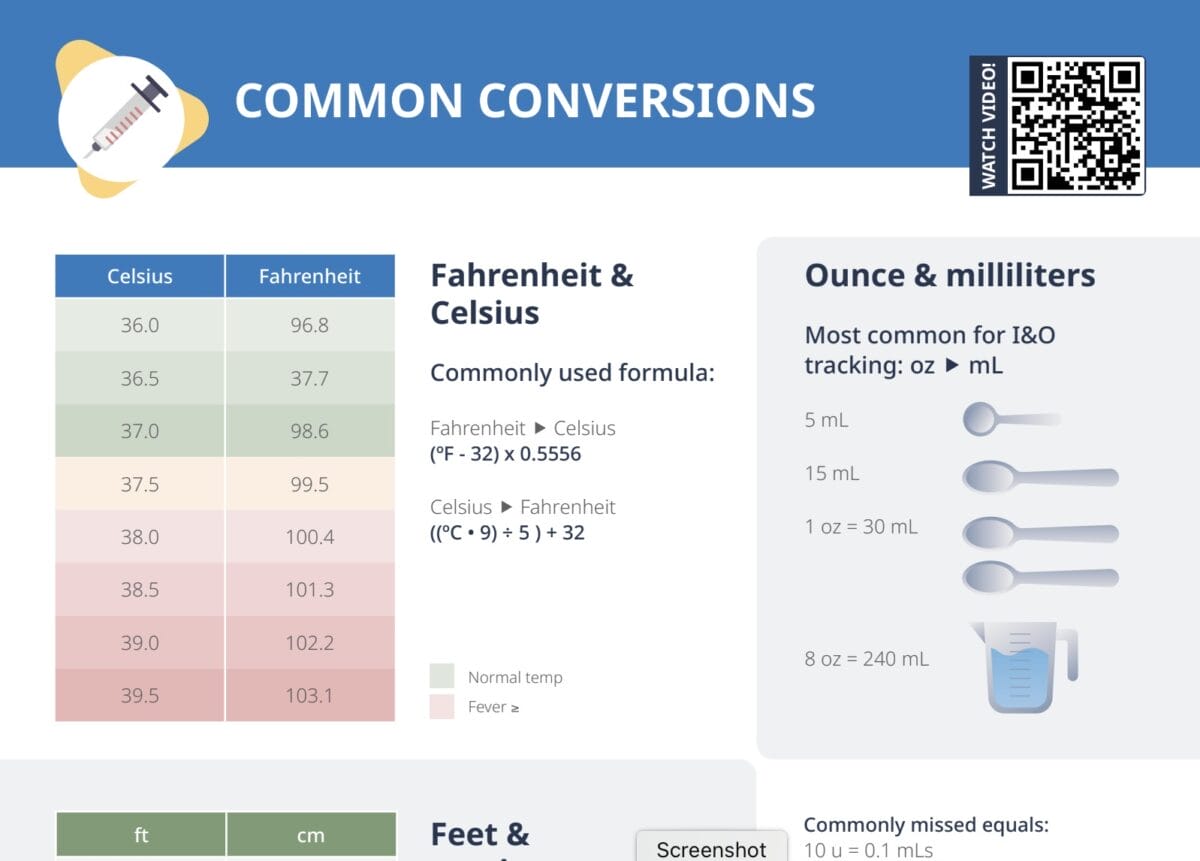
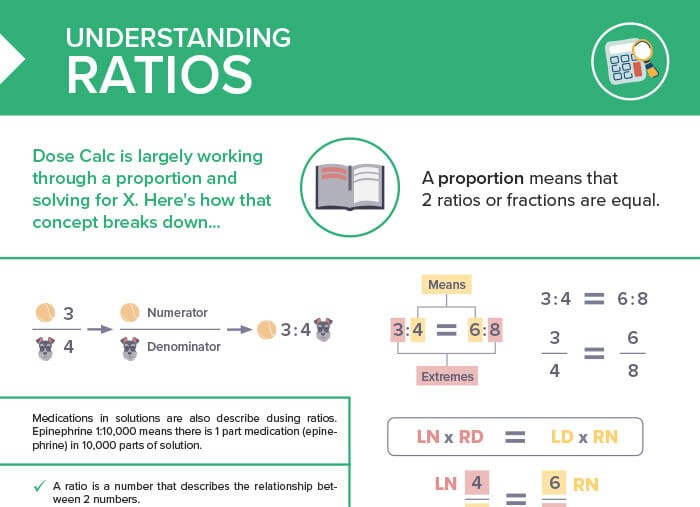
What is a ratio?
A ratio is a number that describes the relationship between 2 numbers.
What is a proportion?
A proportion means that 2 ratios or fractions are equal.
Why are ratios and proportions important in dosage calculation?
Ratios and proportions help nurses accurately scale dosages up or down based on patient-specific factors like weight. If a medication is prescribed at a certain amount per kg of body weight, the nurse needs to figure out how much medication to give a patient according to their weight.
Medications in solutions are also described using ratios.
For example: epinephrine 1:10,000 means that there is 1 part medication (epinephrine) in 10,000 parts of solution.
Example calculations
Identifying proportions: Does 3:4 equal 6:8?
To determine if a ratio is equal, multiply the means by the extremes: In proportions, the product of the means always equals the product of the extremes. Cross-multiplication of the ratios as fractions will determine if they are equal and a proportion.
3/4 = 6/8
Multiplying means by extremes/cross-multiplying the ratios as fractions:
3*8 = 4*6; 24 =24 → 3/4 = 6/8 is true, so the ratio is a proportion.
Medication example
Let’s say a medication is prescribed at 5 mg/kg and you have a patient who weighs 70 kg. Using ratios, set up the equation first:
- 5 mg / 1 kg = x mg / 70 kg
- Solve for x to find the correct dosage: x = 5 mg/kg × 70 kg = 350 mg
- So, you would administer 350 mg of the medication for this 70 kg patient.
Following the rule of multiplying means and extremes:
- 5 mg / 1 kg = x mg / 70 kg
- 5*70 = 1*x
- 350 = x
Multiple the units, and you reach 350 mg for this patient.