What is croup?
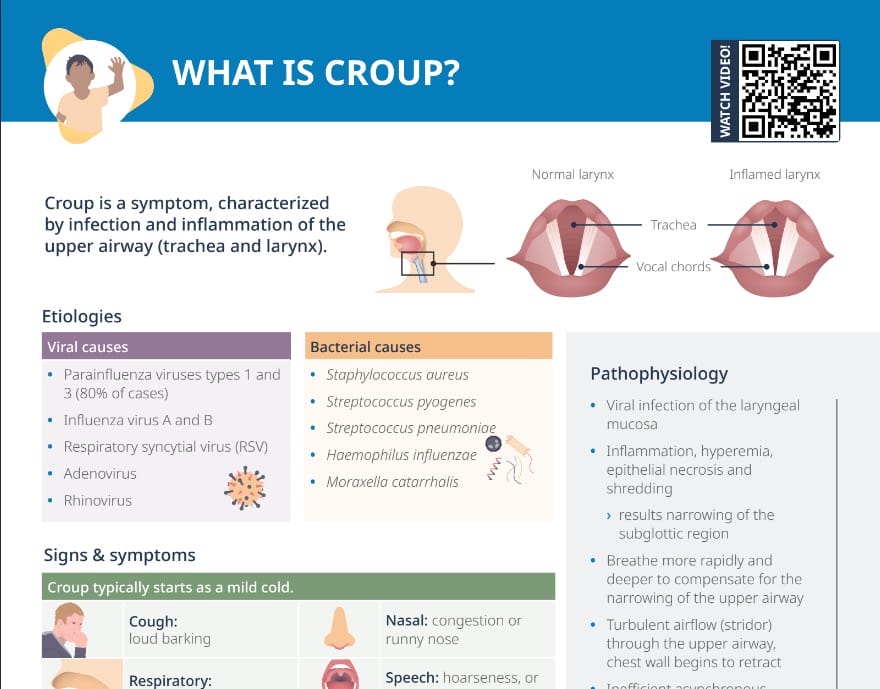
Croup is characterized by infection and inflammation of the upper airway (trachea and larynx).
An infection of the laryngeal mucosa causes inflammation, hyperemia, epithelial necrosis and shredding and therefore a narrowing of the subglottic region, which speeds up and intensifies breathing to compensate.
Through the turbulent airflow (stridor) through the upper airway, the chest wall begins to retract. Inefficient asynchronous chest and abdominal movements lead to fatigue. Hyperoxia and hypercapnia can progress to respiratory failure and arrest.
What causes croup?
Croup can be caused by viruses or bacteria.
Viral causes:
- Parainfluenza viruses types 1 and 3 (80% of cases)
- Influenza virus A and B
- RSV
- Adenovirus
- Rhinovirus
Bacterial causes:
- Staphylococcus aureus
- Streptococcus pyogenes
- Streptococcus pneumoniae
- Haemophilus influenzae
- Moraxella catarrhalis
What does croup sound like? Signs and symptoms
Typically, croup starts as a mild cold.
It is characterized by:
- Cough
- Difficulty/fast breathing, noisy breathing, shortness of breath, wheezing, or stridor
- Nasal congestion or runny nose
- Hoarseness or impaired voice
- Agitation, anxiety, phlegm, sore throat
For most children, croup is a mild illness that can be managed at home.
A croup cough sounds particularly loud and barking.
Potential (but rare) complications of croup include secondary bacterial infections, dehydration, and respiratory distress. They can be addressed with oxygen support, fluids, and racemic epinephrine.
How contagious is croup?
Croup is contagious, especially in the early stages. Transmission occurs through respiratory droplets from coughing or sneezing, or by touching contaminated surfaces. Measures that can help avoid transmission include washing hands frequently, covering mouth and nose when coughing/sneezing and isolation of infected individuals.
How to treat croup
Treatment options for croup include:
- Corticosteroids
- Acetaminophen and/or ibuprofen
- Humidified air (efficacy debated)
- Racemic epinephrine nebulizer (severe cases)
Why is croup worse at night?
Worsening symptoms at night time are typical for croup. This is due to multiple factors, including:
- Colder air at night irritating airways
- Mucus pooling and airway narrowing due to lying down
- Influence of circadian rhythm
- Lower cortisol levels
Can adults get croup?
Yes, adults can get croup, although it is much less common than in children. The symptoms in adults are generally milder due to larger airways, but complications can still occur, especially in those with pre-existing respiratory conditions. If an adult exhibits symptoms like a “barking” cough, stridor, and difficulty breathing, consult a healthcare provider for appropriate diagnosis and treatment.
What is whooping cough?
Whooping cough (also called pertussis), is a highly contagious bacterial infection of the respiratory tract caused by Bordetella pertussis. It is characterized by paroxysms of intense coughing followed by an inspiratory “whooping” sound and can be potentially life-threatening.
Is it croup or whooping cough?
When trying to differentiate between croup and whooping cough, pay attention to the following:
- Sound of cough: Croup presents with a loud, barking cough, whereas coughing fits in whooping cough end with a characteristic “whooping” sound.
- Client age: Croup is much more common in young children, while pertussis can affect clients at any age.
- Duration and clinical progression: Croup is usually acute and lasts up to a week, whereas whooping cough is much longer-lasting, progressing over weeks.
- Cause: Croup has several potential bacterial and viral causes; whooping cough is caused by Bordetella pertussis.
- Diagnostic tests: PCR test or culture confirming pertussis
Final diagnosis will be made by the healthcare provider.
Related videos
Croup vs Covid
When trying to differentiate between croup and Covid-19, pay attention to the following:
- Client age: Croup is most common in young children, while Covid-19 affects all ages.
- Symptoms: Covid-19’s symptoms have a much wider range, while croup is characterized by its distinctively loud and barking cough.
- Severity: Variants of Covid-19 may cause severe respiratory distress with systemic implications.
- Diagnostic tests: PCR or antigen test confirming Covid-19
Related videos
RSV vs croup
When trying to differentiate between croup and RSV, pay attention to the following:
- Cough sound: The croup presents with a loud, barking cough sound, whereas the RSV condition is more typical cough/potential wheezing.
- Symptoms: RSV often involves more upper respiratory symptoms like runny nose and congestion.
- Severity: Both can progress to severe illness but manifest differently (e.g., stridor in croup, wheezing in RSV).
- Diagnostic tests: nasal swab test confirming RSV
Related videos
Croup vs epiglottitis
When trying to differentiate between croup and epiglottitis, pay attention to the following:
- Onset: Croup typically develops over a few days, while epiglottitis is characterized by a rapid onset.
- Symptoms: The barking cough in croup contrasts with epiglottitis patients often being unable to swallow, having high fever, and drooling.
- Severity: Epiglottitis is a medical emergency requiring immediate intervention.