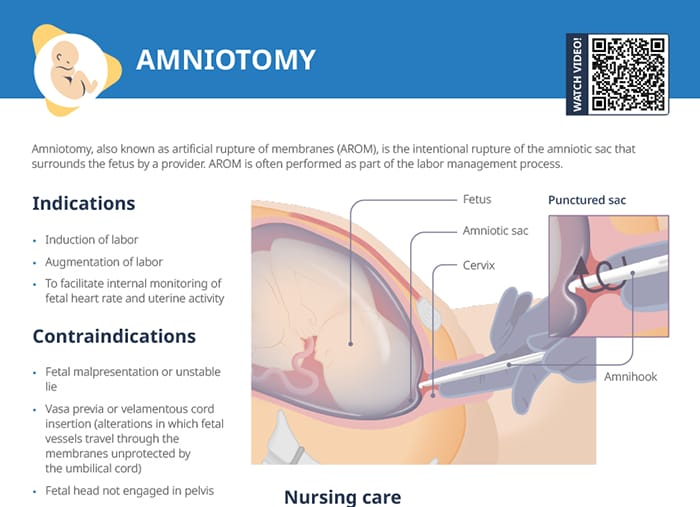
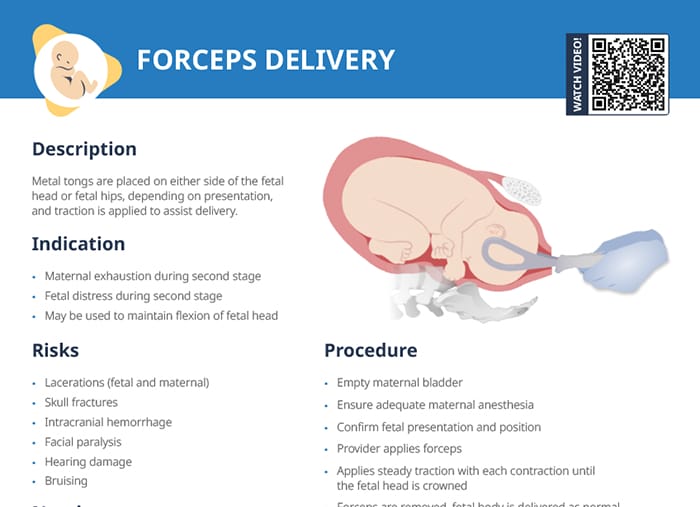
What is forceps delivery?
Forceps are specialized surgical instruments that resemble large, curved metal tongs.
They can be used in childbirth to assist delivery by carefully applying traction on the fetal head (or hips, depending on presentation), holding it on either side with the forceps.
Forceps can be used with certain types of breech presentations, unlike vacuum-assisted deliveries.
Related videos
Forceps delivery indications and contraindications
Assisting the delivery with forceps is an option if the mother is exhausted during the second stage of labor. Fetal distress is another indication. Forceps can also be used to maintain flexion of the fetal head.
Forceps delivery is contraindicated in the following situations:
- Incomplete cervical dilation
- Fetal prematurity (< 34 weeks)
- Unengaged fetal head
- Face presentation
- Hemophilia
- Suspected macrosomia
- Thrombocytopenia
- Inexperienced or untrained provider
Procedure
Clients should be informed on benefits and risks to mother and fetus prior to procedure and give clear informed consent.
Nurses are not performing the forceps delivery. Nursing tasks include gathering the equipment before the procedure, monitoring the fetal heart rate, and providing support to the birthing client. After delivery, assess the infant and check for lacerations in the baby and mother.
Tip: Have hemorrhage supplies ready at all times.
Steps:
- Empty maternal bladder
- Ensure adequate maternal anesthesia
- Confirm fetal presentation and position
- Provider applies forceps and applies steady traction with each contraction until the fetal head is crowned
- Forceps are removed, fetal body is delivered as normal
Risks and complications
The potential complications of forceps delivery include lacerations to both fetus and birthing client, and various other injuries to the fetus:
- Skull fractures
- Intracranial hemorrhage
- Facial paralysis
- Hearing damage
- Bruising
Especially if the forceps are not placed well, the metal tong can cause extensive damage.
Clients should be aware that if a forcep-assisted delivery is not successful, a cesarean section may be necessary.