What is an intramuscular injection?
An intramuscular injection is a technique used to deliver medication deep into the muscle tissue. This allows the medication to be absorbed into the bloodstream quickly. It’s often used for vaccines, antibiotics, and hormonal therapies.
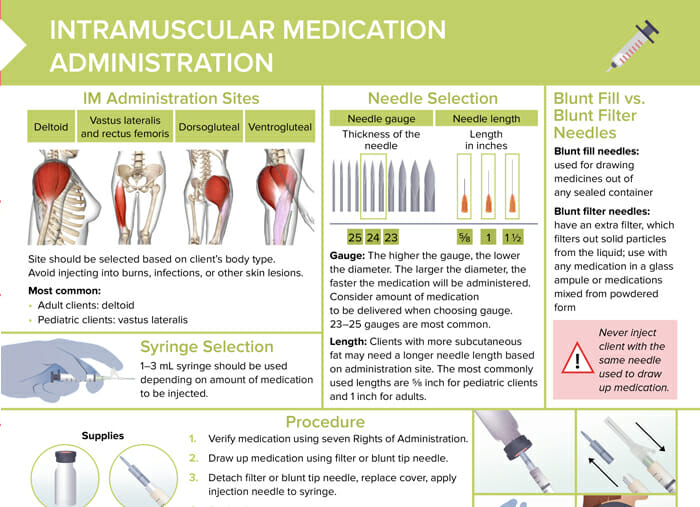
Intramuscular injection sites
Site should be selected based on client’s body type. Avoid injecting into burns, infections, or other skin lesions.
Possible sites:
- Deltoid (most common for adults)
- Vastus lateralis (most common for children) and rectus femoris
- Dorsogluteal
- Ventrogluteal
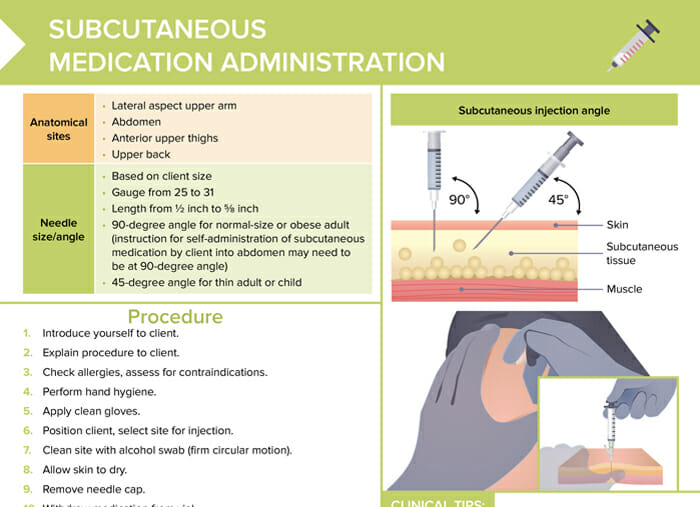
Subcutaneous injection needle size and syringe selection
The choice of syringe is based on the amount of medication to be injected, typically 1–3 mL syringes should be used.
Note about needle size: Clients with more subcutaneous fat may need a longer needle length based on administration site (most common: ⅝ inch for children and 1 inch for adults). Choice of needle gauge should consider the amount of medication to be delivered.
Which supplies do I need for an intramuscular injection?
- Medication
- 1–3 mL syringe
- Needle of appropriate size
- Antiseptic pads
- Gauze pad
How to give an intramuscular injection (technique for nurses)
- Verify medication using seven Rights of Administration.
- Draw up medication using filter or blunt tip needle.
- Detach filter or blunt tip needle, replace cover, apply injection needle to syringe.
- Apply gloves.
- Expose the administration site and clean with an antiseptic pad in a circular motion.
- Remove the needle sheath.
- Position syringe at a 90-degree angle.
- Quickly and smoothly insert the needle into the muscle.
- If no blood is aspirated (for dorsogluteal sites only), slowly inject the medication into the muscle.
- After 10 seconds, withdraw the syringe and activate the safety cover.
- Place gauze over injection site and apply pressure for a few seconds.
- Remove gauze and check for bleeding or bruising
How to monitor clients after an intramuscular injection
- Watch for any signs of adverse reactions or allergies, such as swelling, redness, or difficulty breathing.
- Check the injection site for any signs of infection.
- Ensure the medication is having its intended effect, and report any unexpected outcomes to the healthcare provider.