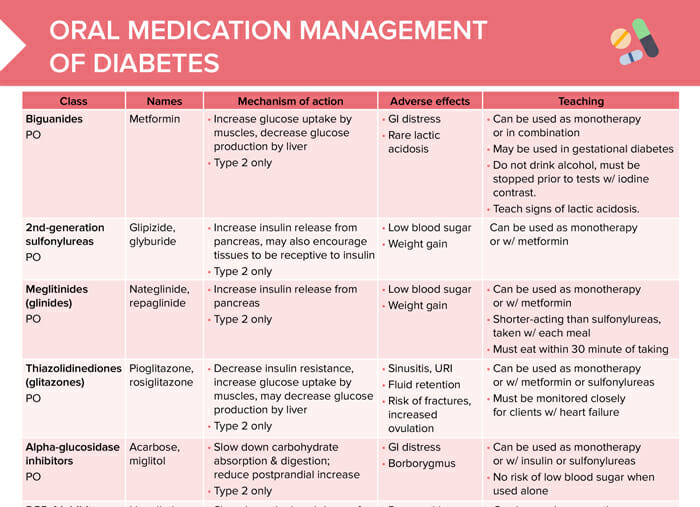
Biguanides
Biguanides can be used as monotherapy or in combination. They may be used in gestational diabetes. Clients instructed not to drink alcohol and educated about signs of lactic acidosis. Stop medication prior to tests with iodine contrast.
Names
Metformin
Mechanism of action
- Increase glucose uptake by muscles
- Decrease glucose production by liver
Adverse effects
- GI distress
- Rare lactic acidosis
2nd-generation sulfonylureas
2nd-generation sulfonylureas can be used as monotherapy or with metformin.
Names
- Glipizide
- Glyburide
Mechanism of action
- Increase insulin release from pancreas
- May also encourage tissues to be receptive to insulin
Adverse effects
- Low blood sugar
- Weight gain
Meglitinides (glinides)
Meglitinides can be used as monotherapy or with metformin. They are shorter-acting than sulfonylureas and are taken with each meal. The client must eat within 30 minutes after taking the medication.
Names
- Nateglinide
- Repaglinide
Mechanism of action
- Increase insulin release from pancreas
Adverse effects
- Low blood sugar
- Weight gain
Thiazolidinediones (glitazones)
Thiazolidinediones can be used as monotherapy or with metformin or sulfonylureas. Clients with heart failure must be monitored closely.
Names
- Pioglitazone
- Rosiglitazone
Mechanism of action
- Decrease insulin resistance
- Increase glucose uptake by muscles
- May decrease glucose production by liver
Adverse effects
- Sinusitis
- URI
- Fluid retention
- Risk of fractures
- Increased ovulation
Alpha-glucosidase inhibitors
Alpha-glucosidase inhibitors can be used as monotherapy or with insulin or sulfonylureas. There is no risk of low blood sugar when used alone.
Names
- Acarbose
- Miglitol
Mechanism of action
- Slow down carbohydrate absorption and digestion
- Reduce postprandial increase
Adverse effects
- GI distress
- Borborygmus
DPP-4 inhibitors (gliptins)
DPP-4 inhibitors can be used as monotherapy or in combination. Clients need teaching on the signs of pancreatitis.
Names
- Linagliptin
- Saxagliptin
Mechanism of action
- Slow down breakdown of incretins by DPP-4
- Increase insulin release
- Reduce glucagon release and liver glucose production
Adverse effects
- Pancreatitis
- Hypersensitivity reactions
Dopamine antagonists
Dopamine agonists can be used as monotherapy or in combination. Marketed under a different name for Parkinson and hyperprolactinemia.
Names
Bromocriptine
Mechanism of action
- Activate dopamine receptors in the CNS
- Improve glycemic control, but unknown how exactly
Adverse effects
- Orthostatic hypertension
- Exacerbation of psychosis
Sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors
SGLT-2 inhibitors can be used as monotherapy or in combination. There is ongoing research for use with Type 1 diabetes.
Names
- Canagliflozin
- Dapagliflozin
Mechanism of action
- Block SGLT-2 in the tubules of the kidney
- Increase glucose excretion in urine
Adverse effects
- Genital fungal infections
- UTI, polyuria
- Orthostatic hypertension
Overview chart of oral diabetes medications + teachings
Download full chart as PDF below!
Table: Oral diabetes medication classes and nursing teachings
| Medication class | Teaching |
| Biguanides | Biguanides can be used as monotherapy or in combination. They may be used in gestational diabetes. Clients must not not drink alcohol and be educated about signs of lactic acidosis. Stop medication prior to tests with iodine contrast. |
| 2nd-generation sulfonylureas | 2nd-generation sulfonylureas can be used as monotherapy or with metformin. |
| Meglitinides (glinides) | Meglitinides can be used as monotherapy or with metformin. They are shorter-acting than sulfonylureas and are taken with each meal. The client must eat within 30 minutes after taking the medication. |
| Thiazolidinediones (glitazones) | Thiazolidinediones can be used as monotherapy or with metformin or sulfonylureas. Clients with heart failure must be monitored closely. |
| Alpha-glucosidase inhibitors | Alpha-glucosidase inhibitors can be used as monotherapy or with insulin or sulfonylureas. There is no risk of low blood sugar when used alone. |
| DPP-4 inhibitors (gliptins) | DPP-4 inhibitors can be used as monotherapy or in combination. Clients need education on signs of pancreatitis. |
| Dopamine antagonists | Dopamine agonists can be used as monotherapy or in combination. Marketed under a different name for Parkinson and hyperprolactinemia. |
| Sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors | SGLT-2 inhibitors can be used as monotherapy or in combination. There is ongoing research for use with Type 1 diabetes. |