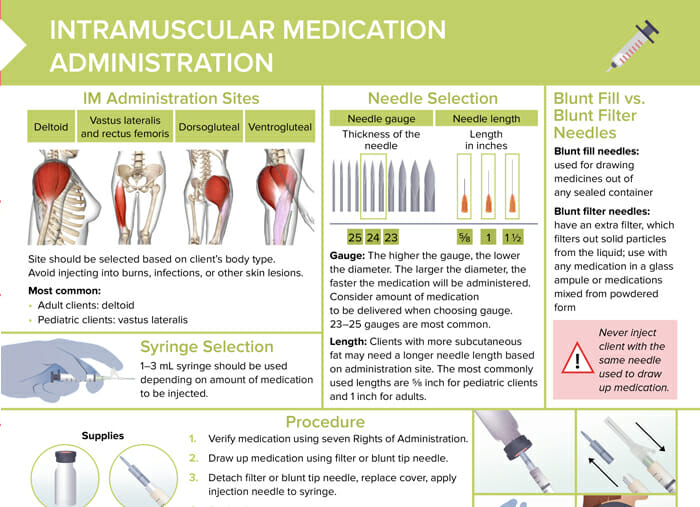
What is a subcutaneous injection?
A subcutaneous injection is a method of administering medication into the layer of skin directly below the dermis and epidermis, known as the subcutaneous layer or subcutis. Common sites for subcutaneous injections include the fatty areas of the upper arm, abdomen, or thigh. Common medications typically administered subcutaneously include insulin and heparin.
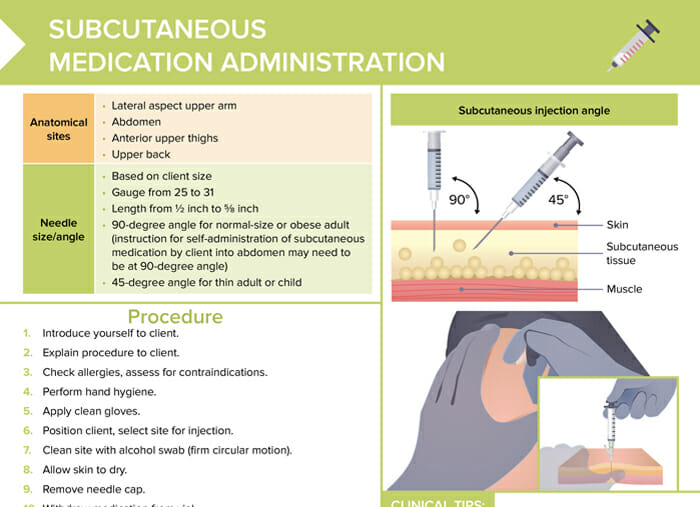
Subcutaneous injection sites
Common anatomical sites for subcutaneous injections include:
- Lateral aspect upper arm
- Abdomen
- Anterior upper thighs
- Upper back
Subcutaneous injection angle
- For normal-size or obese adults: 90-degree angle
- For children or thin adults: 45-degree angle
Subcutaneous injection needle size
Needle size is based on client size, with a range of 25–31 gauges and a length from ½ inches to ⅝ inches.
How to give a subcutaneous injection (technique for nurses)
- Introduce yourself to client.
- Explain procedure to client.
- Check allergies, assess for contraindications.
- Perform hand hygiene.
- Apply clean gloves.
- Position client, select site for injection.
- Clean site with alcohol swab (firm circular motion).
- Allow skin to dry.
- Remove needle cap.
- Withdraw medication from vial.
- Pinch area selected for injection.
- Hold syringe in dominant hand.
- Insert needle at the appropriate angle (45- or 90-degree).
- Inject medication slowly.
- Withdraw needle at the same angle.
- Apply pressure with sterile gauze gently.
- Do not massage site of injection.
- Do not recap needle.
- Apply safety mechanism.
- Dispose of needle in sharps container.
- Remove gloves.
- Perform hand hygiene.
What happens if you give a subcutaneous injection intramuscularly?
If a medication intended for subcutaneous injection is given intramuscularly, several issues could arise:
- Drug levels in the bloodstream could end up higher than expected because medications intended for subq injection may be absorbed more quickly when given intramuscularly.
- Pain level for the client could be higher as subq injections are typically less painful.
- The medication may cause damage or irritation to the muscle tissue.
- The medication may not work as intended if it’s not administered in the right layer of tissue.
How to give an insulin injection
- Check correct type and amount.
- Use insulin syringe to administer medication (they come in 30, 50, 100 units).
- Do not store insulin near heparin.
How to give a heparin injection
- Check correct amount.
- Do not massage site of injections, contributes to formation of hematoma.
- Note that subq solution is less concentrated than IV solution.
- Do not store heparin near insulin.