Nursing Knowledge
Inspect the anterior and posterior thorax to identify any abnormalities, such as:
Percussion of a well-ventilated lung should sound resonant, with dullness over ribs or pathology.
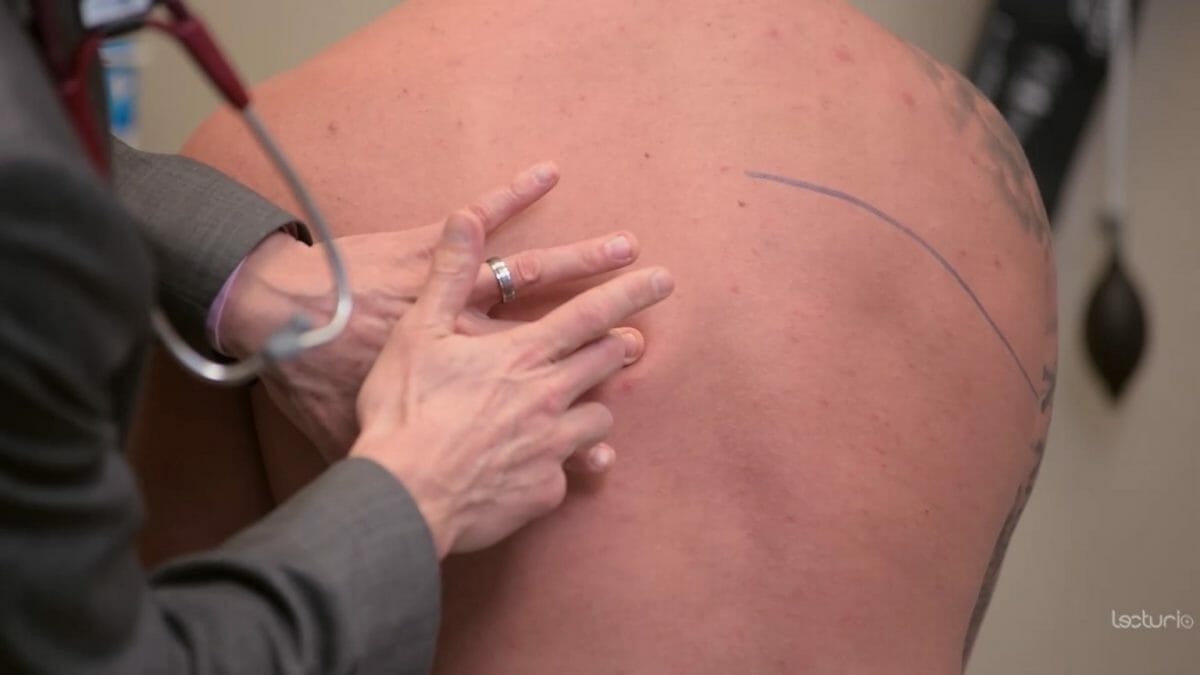
In a lung assessment, landmarks help you correctly position your stethoscope to listen to lung sounds. Key landmarks include:
If you hear any adventitious lung sounds during a respiratory assessment, you should document the finding, alert the healthcare provider for evaluation and orders, and monitor the patient’s respiratory status and vital signs.
Be mindful any of the following:
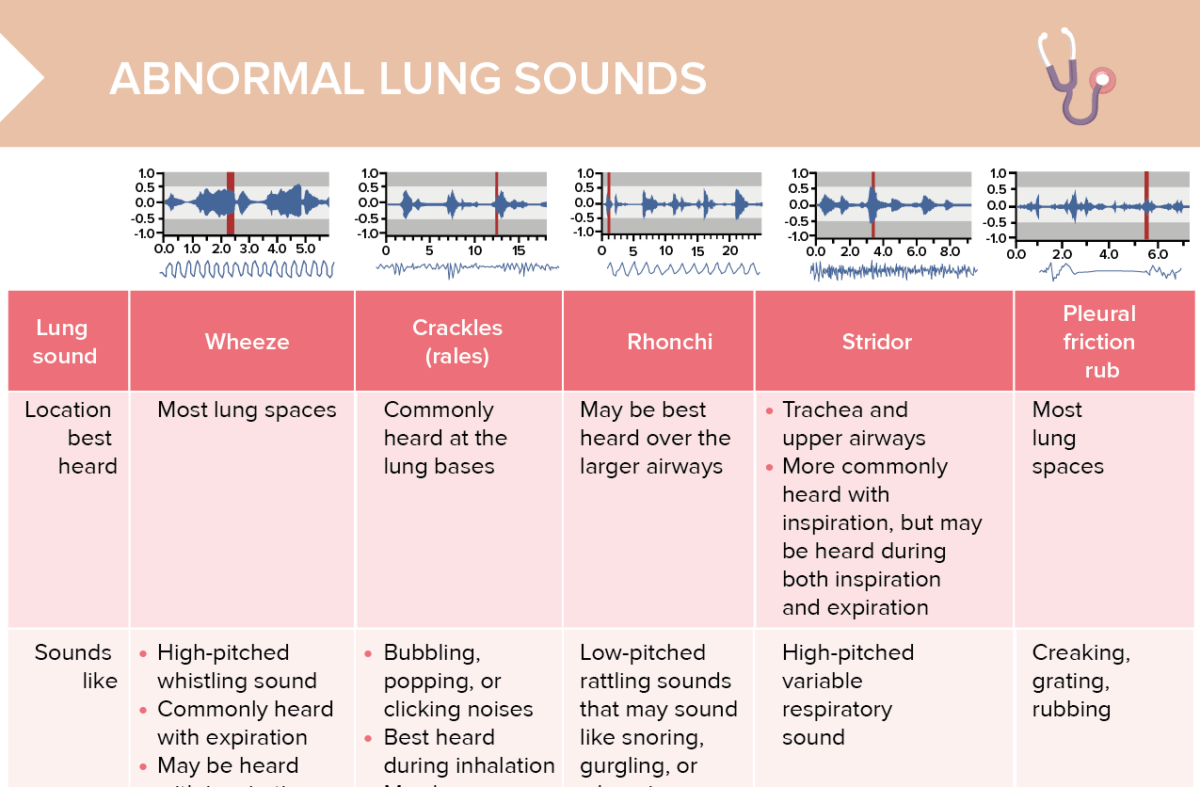
An overview of abnormal lung sounds, such as stridor and crackles
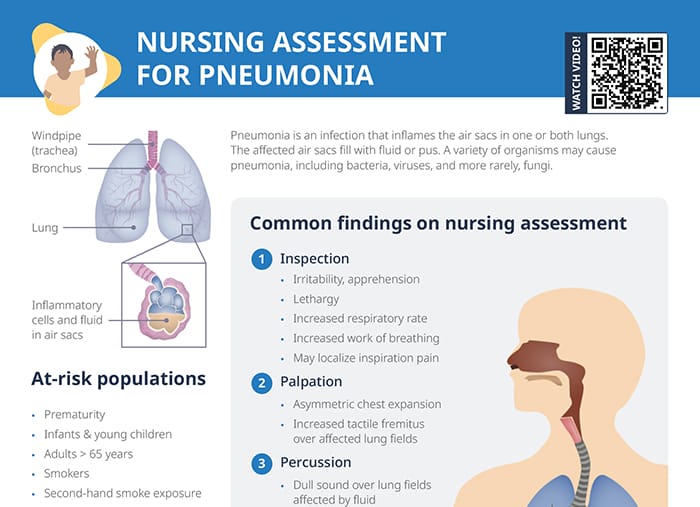
Pneumonia risk factors, signs/symptoms and common assessment findings in pediatric clients with suspected pneumonia.
Evaluation of the breathing pattern is done during the auscultation of the lungs by listening to the breath sounds. Potential findings include:
Proper documentation of a lung assessment typically includes:
RELATED TOPIC:
Free Download
Master the topic with a unique study combination of a concise summary paired with video lectures.
USMLE™ is a joint program of the Federation of State Medical Boards (FSMB®) and National Board of Medical Examiners (NBME®). MCAT is a registered trademark of the Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC). NCLEX®, NCLEX-RN®, and NCLEX-PN® are registered trademarks of the National Council of State Boards of Nursing, Inc (NCSBN®). None of the trademark holders are endorsed by nor affiliated with Lecturio.
Your free account gives you access to:
or