What is intrauterine resuscitation?
Intrauterine resuscitation measures are medical interventions performed during labor to improve oxygen delivery, optimize fetal well-being, and prevent fetal compromise.
The main goals of every method are increasing fetal oxygenation and improving fetal heart rate.
Possible indications
- Signs of fetal distress or insufficient oxygenation during labor
- Abnormal fetal heart rate (decelerations)
- Prolonged labor
- Umbilical cord complications
4 primary types of interventions
- Tocolytic therapy
- Intravenous fluid administration
- Maternal position changes
- Maternal oxygen administration
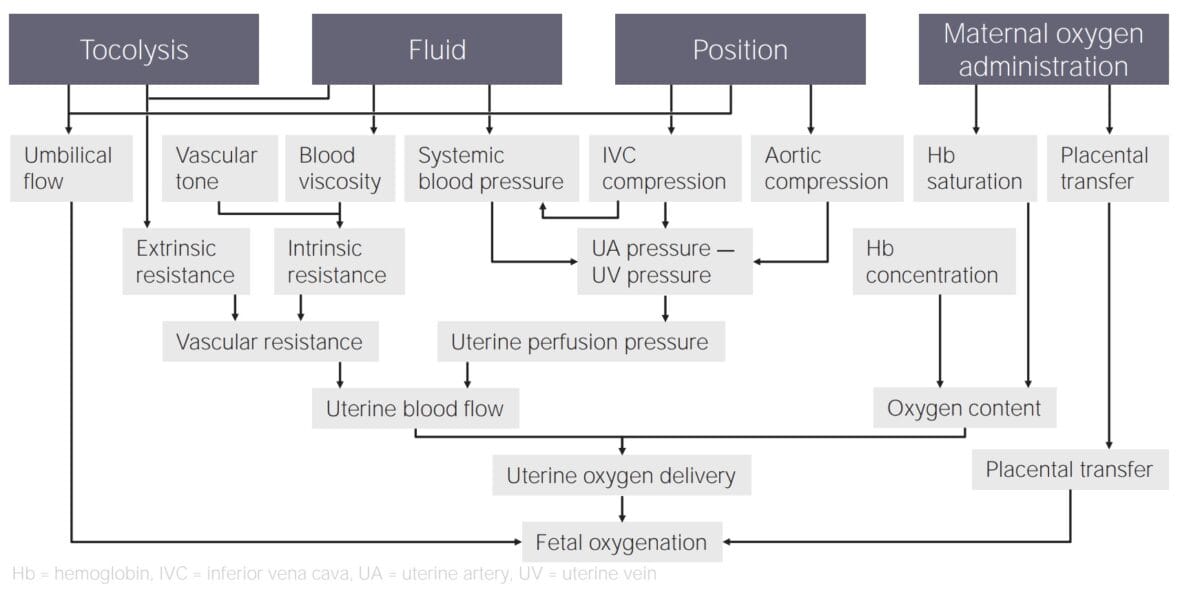
Tocolysis/tocolytic therapy
Tocolysis involves stopping the contraction, which leads to increased blood flow and oxygenation.
IV fluid administration for intrauterine resuscitation
Administering IV fluids can increase oxygenation by increasing blood viscosity and bringing up blood pressure, increasing the flow through the placenta.
Maternal position changes
Certain labor positions might lower blood pressure, such as lying flat on the back compressing the vena cava. Repositioning the client into a more favorable position for fetal oxygenation can increase the blood flow.
The best labor position for optimizing oxygenation of the fetus can vary depending on individual circumstances. Often recommended positions that improve maternal circulation include:
- Left-lateral position
- On all fours
- Upright positions
- Side-lying with a tilt to prevent compression of the vena cava
- Semi-reclining
Maternal oxygen administration
To get the highest possible amount of oxygen from the client to the fetus, a high concentration of oxygen needs to be given, making a nasal cannula insufficient. A non-rebreather mask with 10 liters per minute gives sufficient oxygen.

