What is a complete blood count?
A complete blood count (CBC) is a common blood test that provides detailed information about three types of cells in the blood: red blood cells (RBCs), white blood cells (WBCs), and platelets.
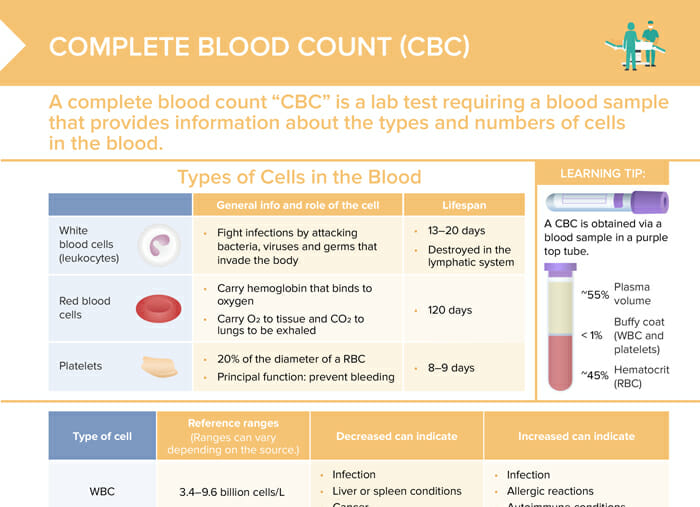
A CBC is obtained via a blood sample in a purple top tube and provides valuable information about the overall health status and can be used to diagnose and monitor many different conditions, including anemia, infection, clotting disorders, leukemia, and response to treatment. It’s a standard test that’s often part of routine health examinations or performed to help diagnose symptoms.
Overview: types of cells in the blood
Table: Blood cell types
| Cell | Role | Lifespan |
| White blood cells (leukocytes, WBC) | Fight infections by attacking bacteria, viruses, germs that invade the body | 13–20 days (destroyed in the lymphatic system) |
| Red blood cells (RBC) | Carry hemoglobin that binds to oxygen, carry O2 to tissue and CO2 to lungs to be exhaled | 120 days |
| Platelets | 20% of the diameter of a RBC, principal function is to prevent bleeding | 8–9 days |
Complete blood count: normal ranges chart
Table: Normal cell counts in the blood
| Type of cell | Reference range (can vary depending on source) |
| WBC | 5000–10,000 cells/mm3 |
| RBC | Male: 4.7–6.1 × 106/μL, elderly: 4.7–6.1 × 1012/L, female: 4.2–5.4 × 106/μL, elderly: 4.2–5.4 × 1012/L |
| Hemoglobin (HgB) | Male: 14–18 g/dL (140–180 g/L), female: 12–16 g/dL (120–160 g/L) |
| Hematocrit (Hct) | Male: 42%–50% (0.40–0.50), female: 37%–47% (0.37–0.47) |
| Platelet count | 150,000–400,000/mm3 (150 to 400 × 109/L) |
Complete blood count interpretations: How to read a CBC blood test
Cell count values may vary based on the laboratory, population, or age and overall health of the client. Any abnormalities should be correlated with clinical signs, symptoms, and other diagnostic information.
Indications of decreased cell counts
Table: Indications of decreased cell counts
| Type of cell | Indication |
| WBC | Infection, liver or spleen conditions, cancer |
| RBC | Hemorrhage, anemia, cancer, malnutrition |
| Hemoglobin (Hgb) | Any abnormalities in Hgb can indicate concerns in the blood‘s oxygen-carrying capacity. |
| Hematocrit (Hct) | Low levels of iron, heavy menses, anemia |
| Platelet count | Higher risk for bleeding |
Indications of increased cell counts
Table: Indications of increased cell counts
| Type of cell | Indication |
| WBC | Infections, allergic reactions, autoimmune conditions |
| RBC | Dehydration, heart or lung disease, polycythemia vera |
| Hemoglobin (Hgb) | Any abnormalities in Hgb can indicate concerns in the blood‘s oxygen-carrying capacity. |
| Hematocrit (Hct) | Polycythemia vera, dehydration, shock |
| Platelet count | Higher risk for blood clots |
What CBC blood test indicates cancer?
A Complete Blood Count (CBC) alone does not diagnose cancer, but it can show abnormalities that may be indicative of cancer or various benign conditions as well.
For example, unusually high or low WBC counts can indicate leukemia or lymphoma. Some cancers can cause elevated platelet counts, and a low red blood cell count can be a sign of certain cancers as well.
Do you need to fast for a CBC blood test?
Clients do not need to be advised to fast before a CBC blood test.