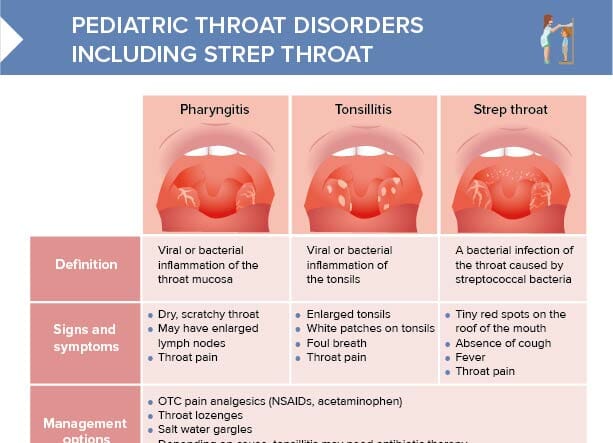
Definition of strep throat, tonsillitis, and pharyngitis
Pharyngitis is a viral or bacterial inflammation of the throat mucosa that is very common especially in school-age children.
Tonsillitis is a viral or bacterial inflammation of the tonsils that is especially common between the ages 4 and 7.
Strep throat is a bacterial infection of the throat caused by streptococcal bacteria. It’s estimated that about 20–30% of sore throats in school-age children are due to strep throat.
Signs and symptoms of the throat disorders: how to differentiate them
All three disorders present with throat pain, but have individual symptoms on top of that:
- Pharyngitis presents with a dry, scratchy throat and may have enlarged lymph nodes.
- Characteristic for tonsillitis are enlarged tonsils and white patches on the tonsils, as well as foul-smelling breath.
- Strep throat patients have tiny red spots on the roof of the mouth, a fever, and notably will not suffer from a cough.
For definitive diagnosis, a rapid strep test or throat culture is generally performed, especially to confirm or rule out strep throat, which requires antibiotic treatment.
Management options
All three throat disorders largely are treated similarly with OTC pain analgesics (NSAIDs, acetaminophen), throat lozenges, and salt water gargles.
Depending on the cause, tonsillitis may need antibiotic therapy.
Strep throat always requires antibiotic therapy.
Comparison of the possible complications
Pharyngitis complications
- Dehydration
- Chronic throat pain
- Ear infections
Pharyngitis often precedes other viral infections and if symptoms persist, needs to be evaluated for viral or other bacterial illness.
Tonsillitis complications
- Sleep apnea (if severely swollen tonsils)
- Ear infections
- Peritonsillar abscess
Strep throat complications
- Rheumatic fever
- Otitis media
- Kidney infection
- Pneumonia
- Toxic shock syndrome
- Meningitis