The process of ovulation
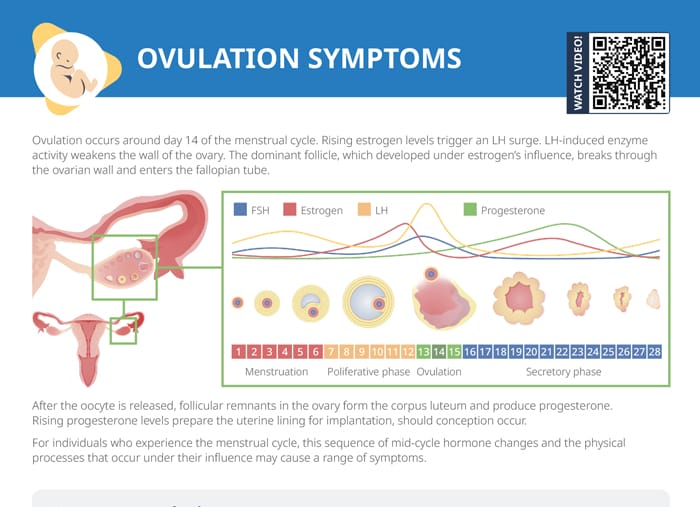
Ovulation occurs around day 14 of the menstrual cycle. Rising estrogen levels trigger the luteinizing hormone (LH) surge. LH-induced enzyme activity weakens the wall of the ovary. The dominant follicle, which developed under estrogen’s influence, breaks through the ovarian wall and enters the fallopian tube.
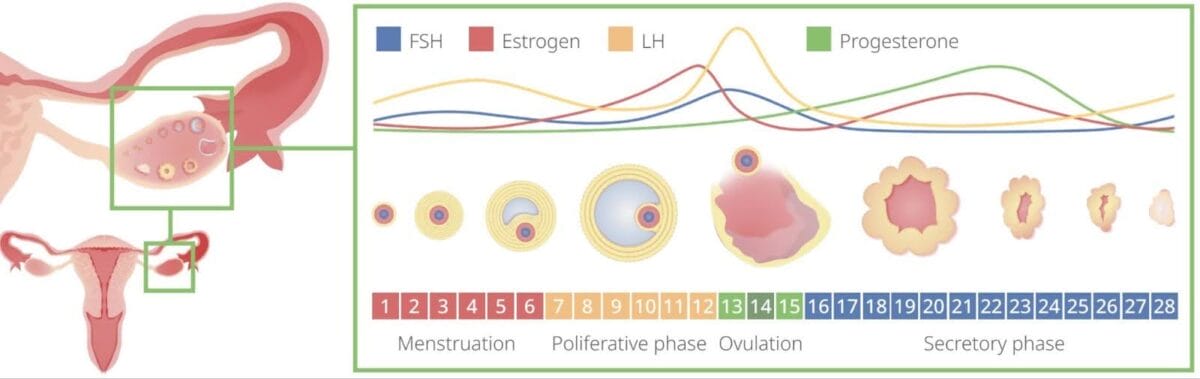
After the oocyte is released, follicular remnants in the ovary form the corpus luteum and produce progesterone. Rising progesterone levels prepare the uterine lining for implantation, should conception occur.
What are ovulation symptoms?
For individuals who experience the menstrual cycle, the sequence of mid-cycle hormone changes that come with ovulation and the physical processes that occur under their influence may cause a range of symptoms.
Common ovulation symptoms: mood, discharge, bloating, and others
Some of the most commonly experienced symptoms of ovulation include:
- Ovulation pain (also known as “Mittelschmerz”)
- Breast tenderness
- Nausea/bloating
- Heightened sense of smell
- Increased libido
- Mood changes
- Fertile, “egg-white” cervical mucus
- Increased basal body temperature
Client education and common client questions
“Why do I have ovulation symptoms while on the pill?”
The pill often suppresses ovulation, but some may still feel ovulation-like symptoms due to hormonal fluctuations. These symptoms are generally milder and shouldn’t be a cause for concern. However, if symptoms are more severe, it’s important to recommend the client consult with a healthcare provider.
“Does ovulation cause bloating?”
Ovulation can cause bloating due to hormonal changes that affect fluid retention. To alleviate bloating, clients should try reducing salt intake, staying hydrated, and engaging in regular exercise.
“How can I deal with back and pelvic pain due to ovulation?”
Ovulation can cause mild back pain and pelvic pain, known as mittelschmerz. This is usually short-lived and can be managed with over-the-counter pain relievers, warm baths, or heating pads. If the pain is severe or accompanied by other symptoms, it’s important to seek medical advice.
“Could my mood swings be due to ovulation?”
Mood changes can be a symptom of ovulation. The hormonal fluctuations occurring with ovulation may cause mood swings, increased libido, heightened energy, but also anxiety or irritability.
These mood changes vary greatly among individuals and not everyone experiences them. Also, mood changes and mood swings can be symptoms of many different things. If mood changes are severe or affecting daily life, the client should seek medical advice.
“Should I worry if my discharge changes during ovulation?”
Around ovulation, estrogen levels peak, leading to an increase in cervical mucus production. The discharge at this time typically becomes clearer, stretchier, and more slippery, similar to the consistency of raw egg whites. This change is nature’s way of creating a sperm-friendly environment to facilitate conception and not a cause for concern.
If the client is not trying to conceive, this is a key time to be aware of if using natural family planning methods.
Instruct the client to seek medical advice if the discharge has an unusual color, odor, or is accompanied by itching or irritation.
“Why am I so tired during ovulation?”
Ovulation can cause fatigue due to the hormonal fluctuations and potential physical and mental symptoms that accompany it. Clients should be advised to ensure adequate rest and stress management. A balanced diet, good hydration, exercise and avoiding caffeine and sugar are further pieces of advice.
Client education tips
- Educate clients about the menstrual cycle, hormone changes, symptoms that may occur at different phases in the cycle, and comfort measures.
- Encourage use of a calendar or phone app to track the menstrual cycle and note symptom patterns.
- Explain how awareness of menstrual cycle and ovulation timing can be used to prevent or promote pregnancy, if desired.
Hyperovulation: “double ovulation” symptoms
Hyperovulation occurs when more than one egg is released during a single menstrual cycle. This can be influenced by genetics, sometimes medications (e.g., fertility treatments) and other patient factors. Hyperovulation can lead to the conception of fraternal twins if both eggs are fertilized.
Ovulation symptoms may be more pronounced than usual, but there also may be no noticeable symptoms. The most reliable way to confirm hyperovulation is through ultrasound, visualizing multiple developing follicles in the ovaries.