Types of reflexes in newborn babies
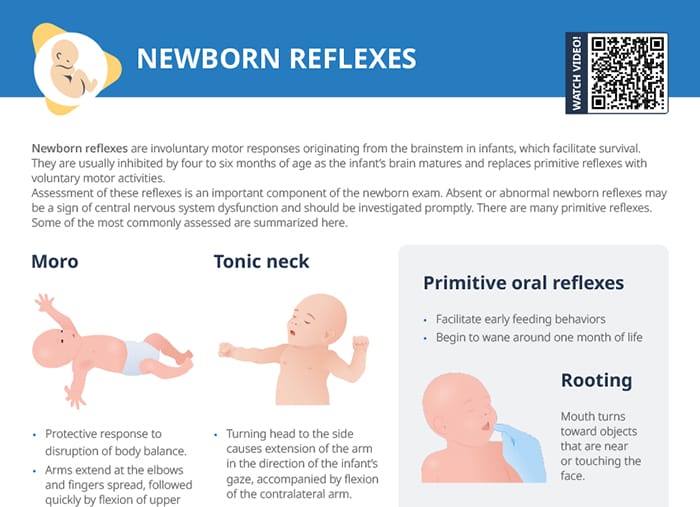
Assessment of primitive reflexes is an important component of the newborn exam. Absent or abnormal newborn reflexes may be a sign of central nervous system dysfunction and should be investigated promptly.
Types of reflexes:
- Oral reflexes (rooting and sucking) facilitate early feeding behaviors and begin to wane around one month of life.
- The Moro reflex could be theorized to be a protective reflex, helping the baby cling to the mother after sudden movements.
- Most reflexes are developmental reflexes, preparing the baby for future voluntary movements.
Clinical tip: Persistence of primitive reflexes beyond the expected time period or reemergence of a formerly extinguished reflex can point to neurological disease.
Clinical tip: The presence of five or more abnormal reflexes is correlated with the development of cerebral palsy or other intellectual delays.
Rooting and sucking
The rooting reflex helps the baby find the nipple for feeding.
Triggering the rooting reflex
Touch or stroke the baby’s cheek. Reflex may be elicited by objects near the baby’s face as well. The mouth opens and the head turns toward the object near or touching the face.
Triggering the sucking reflex
Anything touching the roof of the baby’s mouth triggers the sucking reflex.
Palmar grasp reflex
The palmar grasp reflex is an evolutionary trait potentially linked to clinging to the caregiver.
Trigger
Stroke the palm of the baby’s hand.
Response
The baby grasps the finger with their hand.
Plantar grasp reflex
Trigger
Stroke the sole of the baby’s foot.
Response
The baby’s toes curl downward.
Moro reflex
The Moro reflex is a protective response to a disruption of body balance. It disappears by about six months of age.
Trigger
A sudden loss of head support or loud noises can elicit the Moro response. The reflex can be tested by tilting the baby’s trunk and head quickly about 30 degrees.
Response
The baby extends the arms at the elbows, spreading the fingers. This movement is quickly followed by a flexion of the upper extremities and crying.
Babinski reflex
The Babinski reflex in babies disappears by twelve months of age. Longer persistence can indicate neurological problems.
Trigger
Stroking the sole of the foot of the baby should elicit the Babinski reflex.
Response
The baby’s toes flare out, with the big toe bending upwards.
Tonic neck reflex
The tonic neck reflex (“fencer’s pose”) disappears around three months of age.
Trigger
Turn the baby’s head to one side.
Response
The baby extends the arm on the side the head is turned to. The other arm is flexed at the elbow.
Reflex integration exercises
If reflexes persist after the expected age, further assessments for neurological issues need to be done.
Reflex integration exercises are therapeutic activities designed to facilitate the transition from reflex to voluntary movement.
Types of reflex integration exercises:
- Repetitive movements mimicking natural movements
- Sensory integration exercises to support the maturation of the CNS
- Specific exercises meant to inhibit a specific retained reflex
For example, a common Moro reflex integration exercise involves the child lying on their back with the head back, arms lifted up and the legs spread, then repeatedly crossing the arms and legs while breathing out slowly. Also, when the child is awake, provide natural movement, such as increasing ‘tummy time’.