium, prescription opioid pain relievers)
- Hallucinogens (mescaline, psilocybin)
- Cannabinoids (marijuana, hashish)
- Alcohol
What are the signs of substance use?
| Substance | Signs of use |
| Alcohol | Euphoria, relaxation, lowered inhibitions, drowsiness, slurred speech |
| Cannabinoids | Euphoria, increased appetite, dry mouth, impaired judgment, slowed reactions |
| Depressants | Slurred speech, mood swings, lack of coordination, dizziness |
| Stimulants | Dilated pupils, irritability, increased energy, decreased appetite, insomnia |
| Opiates | Sedation, slurred speech, constricted pupils, confusion, drowsiness |
| Hallucinogens | Euphoria, hallucinations, bizarre behavior, tremors, altered perception |
What are the risk factors for substance abuse disorder?
No single factor can predict whether a person will develop substance abuse disorder. A combination of genetic, environmental, and developmental factors influences risk for addiction.
Risk factors for substance abuse disorder include:
- Family history of substance use
- Mental health disorder
- Peer pressure
- Use at an early age
- Using highly addictive drugs
- History of trauma
- Genetic predisposition
How can nurses identify and address substance abuse disorders in their clients?
Healthcare professionals can identify and address substance abuse disorders in their clients by conducting a thorough assessment, including a physical exam, laboratory tests, and a mental health evaluation. They can also use screening tools to identify clients who may be at risk for substance abuse disorder. Treatment options include medication-assisted treatment, behavioral therapy, and support groups.
Related videos
What is the substance use continuum?
Substance use occurs on a continuum.
Use → Abuse → Dependence
- Use: occasional use (e.g., in social settings that does not appear to affect activities of daily living
- Abuse: recurrent use, related legal problems, failure to fulfill role obligations (school, work, family)
- Dependence: tolerance, withdrawal, large amounts, persistent desire
How can nurses educate clients about substance abuse and prevent addiction?
Effective ways to educate clients about substance abuse and prevent addiction include:
- Using non-stigmatizing, person-first language: for example, say “person with substance use disorder” instead of “addict” or “alcoholic”
- Educating clients on available treatment methods
- Connecting clients to community resources and treatment providers
- Providing information on the risks associated with substance abuse and strategies for reducing those risks
What are potential nursing diagnoses for substance use disorder?
Potential nursing diagnoses for substance use disorder could include:
- Ineffective coping: related to reliance on substances as a coping mechanism
- Impaired social interaction: difficulty establishing or maintaining relationships due to effects of substance use
- Self-neglect: potentially due to prioritizing substance use
- Imbalanced nutrition: due to effects or side effects of substance use
- Risk for injury: due to impaired coordination, altered judgment, or withdrawal symptoms