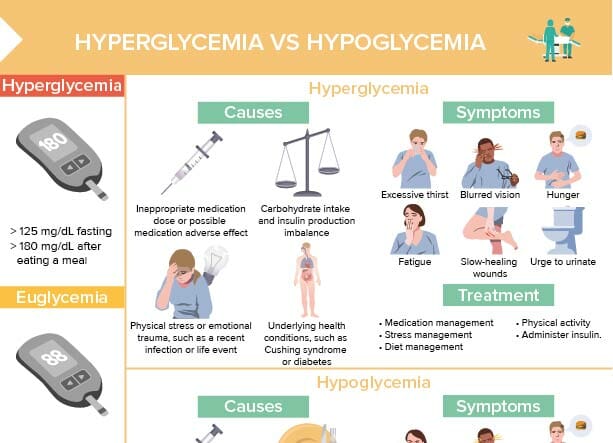
What are diabetes mellitus complications?
Diabetes complications are medical problems that arise as a result of prolonged high blood sugar levels associated with poorly controlled diabetes.
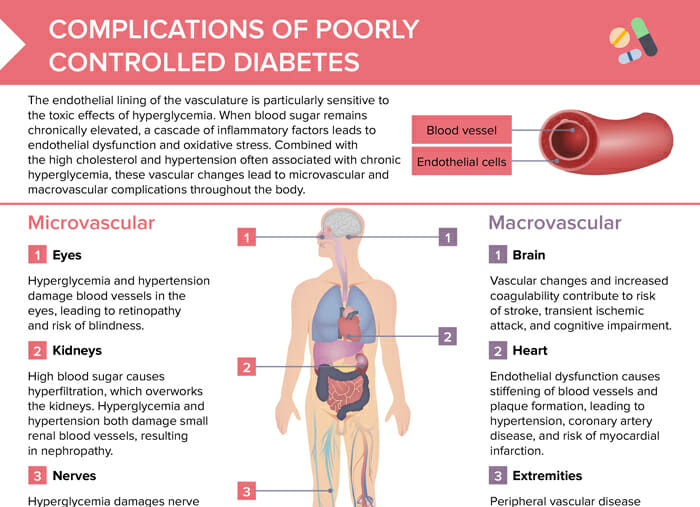
The endothelial lining of the vasculature is particularly sensitive to the toxic effects of hyperglycemia. When blood sugar remains chronically elevated, a cascade of inflammatory factors leads to endothelial dysfunction and oxidative stress. Combined with the high cholesterol and hypertension often associated with chronic hyperglycemia, these vascular changes lead to microvascular and macrovascular complications throughout the body.
Patient education for diabetes
Educating clients on how to manage their condition can help prevent complications:
- Explain the importance of regular monitoring and maintaining blood glucose levels within the target range.
- Encourage a healthy lifestyle (balanced diet, regular physical activity, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol).
- Stress the importance of regular medical check-ups, including eye exams, dental checks, foot exams, and screenings for heart disease and kidney problems.
- Educate about the necessity of adhering to the medication plan consistently and correctly.
- Teach self-care skills such as foot care, recognizing symptoms of hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia, and managing sick days.
- Address emotional well-being as stress and mental health can impact blood glucose control.
Type 1 vs Type 2 diabetes complications
The complications of Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes are largely the same, since they both involve chronic high blood glucose levels which can damage various organs and tissues over time. There can be differences in the timing and prevalence of these complications. For example, individuals with Type 1 diabetes may be more prone to certain conditions such as diabetic ketoacidosis, while those with Type 2 are often more susceptible to cardiovascular disease due to frequently associated factors like obesity and hypertension.
Overview list: complications of diabetes
The key to preventing complications of diabetes is good glycemic control and management of other risk factors.
Microvascular complications
- Eyes: damage in blood vessels due to hyperglycemia/hypertension → retinopathy, risk of blindness
- Kidneys: hyperfiltration due to high blood sugar, overworking kidneys; nephropathy due to hyperglycemia/hypertension damaging small renal blood vessels
- Nerves: nerve cell damage in peripheral nervous system due to hyperglycemia → neuropathic pain or numbness → risk of injuries going undetected/infection
Macrovascular complications
- Brain: risk of stroke, TIA, and cognitive impairment due to vascular changes and increased coagulability
- Heart: hypertension, coronary artery disease, and risk of myocardial infarction due to endothelial dysfunction causing stiffening of blood vessels and plaque formation
- Extremities: peripheral vascular disease (from stiffening and narrowing of blood vessels compromising blood flow to extremities); risk of infection/amputation due to impaired wound healing
Other complications
- Cancer: chronically elevated blood sugar encourages proliferation of cancer cells.
- Infection: hyperglycemia creates an ideal environment for rapid growth of bacterial cells.