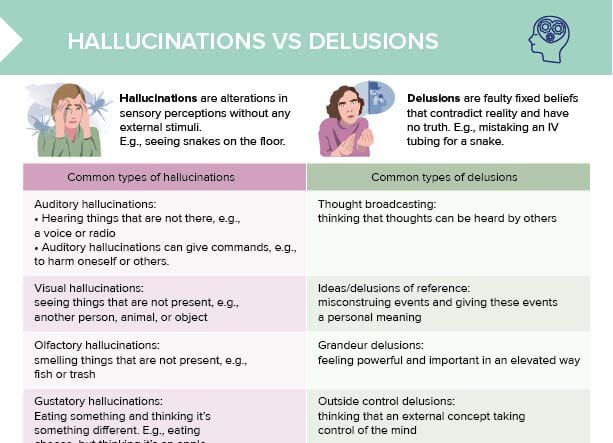
What are hallucinations?
Hallucinations are alterations in sensory perceptions without any external stimuli. An example would be seeing snakes on the floor that are not actually there.
What are delusions?
Delusions are faulty fixed beliefs that contradict reality and have no truth. An example would be mistaking an IV tubing for a snake.
Types of hallucinations
Visual hallucinations
Visual hallucinations mean seeing things that are not present, (e.g. another person, animal, or object).
Auditory hallucinations
Auditory hallucinations involve hearing things that are not there, (e.g., a voice or radio).
Note: auditory hallucinations can give commands (e.g., harming oneself or others).
Tactile hallucinations
Tactile hallucinations involve sensations that feel like being touched by something or someone.
Olfactory hallucinations
Olfactory hallucinations mean smelling things that are not present, (e.g., fish or trash). Gustatory hallucinations happen when the person experiencing them is eating something and thinks it is something different (e.g., eating cheese but thinking it is an apple).
Somatic hallucinations
Somatic hallucinations can affect the entire body, causing unreal sensations, (e.g., the perception of worms in the skin).
Closed-eye hallucinations
Closed-eye hallucinations occur when individuals see visual patterns or images while their eyes are closed. These can range from simple shapes and colors to more complex images.
Fever hallucinations
High fever can lead to visual, auditory, or tactile hallucinations. They are most commonly seen in children but can occur in adults as well. Fever hallucinations usually resolve as the fever subsides.
Hypnagogic hallucinations
Hypnagogic hallucinations occur during the transition from wakefulness to sleep, typically just as a person is falling asleep. These can involve visual, auditory, or tactile sensations.
Types of delusions
Outside-control delusions
This type of delusion involves thinking that an external concept is taking control of the mind.
Thought broadcasting
Thought broadcasting is thinking that one’s thoughts can be heard by others.
Delusions of grandeur
Grandiose delusions involve feeling powerful and important in an elevated way.
Persecutory delusions
Individuals experiencing persecutory delusions:
- Feel singled out for harm by others
- Feel plotted against by people
Delusions of reference/referential delusions
Ideas or delusions of reference involve misconstruing events and giving these events a personal meaning.
Somatic delusions
Somatic delusions are characterized by a false set of beliefs about the body, such as that one’s body is decomposing.
Hallucinations vs delusions vs illusions: comparison
Both hallucinations and delusions can be observed in people who have mental health conditions, including substance abuse or withdrawal, and medical conditions (senile dementias, Parkinson disease, adverse reactions to narcotic pain medications or new medications).
They can be differentiated by the type of distortion in perception or thought:
While hallucinations involve perceiving something that is not there, delusions mean that something that is happening is being interpreted falsely despite contrary evidence. Illusions are misinterpretations of actual external stimuli, like mistaking a dog for a cat because the lighting is dim.