Normal newborn vital signs
Normal newborn heart rate
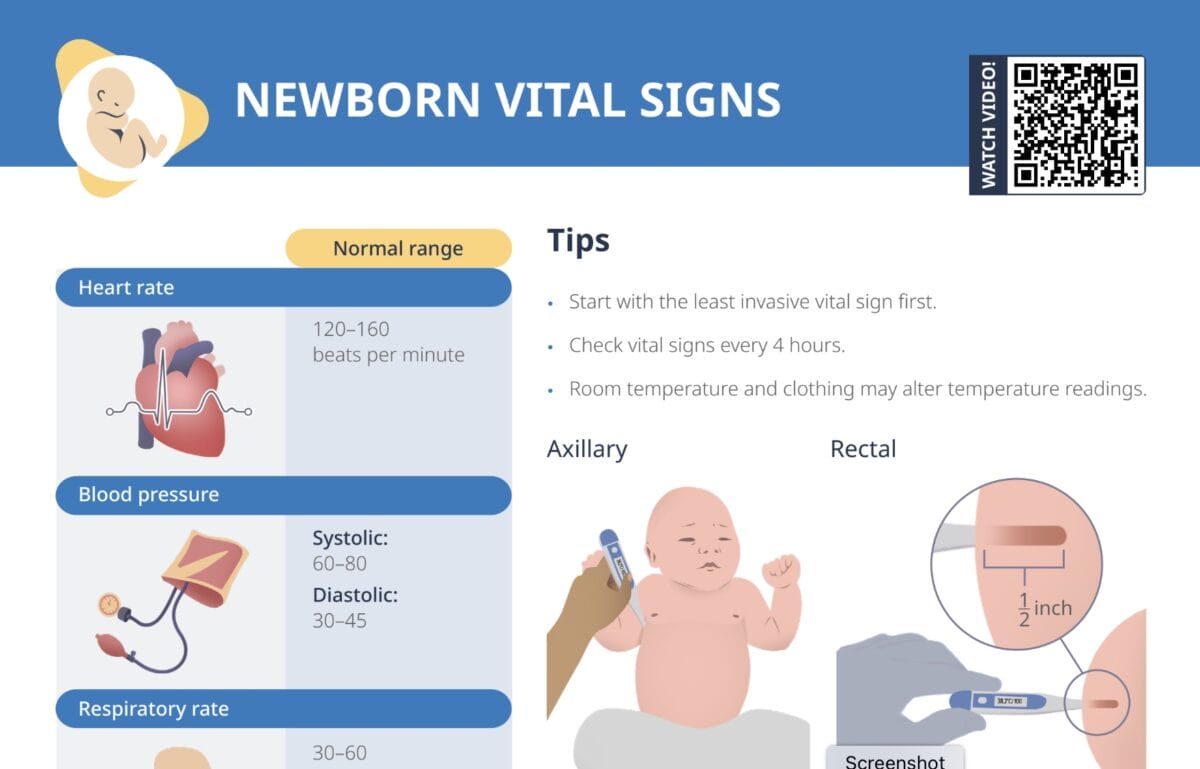
A newborn’s heart rate should be between 120–160 beats per minute. Newborn heart rates can fluctuate significantly during activity or crying, often reaching higher rates.
Normal newborn blood pressure
A newborn’s blood pressure is supposed to be significantly lower than adult values. Normal values are systolic: 60–80, diastolic: 30–45.
Blood pressure in newborns is usually measured using an appropriate-sized cuff and a Doppler device or oscillometric method.
Normal newborn respiratory rate
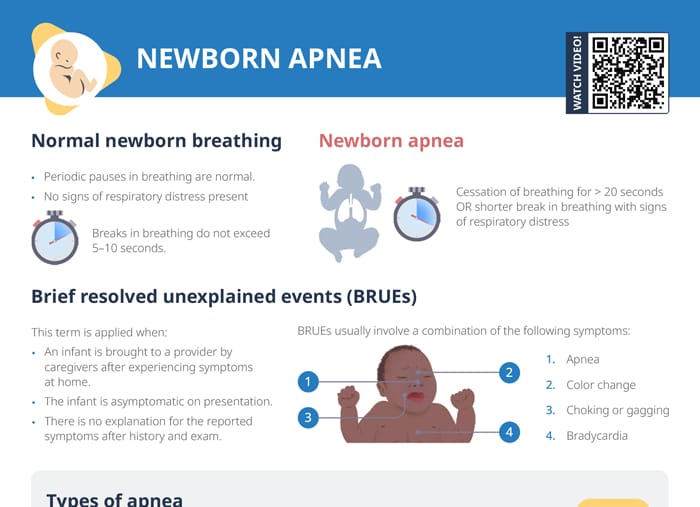
A normal respiratory rate in a newborn is 30–60 breaths per minute. It’s common for infants to have irregular breathing, which can include short pauses of no breathing (learn how to differentiate normal pauses from newborn apnea here).
Normal newborn temperature
A proper thermal environment needs to be maintained around newborns, as they can easily become too cold or too hot. Normal values:
- Axillary: 97°F–99°F (36.1°C–37.2°C)
- Rectal: 97.7°F–100.2°F (36.5°C–37.8°C)
Normal newborn oxygen saturation
Oxygen saturation should be 95%–100% on room air.
Interventions for abnormal vital signs
When encountering abnormal vital signs in a newborn, notify the provider and frequently reassess.
- Abnormal respiratory rate: Look for signs of respiratory distress, such as wheezing, labored breathing, or apnea.
- Abnormal temperature: Keep the newborn dry and tightly wrapped in a blanket. Provide a warm environment.
- O2 saturation: Stimulate the infant. Suction the airway as needed.
Nursing tips for the newborn assessment
It is helpful to start with the least invasive vital sign. Vital signs in newborns should be checked every 4 hours. Take one full minute to count respirations and apical pulse. The apical pulse on a newborn is lateral to the left midclavicular line, at the 4th intercostal space.
Note that environmental and circumstantial factors can impact vital sign values:
- Crying may lead to irregular heart rate.
- Room temperature and clothing may impact temperature readings.