What are developmental milestones?
Developmental milestones are specific skills or behaviors that most children achieve by a certain age, such as walking or talking. They are used to assess a child’s developmental progress. Monitoring these helps identify potential developmental delays or concerns.
What are growth stages?
Growth stages refer to specific periods in human development characterized by rapid physical and/or psychological change. Examples include infancy, childhood, adolescence, and adulthood. Monitoring growth stages helps in understanding and anticipating health needs relevant to each stage.
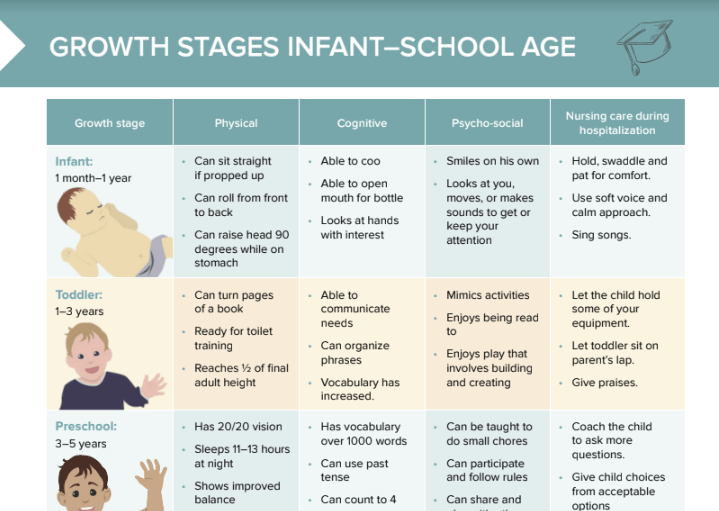
Infant milestones: 1 month–1 year
Physical milestones for infants
- Can sit straight if propped up
- Can roll from front to back
- Can raise head 90 degrees while on stomach
Cognitive milestones for infants
- Able to coo
- Able to open mouth for bottle
- Looks at hands with interest
Psychosocial milestones for infants
- Smiles on his own
- Looks at you, moves, or makes sounds to get or keep your attention
Nursing care tips for infants
- Hold, swaddle and pat for comfort.
- Use soft voice and calm approach.
- Sing songs.
Toddler developmental milestones: 1–3 years
Physical milestones for toddlers
- Can turn pages of a book
- Ready for toilet training
- Reaches 1⁄2 of final adult height
Cognitive milestones for toddlers
- Able to communicate needs
- Can organize phrases
- Vocabulary has increased.
Psychosocial milestones for toddlers
- Mimics activities
- Enjoys being read to
- Enjoys play that involves building and creating
Nursing care tips for toddlers
- Let the child hold some of your equipment.
- Let toddler sit on parent’s lap.
- Give praises.
Preschool children milestones: 3–5 years
Physical milestones for preschool children
- Has 20/20 vision
- Sleeps 11–13 hours at night
- Shows improved balance
Cognitive milestones for preschool children
- Has vocabulary over 1000 words
- Can use past tense
- Can count to 4
Psychosocial milestones for preschool children
- Can be taught to do small chores
- Can participate and follow rules
- Can share and play with other children
Nursing care tips for preschool children
- Coach the child to ask more questions.
- Give child choices from acceptable options (e.g., do you want your shot in the right arm or left arm?).
- Use drawings to explain procedures.
Children in elementary school: 6–10 years
Physical milestones for elementary school children
- Ability to make bed
- Dresses appropriately
- Writes neatly
Cognitive milestones for elementary school children
- Rapid mental skill development
- Less focused on oneself
- Uses five- to seven-word sentences
Psychosocial milestones for elementary school children
- Begins thinking about future
- Wants to be accepted
- More independent of family
Nursing care tips for elementary school children
- Knock on door before entering.
- Provide fresh air.
- Encourage deep breathing to allay anxiety.
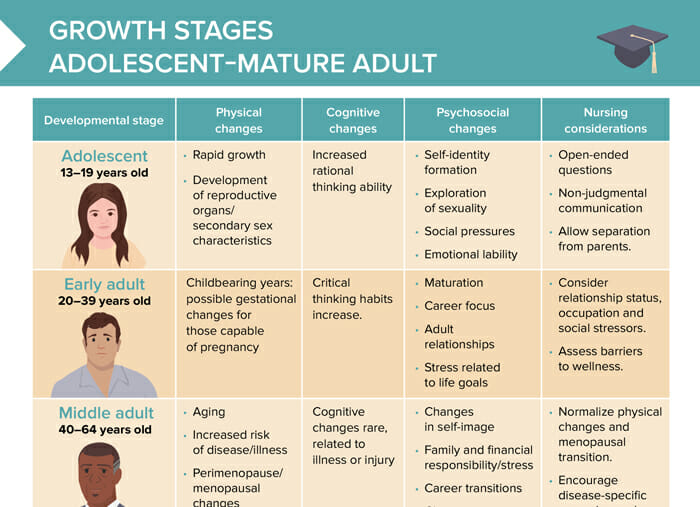
Adolescents: 13–19 years
Physical changes in adolescents
- Rapid growth
- Development of reproductive organs/secondary sex characteristics
Cognitive changes in adolescents
Increased rational thinking ability
Psychosocial changes in adolescents
- Self-identity formation
- Exploration of sexuality
- Social pressures
- Emotional lability
Nursing care tips for adolescents
- Open-ended questions
- Non-judgmental communication
- Allow separation from parents.
Bonus download: growth stages: adolescent–mature adult
Understand growth and development in order to provide appropriate, individualized care across the lifespan
Early adults: 20–39 years
Physical changes in early adults
Childbearing years: possible gestational changes for those capable of pregnancy
Cognitive changes in early adults
Critical thinking habits increase.
Psychosocial changes in early adults
- Maturation
- Career focus
- Adult relationships
- Stress related to life goals
Nursing care tips for early adults
- Consider relationship status, occupation and social stressors.
- Assess barriers to wellness.
Middle adults: 40–64 years
Physical changes in middle adults
- Aging
- Increased risk of disease/illness
- Perimenopause/menopausal changes
Cognitive changes in middle adults
Cognitive changes rare, related to illness or injury
Psychosocial changes in middle adults
- Changes in self-image
- Family and financial responsibility/stress
- Career transitions
- Changes in sexuality
Nursing care tips for middle adults
- Normalize physical changes and menopausal transition.
- Encourage disease-specific screening and prevention.
Mature adult: 65 years and older
Physical changes in mature adults
Physical and functional decline often occurs as age progresses.
Cognitive changes in mature adults
- Cognitive function and short term memory often decline with progressive aging.
- Possible depression related to role transition and isolation
Psychosocial changes in mature adults
- Retirement
- Changes to daily routine, environment, housing
- Social isolation
- Changes in sexuality
Nursing care tips for mature adults
- Assess functional and cognitive baseline, monitor changes.
- Continue disease-specific screening and prevention.
- Consider stressors related to isolation, loss and grief.