What is pharmacology in nursing?
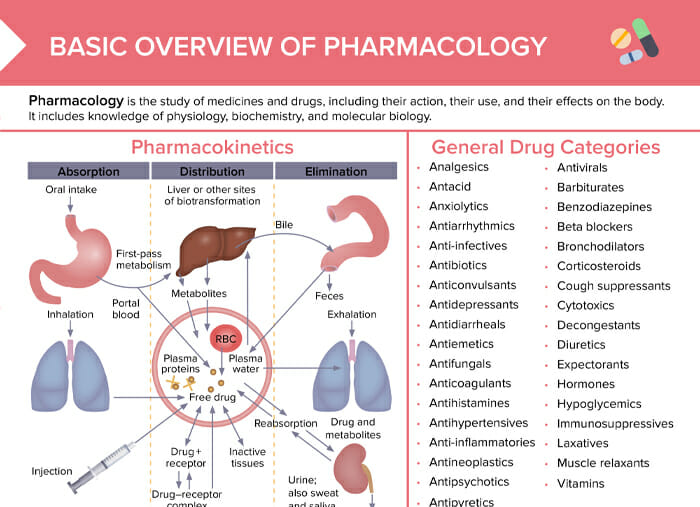
Pharmacology is the study of medicines and drugs, including the action, use, and effects on the body. It includes knowledge of physiology, biochemistry, and molecular biology.
For nursing students, pharmacology is known as an intimidating challenge to pass in nursing school.
For practicing nurses, pharmacology plays a big role in daily practice:
- Calculating dosages and administering medications
- Monitoring clients for adverse reactions and effectiveness
- Ensuring client safety by minding drug interactions and contraindications
- Educating clients and families about medication management and usage
Related videos
What is pharmacokinetics?
Pharmacokinetics is the study of the movement of the drug within the body and how the body acts on the drug, including absorption, bioavailability, distribution to tissues, metabolism, and elimination/excretion.
What is pharmacodynamics?
Pharmacodynamics involves receptor binding, postreceptor effects, and chemical interactions. The pharmacodynamics of a drug determine the onset, duration, and intensity of a drug’s effect.
What are pharmacotherapeutics?
Therapeutic action of a drug is the effect or reaction of such drug on biological tissue, including beyond the desired action of the drug.
What is chemotherapy?
Chemotherapy is the use of chemicals to destroy fast-growing cells within the body, used for treatment of cancer and cancerous tumors.
What is toxicology?
Toxicology is the study of harmful effects of chemical substances on living tissue and predicting how such chemicals may cause harm. It is also the study of poisons.
Types of drugs: general category overview
• Analgesics
• Antacid
• Anxiolytics
• Antiarrhythmics
• Anti-infectives
• Antibiotics
• Anticonvulsants
• Antidepressants
• Antidiarrheals
• Antiemetics
• Antifungals
• Anticoagulants
• Antihistamines
• Antihypertensives
• Anti-inflammatories
• Antineoplastics
• Antipsychotics
• Antipyretics
• Antivirals
• Barbiturates
• Benzodiazepines
• Beta blockers
• Bronchodilators
• Corticosteroids
• Cough suppressants
• Cytotoxics
• Decongestants
• Diuretics
• Expectorants
• Hormones
• Hypoglycemics
• Immunosuppressives
• Laxatives
• Muscle relaxants
• Vitamins