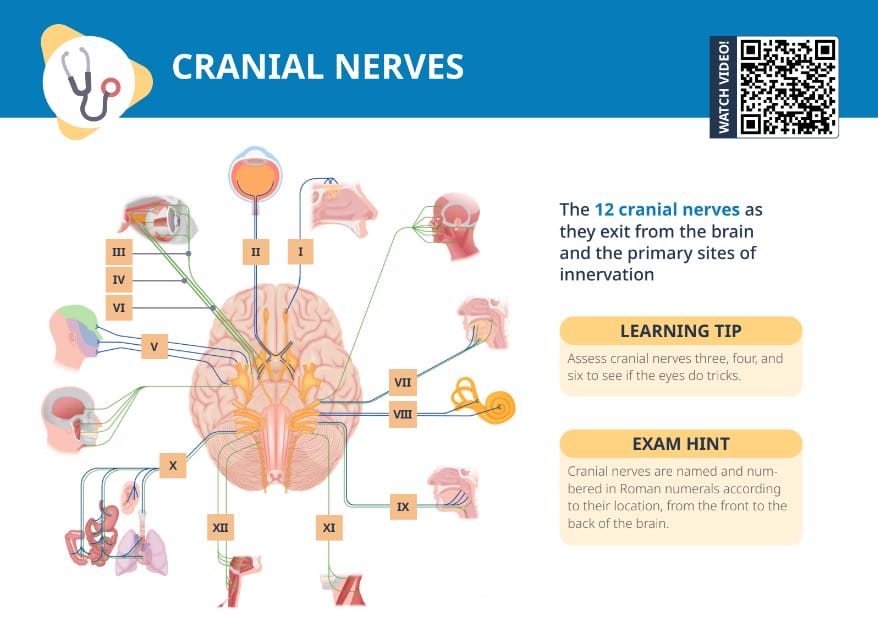
What are the 12 cranial nerves and their functions?
The cranial nerves are twelve pairs of nerves that originate in the brain and control a variety of functions including sensory perception, motor control, and autonomic functions.
| Nerve | # | Function |
| Olfactory | I | Smelling |
| Optic | II | Vision |
| Oculomotor | III | Eye movementPupillary constrictionAccommodationEyelid opening |
| Trochlear | IV | Eye movement (up & down, back & forth) |
| Trigeminal | V | Facial sensationTastingJaw movements |
| Abducens | VI | Abduction of eyes |
| Facial | VII | Facial expressions and tasting |
| Vestibulocochlear | VIII | HearingBalance |
| Glossopharyngeal | IX | Tasting and swallowing |
| Vagus | X | DigestionHeart rate |
| Accessory | XI | Movement of head and shoulders |
| Hypoglossal | XII | Tongue movements |
How to remember the cranial nerves
| Cranial nerve | Mnemonic | Sensory (S), Motor (M), or both (B) |
| Olfactory | Only | Some |
| Optic | One | Say |
| Oculomotor | Of | Marry |
| Trochlear | The | Money |
| Trigeminal | Two | But |
| Abducens | Athletes | My |
| Facial | Felt | Brother |
| Vestibulocochlear | Very | Says |
| Glossopharyngeal | Good | Big |
| Vagus | Victorious | Brains |
| Accessory | And | Matter |
| Hypoglossal | Healthy | More |
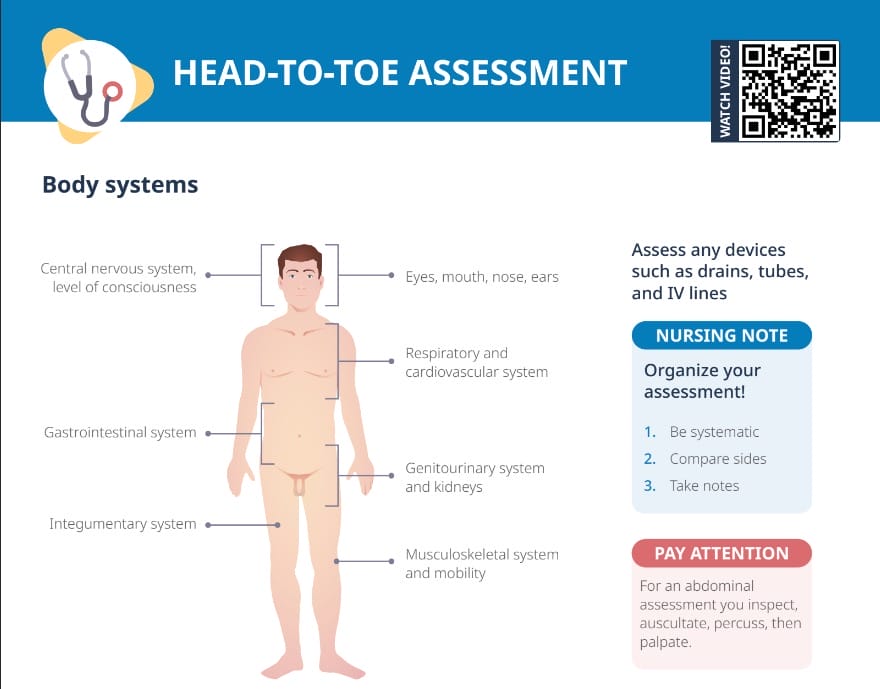
Exam hint
CNs are named and numbered in Roman numerals according to their location, from the front to the back of the brain.
Learning tip
Assess CNs three, four and six to see if the eyes do tricks.
How to assess the cranial nerves
The cranial nerves are assessed through specific tests during a neurological examination.
- Olfactory (CN I): Ask client to identify different smells.
- Optic (CN II): Test visual acuity with Snellen chart.
- Oculomotor (CN III), trochlear (CN IV), abducens (CN VI): Check for pupil size and reactivity to light, ask client to follow your finger with their eyes in an “H” pattern to test extraocular movements.
- Trigeminal (CN V): Assess facial sensation in three areas (forehead, cheeks, and jaw) and check the jaw-jerk reflex. Also, evaluate the muscles of mastication.
- Facial (CN VII): Ask client to smile, frown, or puff out their cheeks.
- Vestibulocochlear (CN VIII): Check hearing using the Rinne and Weber tests and assess balance.
- Glossopharyngeal (CN IX): Assess the gag reflex and the sense of taste on the posterior third of the tongue.
- Vagus (CN X): Assess swallowing and speech. The gag reflex also tests the vagus nerve.
- Accessory (CN XI): Check shoulder shrug strength and head rotation against resistance.
- Hypoglossal (CN XII): Ask client to stick out their tongue and move it side to side. Assess tongue strength and symmetry.
How does cranial nerve dysfunction impact nursing care?
Cranial nerve dysfunction can significantly impact a client’s quality of life and ability to perform daily activities. As a nurse, you might need to assist with feeding if the client has difficulty swallowing, or provide safety measures for clients with vision or balance problems. It’s also important to provide emotional support, as changes in functions like speech, swallowing, and facial expression can be distressing.