What is drug toxicity?
Drug toxicity refers to the harmful effects of a drug when administered at a normal or high dose. It can result in adverse reactions that can be life-threatening, causing damage to organs like the liver or kidneys, or leading to other significant health issues.
Adverse effects also can occur even at therapeutic doses and are generally less severe, although they can still be harmful. While mild adverse effects are usually anticipated and listed by the manufacturer, drug toxicity often results from medication errors, interactions, or individual sensitivities and is generally more severe and urgent. Nurses should monitor for both but treat drug toxicity as a medical emergency requiring immediate intervention.
What is ototoxicity?
Ototoxicity definition
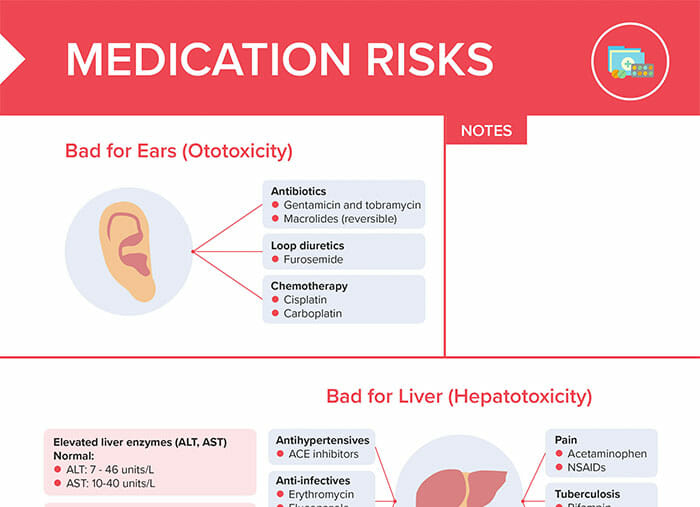
Ototoxicity refers to the harmful effects of certain medications or substances on the inner ear, specifically affecting structures responsible for hearing and balance.
Ototoxic drugs
Antibiotics:
- Gentamicin and tobramycin
- Macrolides (reversible when stopped)
Loop diuretics:
- Furosemide
Chemotherapy:
- Cisplatin
- Carboplatin
Ototoxicity symptoms
Ototoxicity can lead to symptoms like vertigo, tinnitus, and hearing loss.
What is nephrotoxicity?
Nephrotoxicity definition
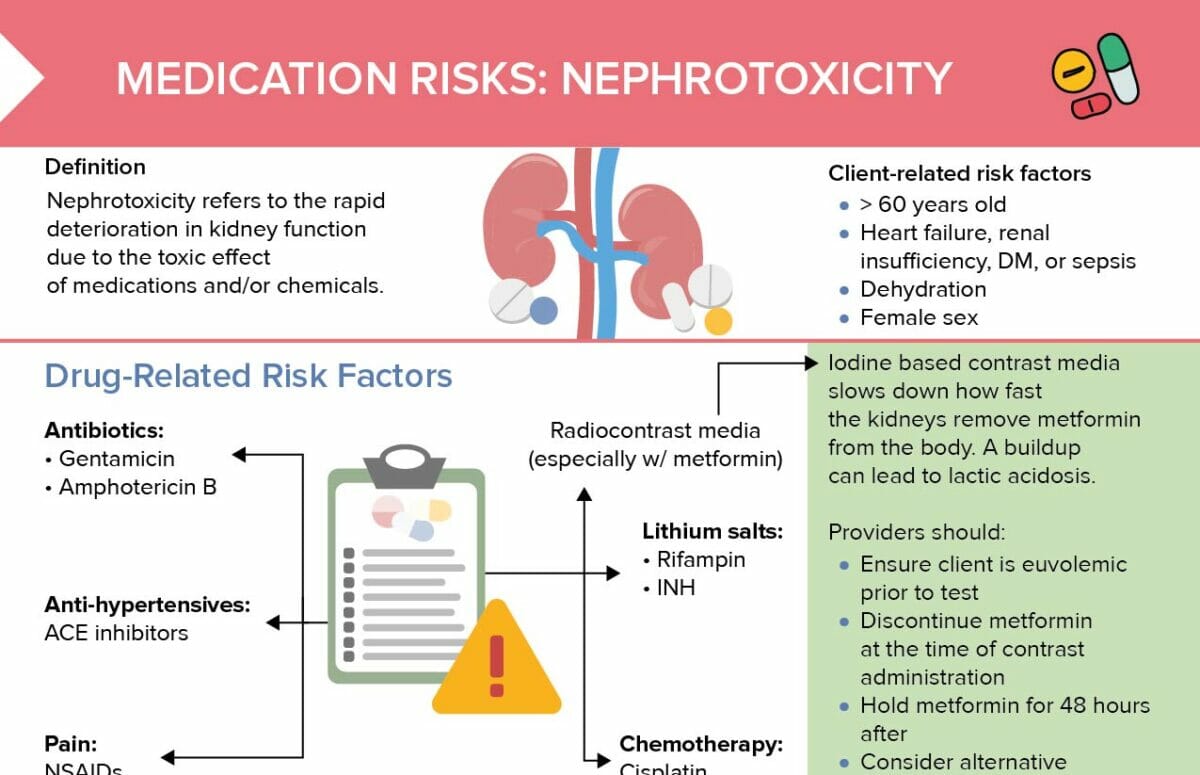
Nephrotoxicity refers to the toxic effect of medication, chemicals, or toxins on the kidneys. It can lead to reduced kidney function and, in severe cases, renal failure.
Nephrotoxic drugs
Antibiotics:
- Gentamicin
- Amphotericin B
ACE inhibitors
NSAIDs
Radiocontrast media (especially with metformin)
Lithium salts:
- Rifampin
- INH
Chemotherapy:
- Cisplatin
Nephrotoxicity symptoms
To detect nephrotoxicity, watch for:
- Elevated BUN (normal 7–20 mg/gL (2.5–7.1 mmol/L)
- Elevated serum creatinine (normal for females: 0.6–1.1 mg/dL [53–97.2 µmol/L] for males 0.7–1.3 mg/dL [61.9–114.9 µmol/L)
Download: Nephrotoxicity Cheat Sheet
Overview of nephrotoxic medications: definition, medications with increased risk, lab values to monitor, and prevention
What is hepatotoxicity?
Hepatotoxicity definition
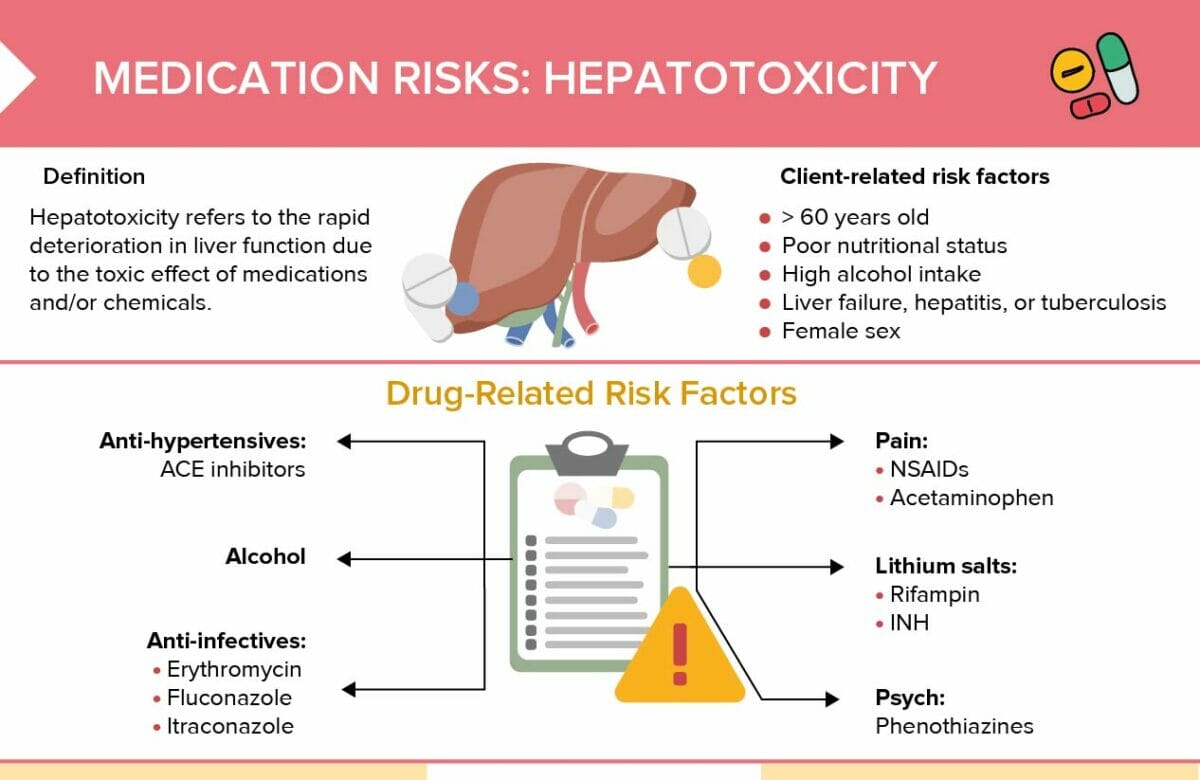
Hepatotoxicity refers to the damaging effects of substances, including medications, on the liver.
Hepatotoxic drugs
Antihypertensives:
- ACE inhibitors
Anti-infectives:
- Erythromycin
- Fluconazole
- Itraconazole
Alcohol
Pain medications:
- Acetaminophen
- NSAIDs
Tuberculosis drugs:
- Rifampin
- INH
Phenothiazines
Hepatotoxicity symptoms
Hepatotoxicity can present with:
- Unusual fatigue/weakness
- Loss of appetite
- Pain in upper abdomen
- Dark-colored urine
- Yellowing of skin or eyes
Download: Hepatotoxicity Cheat Sheet
Overview of hepatotoxic medications: definition, medications with increased risk, lab values to monitor, and symptoms
Practice question: Which statement best describes the term “drug toxicity?”
- Drug toxicity refers to the beneficial effects of a drug when taken in therapeutic doses.
- Drug toxicity refers to the harmful effects of a drug when taken at normal or high doses, leading to adverse reactions or organ damage.
- Drug toxicity is the same as experiencing the adverse effects of a drug and is generally expected.
- Drug toxicity only occurs when two or more drugs interact with each other to produce an undesirable effect.
The correct answer is option 2: “Drug toxicity refers to the harmful effects of a drug when taken at normal or high doses, leading to adverse reactions or organ damage.”
This statement encapsulates the essence of what drug toxicity is—a harmful impact that can cause severe health issues or damage to organs. It specifies that these effects can happen at both normal and high doses, differentiating it from known adverse effects, which can occur even at therapeutic doses.