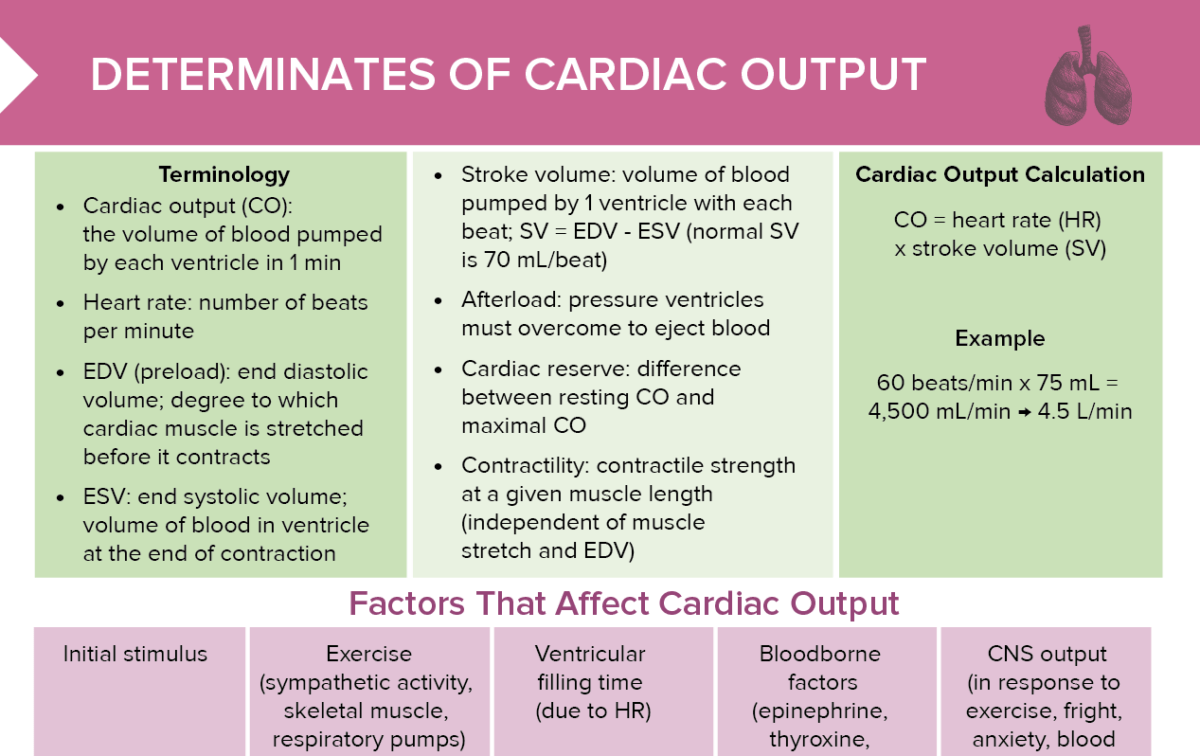
What is done in a cardiovascular assessment in nursing?
A cardiovascular assessment in nursing involves evaluating the heart and blood vessels to identify potential cardiac issues. Here’s a brief outline of the components:
- Taking a thorough history (especially: cases in the family (or past cases in patient) of heart disease, hypertension, diabetes, high cholesterol)
- Asking for symptoms of chest pain, dyspnea, palpitations, leg swelling; assess for edema in the extremities
- Taking vital signs
- Inspection (jugular vein distention, peripheral or central cyanosis)
- Palpation (carotid artery pulses, precordium, peripheral pulses)
- Auscultation (heart sounds)
- Check capillary refill
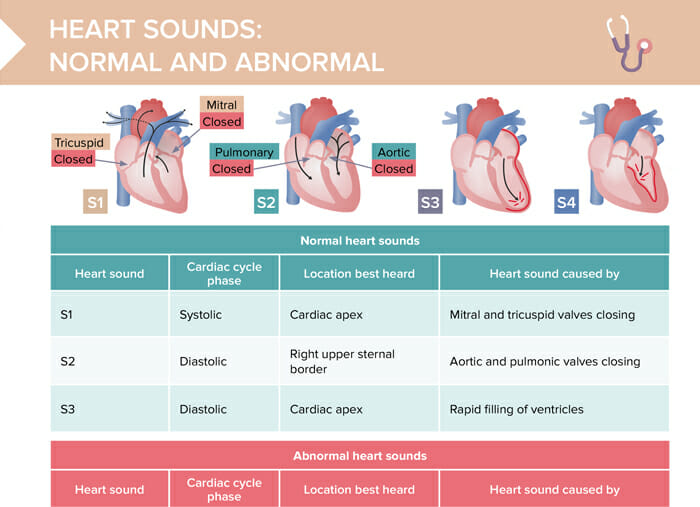
Heart sounds assessment
Heart sounds are noises generated by the closing and opening of the heart valves and the resultant turbulent flow of blood. They provide important information about the heart’s function and potential valve problems.
Normal heart sounds
| Heart sound | Cardiac cycle phase | Location best heard | Caused by |
| S1 | Systolic | Cardiac apex | Mitral and tricuspid valves closing |
| S2 | Diastolic | Right upper sternal border | Aortic and pulmonic valves closing |
| S3 | Diastolic | Cardiac apex | Rapid filling of ventricles |
Abnormal heart sounds
| Heart sound | Cardiac cycle phase | Location best heard | Caused by |
| S4 | Diastolic | Cardiac apex | Occurs at or after S1 and ends beforeor at S2 |
| Systolic murmur | Systolic | Left upper sternal border | Occurs at or after S1 and ends beforeor at S2 |
| Diastolic murmur | Diastolic | Left midclavicular area | The heart relaxing in between beatsafter S2 and before S1 |
| Pericardial rub | Systolic and diastolic | Left sternal border | Parietal and visceral pericardial layers rubbing together |
| Ejection click | Systolic or diastolic | Varies | Maximal opening of the aortic or pulmonary valves |
Heart assessment points
The heart assessment points, also known as the cardiac auscultatory areas, are specific locations on the chest where the nurse or healthcare provider listens to the heart sounds. These areas correspond to the optimal spots to hear specific valves and the flow of blood through the heart. The main assessment points are:
- Aortic area: 2nd intercostal space at the right sternal border
- Pulmonic area: 2nd intercostal space at the left sternal border
- Erb’s point: 3rd intercostal space at the left sternal border
- Tricuspid area: 4th or 5th intercostal space at the left sternal border
- Mitral area: at the apex of the heart, usually in the 5th intercostal space at the midclavicular line
Cardiovascular assessment nursing documentation
Below is a template containing the most important points to include in the documentation of a heart assessment:
| Documentation part | Content | Example |
| History | Chief complaint, history, medications, allergies, habits | Patient complains of chest pain for 2 hours |
| Vital signs | Blood pressure, heart rate, rhythm, resp rate and oxygen saturation | BP: 120/80 mmHg HR: 78 bpm, regular |
| General appearance | Any signs of distress, cyanosis, or fatigue | Respirations at 26/min |
| Inspection | Jugular venous distension? Any deformities or abnormal movements in chest wall? | Symmetrical chest wall |
| Palpation | Describe quality and amplitude of peripheral and carotid pulses | Radial pulse 2+ and regular |
| Auscultation | Document normal and additional heart sounds | S1 and S2 noted, clear and distinct. Grade II/VI systolic murmur heard at mitral area. |
| Edema assessment | Presence, location, degree | 2+ pitting edema noted on bilateral lower extremities |
| Capillary refill | Time taken for color to return | Capillary refill > 2 seconds |
| Diagnostic results | Attach any ECGs or labs | |
| Patient statements | Subjective information | Patient states pain reduced to 2/10 after nitroglycerin |
| Plan and interventions | Medications, further tests, actions taken |
Assessment for heart failure
Specific symptoms to monitor when checking for heart failure include:
- Dyspnea, orthopnea, paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea
- Fatigue
- Swelling/peripheral edema
- When listening to heart sounds, check for S3, murmurs, or gallops
- Palpate for liver enlargement or ascites
- Auscultate lungs for signs of fluid accumulation
- Watch daily weights (sudden gain might indicate fluid retention)
- Be mindful of any limitations in ADLs