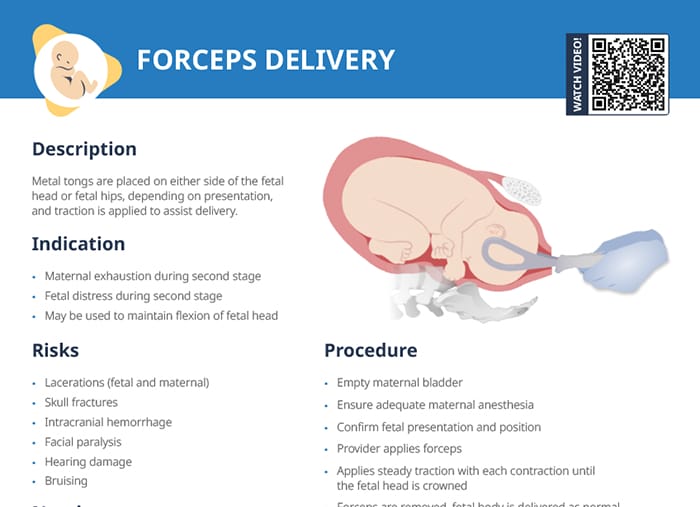
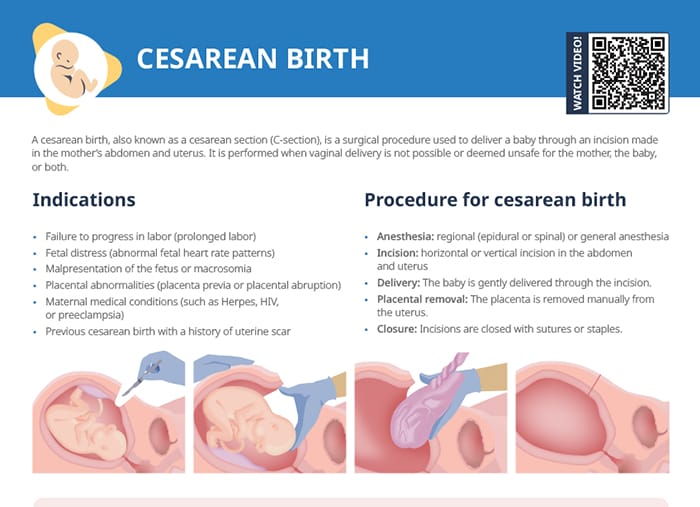
What is a C-section?
A cesarean birth, also known as a cesarean section (C-section), is a surgical procedure used to deliver a baby through an incision made in the mother’s abdomen and uterus. It is performed when vaginal delivery is not possible or deemed unsafe for the mother, the baby, or both.
Related videos
Procedure
- Anesthesia: regional (epidural or spinal) or general anesthesia
- Incision: horizontal or vertical incision in the abdomen and uterus
- Delivery: The baby is gently delivered through the incision.
- Placental removal: The placenta is removed manually from the uterus.
- Closure: Incisions are closed with sutures or staples.
Risks
Risks to the mother
- Infection at the incision site or in the uterus
- Excessive bleeding (hemorrhage)
- Injury to nearby organs (such as bladder or bowel)
- Adverse reactions to anesthesia
Risks to the infant
- Respiratory complications (transient tachypnea, respiratory distress syndrome)
- Surgical injury during delivery
- Increased risk of breastfeeding difficulties
Nursing care and assessment of mother and infant
- Preoperative preparation: Assess the mother’s medical history, administer preoperative medications as ordered, and explain the procedure and expectations.
- Intraoperative support: Monitor vital signs, assist with anesthesia administration, and provide emotional support to the mother.
- Postoperative care: Monitor the mother for signs of hemorrhage, infection, or other complications. Monitor vital signs, urine output, and vaginal discharge. Encourage early ambulation and provide pain management as needed.
- Infant care: Assess the infant’s respiratory status, temperature, and overall well-being. Initiate breastfeeding as soon as possible, and monitor for any signs of distress or complications. Encourage skin to skin. Monitor vital signs.
- Support and education: Provide emotional support to the mother and family, offer guidance on postoperative care, pain management, and breastfeeding. Discuss signs of complications and when to seek medical attention.