What is depression?
Depression (or Major Depressive Disorder) is a mental health disorder characterized by persistent low mood and loss of interest in association with somatic symptoms.
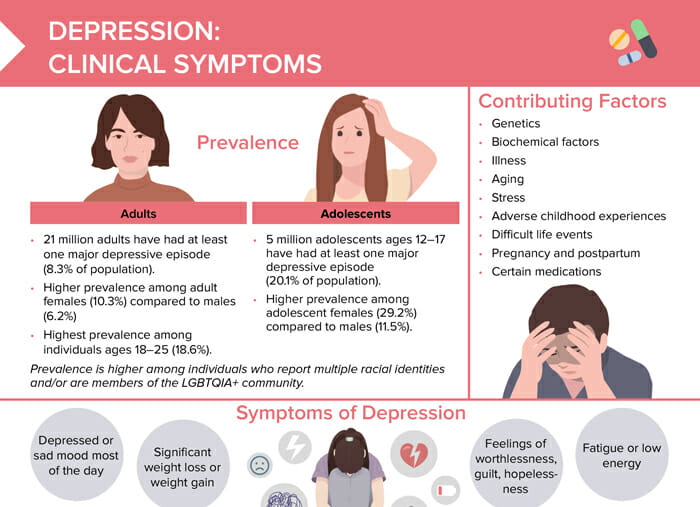
How common is depression?
Prevalence of depression in adults
21 million adults have had at least one major depressive episode (8.3% of population). Depression is more prevalent among adult females (10.3%) compared to males (6.2%). The highest number of people affected by depression can be found among individuals ages 18–25 (18.6%).
Prevalence of depression in adolescents
5 million adolescents ages 12–17 have had at least one major depressive episode (20.1% of population). Adolescent females are more commonly affected (29.2%) than males (11.5%).
What causes depression?
Contributing factors include:
- Genetics
- Biochemical factors
- Illness
- Aging
- Stress
- Adverse childhood experiences
- Difficult life events
- Pregnancy and postpartum
- Certain medications
What are the symptoms of depression?
Symptoms of depression must be present most of the day, more days than not, for at least 2 weeks.
General symptoms of depression
- Depressed or sad mood
- Thoughts of death and/or suicidal behavior
- Significant weight loss or weight gain
- Feelings of worthlessness, guilt, hopelessness
- Difficulty focusing and making decisions
- Fatigue or low energy
- Insomnia or hypersomnia
Nursings tips for recognizing depression in your clients
Depression may manifest differently in clients of different ages, so it is important to look out for the specific signs.
Children may refuse to go to school, have tantrums, pretend to be sick, and may not want to leave their parents.
Teenagers may have low self-esteem, act out, or abuse substances.
Middle-aged adults may have decreased libido, difficulty sleeping, or may be suffering from GI symptoms.
Older adults may report a lack of emotions, memory issues, and are at a higher risk of illness and medications that may contribute.
Note: There can be stigma surrounding a mental health diagnosis. Clients may not openly share their feelings. Ask about symptoms and be prepared with resources.
Nursing diagnosis for depression
- Risk for self-harm related to expressed suicidal ideation or severe hopelessness
- Chronic low self-esteem related to negative self-evaluation, expressed or demonstrated
- Ineffective coping related to inability to meet basic needs or handle stress
- Social isolation related to withdrawal from social interactions or expressed feelings of loneliness
- Disturbed sleep pattern related to insomnia, hypersomnia, or nightmares
- Impaired social interaction related to reduced participation in social or recreational activities
- Hopelessness related to chronic sadness or pessimistic feelings about the future
- Imbalanced nutrition: less than body requirements related to decreased appetite or neglecting self-care