Nursing Knowledge
Checking the brain stem reflexes in comatose patients determines if the brain stem is intact. Failing any brainstem reflex test indicates significant impairment or damage to the brainstem, which is associated with serious neurological conditions and a poor prognosis.
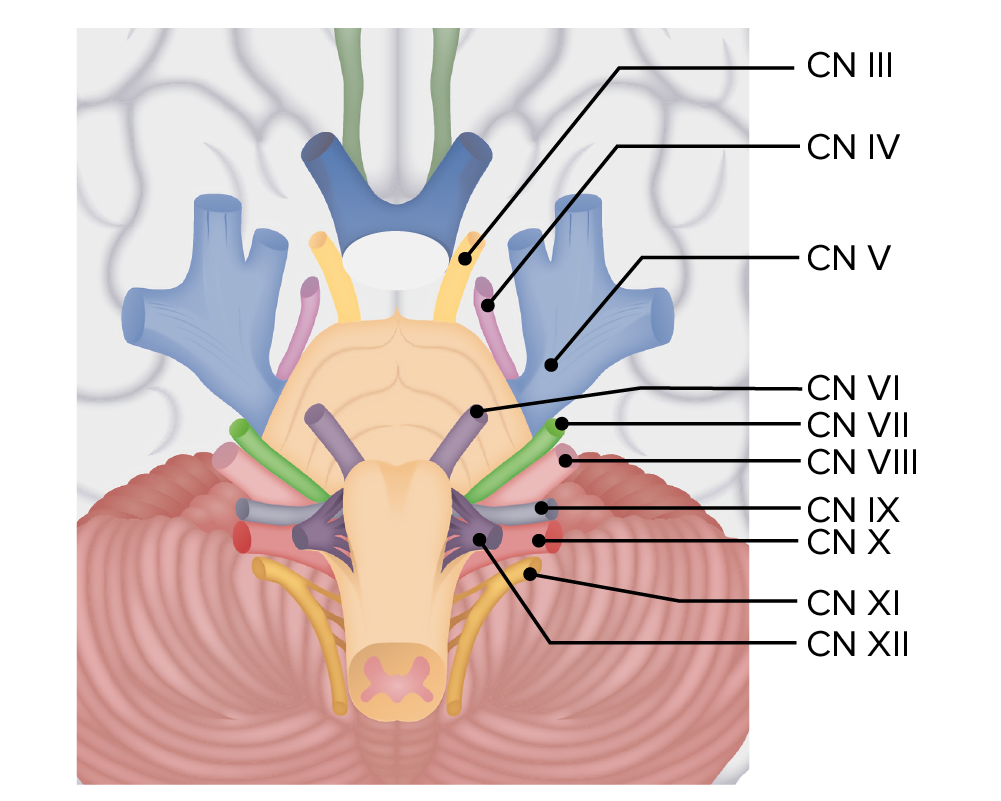
Cranial nerves throughout the brain stem:
Note the 4 cranial nerves that originate from the pons: cranial nerves (CNs) V, VI, VII, and VIII. All of these emerge from the pontine tegmentum.
Key assessments include:
Cranial nerves: II, III
The pupils should directly and consensually constrict in response to the light.
The pupils staying mid-position and not reacting to the light is considered an abnormal response, indicating damage to the optic or oculomotor nerve or significant brain stem damage.
Cranial nerves: III, V, VII
The eyelid should close.
If the eye does not blink in response to the stimulation, it is a sign of damage to the trigeminal nerve or facial nerve.
Cranial nerves: IX, X
The soft palate elevates, and the client coughs.
The assessment for the gag and cough reflex is negative if there is no response to the stimulation. The abnormal response suggests damage to the glossopharyngeal and vagus nerves.
Cranial nerves: III, IV, VIII
Turn the client’s head briskly from side to side.
The eyes should move the opposite way the head is turned.
No eye movement in response to the test indicates severe brain stem damage.
Cranial nerves: III, IV, VI, VIII
Instill at least 20 mL of ice water into the client’s ear.
The eyes should move laterally toward the affected ear.
An abnormal response occurs if there is no eye movement, the eyes remaining midline. This significant brain stem injury, particularly involving the vestibulocochlear nerve and brainstem pathways.
RELATED TOPIC:
Free Download
Master the topic with a unique study combination of a concise summary paired with video lectures.
USMLE™ is a joint program of the Federation of State Medical Boards (FSMB®) and National Board of Medical Examiners (NBME®). MCAT is a registered trademark of the Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC). NCLEX®, NCLEX-RN®, and NCLEX-PN® are registered trademarks of the National Council of State Boards of Nursing, Inc (NCSBN®). None of the trademark holders are endorsed by nor affiliated with Lecturio.
Your free account gives you access to:
or