What is influenza?
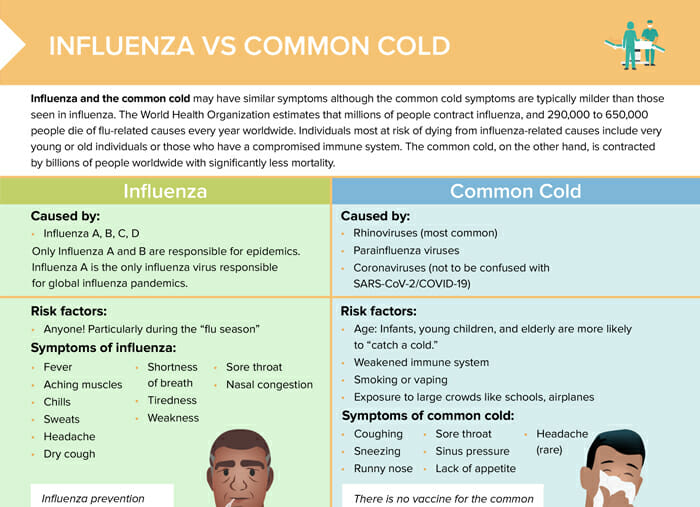
Influenza is a contagious respiratory illness caused by influenza viruses. The World Health Organization estimates that millions of people contract influenza, and 290,000 to 650,000 people die of flu-related causes every year worldwide. Individuals most at risk of dying from influenza-related causes include very young or old individuals or those who have a compromised immune system.
What is the common cold?
The common cold is a common viral infectious respiratory disease. Influenza and the common cold may have similar symptoms, although the common cold symptoms are typically milder than those seen in influenza. The common cold is contracted by billions of people worldwide with significantly less mortality than influenza cases.
Flu vs cold causes
Flu causes
Influenza is caused by the influenza virus A, B, C, and D. Only Influenza A and B are responsible for epidemics. Influenza A is the only influenza virus responsible for global influenza pandemics. The virus is primarily spread through tiny droplets made when people with the flu cough, sneeze, or talk. It can also be contracted by touching a surface or object that has the flu virus on it and then touching one’s mouth, eyes, or nose.
Common cold causes
The common cold is most commonly caused by rhinoviruses. Parainfluenza viruses and coronaviruses (not to be confused with SARS-CoV2/Covid-19) can also be the cause. Transmission is through airborne droplets (infected person coughing or sneezing), or by touching contaminated surfaces.
Flu vs cold risk factors
Risk factors for the common cold include:
- Age (infants, young children, elderly more at risk)
- Weakened immune system
- Smoking or vaping
- Exposure to large crowds (schools, airplanes)
For influenza, anyone is at risk of getting a flu – especially during the “flu season.”
Flu vs cold symptoms
Flu symptoms
Symptoms of influenza include:
- Fever
- Aching muscles
- Chills
- Sweats
- Headache
- Dry cough
- Shortness of breath
- Tiredness
- Weakness
- Sore throat
- Nasal congestion
Common cold symptoms
Symptoms of the common cold include:
- Coughing
- Sneezing
- Runny nose
- Sore throat
- Sinus pressure
- Lack of appetite
- Headache (rare)
Influenza and common cold nursing tips
Influenza symptoms are more severe and occur more abruptly compared to the common cold.
Laboratory testing by nasal swabs can confirm influenza infection and type. Antiviral medication may be prescribed to shorten the duration of illness but must be started early in the course of disease.
There are no laboratory tests available to diagnose a common cold. Treatment is directed to specific symptoms (fever, nasal discharge, sore throat, cough). There are no specific antiviral medications and antibiotics are to be avoided unless there is confirmation of a secondary bacterial infection.
Influenza and common cold prevention
Influenza prevention includes getting the seasonal flu vaccine. There is no vaccine or cure for the common cold. Standard general viral illness prevention methods may reduce the risk:
- Wash hands for at least 20 seconds with soap and water.
- Cover coughs; sneeze into a tissue.
- Clean/disinfect high-touch surfaces like bathroom countertops, doorknobs, light switches, electronics, children’s toys.
- Avoid sick individuals when appropriate.