PTSD meaning: what is PTSD?
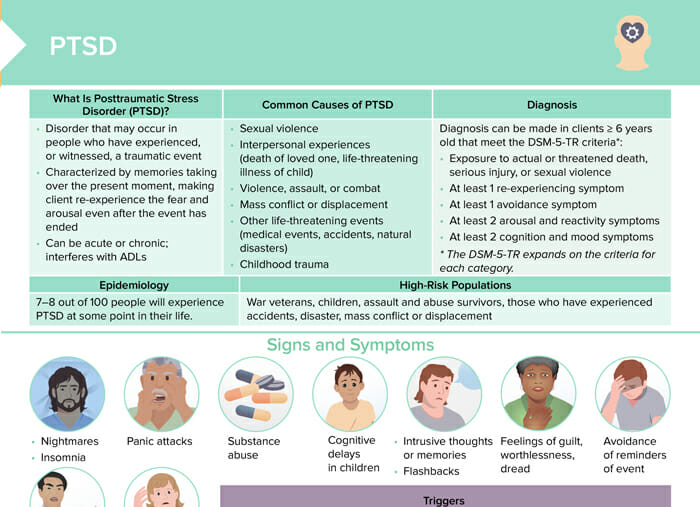
PTSD stands for posttraumatic stress disorder.
It is a disorder that can develop in people that have experienced or witnessed a traumatic event. PTSD is characterized by symptoms such as flashbacks, memories taking over the present moment making the client re-experience the fear even after the traumatic event has ended, nightmares, and avoidance behaviors that interfere with ADLs. PTSD can be acute or chronic.
What is complex PTSD?
Complex post-traumatic stress disorder (C-PTSD) is a condition that results from repeated, prolonged exposure to traumatic events, often occurring in contexts where the individual feels trapped or without a viable escape, such as in cases of long-term abuse, captivity, or ongoing childhood neglect.
Symptoms of C-PTSD can include those seen in PTSD.
Who is at high risk for developing PTSD?
PTSD affects 7–8 out of 100 people at some point in their life. High-risk populations for developing PTSD include:
- War veterans
- Children
- Assault and abuse survivors
- Those who have experienced accidents, disaster, mass conflict or displacement
- Those who have experienced other life-threatening events such as medical events or natural disasters
What causes PTSD?
Common causes of PTSD include:
- Sexual violence
- Interpersonal experiences (death of loved one, life-threatening illness of child)
- Violence, assault, combat
- Mass conflict or displacement
- Other life-threatening events (medical events, accidents, natural disasters)
- Childhood trauma
What are PTSD symptoms?
Signs and symptoms of PTSD include:
- Nightmares/insomnia
- Panic attacks
- Substance abuse
- Cognitive delays in children
- Intrusive thoughts or memories, flashbacks
- Feelings of guilt, worthlessness, dread
- Avoidance of reminders of event
- Changes in arousal, reactivity
- Dissociation, numbness, flat affect when discussing events
What are triggers in PTSD?
Triggers can lead to exhibition of, or worsening, signs and symptoms of PTSD. Triggers can be anything that reminds a client of what happened right before or during the traumatic event.
- Usually tied to senses
- Can be places, sounds, tastes, scents, situations, or anniversaries
How to diagnose PTSD
Diagnosis of PTSD can be made in clients ≥ 6 years old that meet the DSM-5-TR criteria*:
- Exposure to actual or threatened death, serious injury, or sexual violence
- At least 1 re-experiencing symptom
- At least 1 avoidance symptom
- At least 2 arousal and reactivity symptoms
- At least 2 cognition and mood symptoms
* The DSM-5-TR expands on the criteria for each category.
What are options for PTSD treatment?
Positive coping strategies
- Relaxation techniques
- Learning about trauma and PTSD
- Support groups
- Understanding triggers
- Professional support
- Animal-assisted therapy
- Mindfulness
Types of therapy
- Cognitive behavioral therapy and cognitive therapy
- Eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR)
- Sensorimotor psychotherapy
- Group or family therapy
- Prolonged exposure therapy
Medications
- SSRIs
- Other antidepressants
- Beta blockers
- Mood stabilizers
- Anti-psychotics
- Benzodiazepines
- Alternative/complementary therapies
How to help someone with PTSD
As a nurse, you play a vital role in helping a client with PTSD. Here are key steps:
- Create a safe environment.
- Regularly monitor symptoms, mental state, and vital signs.
- Educate the client about PTSD.
- Encourage therapy compliance.
- Teach coping strategies.
- Emphasize the importance of healthy habits, like regular exercise, a balanced diet, and good sleep hygiene.
- Encourage participation in group therapy or support groups.
- Educate family members about PTSD and how they can provide support.
- Advocate for the patient: Be their voice in care meetings, ensure their needs are met, and their rights respected.
Always ensure you’re working as part of a multidisciplinary team, including psychiatrists, psychologists, and social workers, to provide comprehensive care.