El trasplante de órganos es un procedimiento que implica la extracción de un órgano o tejido vivo y su traslado a una parte diferente del cuerpo o en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum una persona diferente. Los LOS Neisseria trasplantes de órganos se han convertido en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la opción terapéutica de elección para muchas personas con insuficiencia orgánica terminal. El trasplante puede ofrecer al AL Amyloidosis individuo un tratamiento definitivo para una determinada entidad patológica. En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria últimos 50 años, el trasplante de órganos se ha HA Hemolytic anemia (HA) is the term given to a large group of anemias that are caused by the premature destruction/hemolysis of circulating red blood cells (RBCs). Hemolysis can occur within (intravascular hemolysis) or outside the blood vessels (extravascular hemolysis). Hemolytic Anemia convertido en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum una práctica exitosa y en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum evolución que beneficia a más de 100 000 personas al AL Amyloidosis año en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum todo el mundo. Tanto los LOS Neisseria órganos sólidos como las células hematopoyéticas derivadas de la médula ósea se pueden trasplantar con éxito para varias indicaciones diferentes. La tolerancia del órgano trasplantado por parte del sistema inmunitario del huésped se logra mediante el uso de estrategias inmunosupresoras e inmunomoduladoras. Las principales complicaciones del trasplante son el rechazo de órganos o fallo del injerto; sin embargo, la inmunosupresión crónica también conlleva el riesgo de complicaciones graves, incluidas infecciones potencialmente mortales.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
El tejido trasplantado puede ser células (e.g., células madre hematopoyéticas), tejidos (e.g., córnea), partes de un órgano (e.g., injertos de hígado y piel) u órganos completos (e.g., riñón, corazón). Hay muchos términos que son importantes para la medicina de trasplantes.
La compatibilidad inmunológica entre un donante de órganos y un receptor Receptor Receptors are proteins located either on the surface of or within a cell that can bind to signaling molecules known as ligands (e.g., hormones) and cause some type of response within the cell. Receptors de órganos es importante para mejorar el éxito de un trasplante y reducir el riesgo de rechazo. La tipificación del antígeno leucocitario humano (HLA, por sus siglas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés) del tejido es fundamental para el trasplante de células madre hematopoyéticas y órganos sólidos, incluidos trasplantes de riñón, corazón, hígado, páncreas y pulmón.
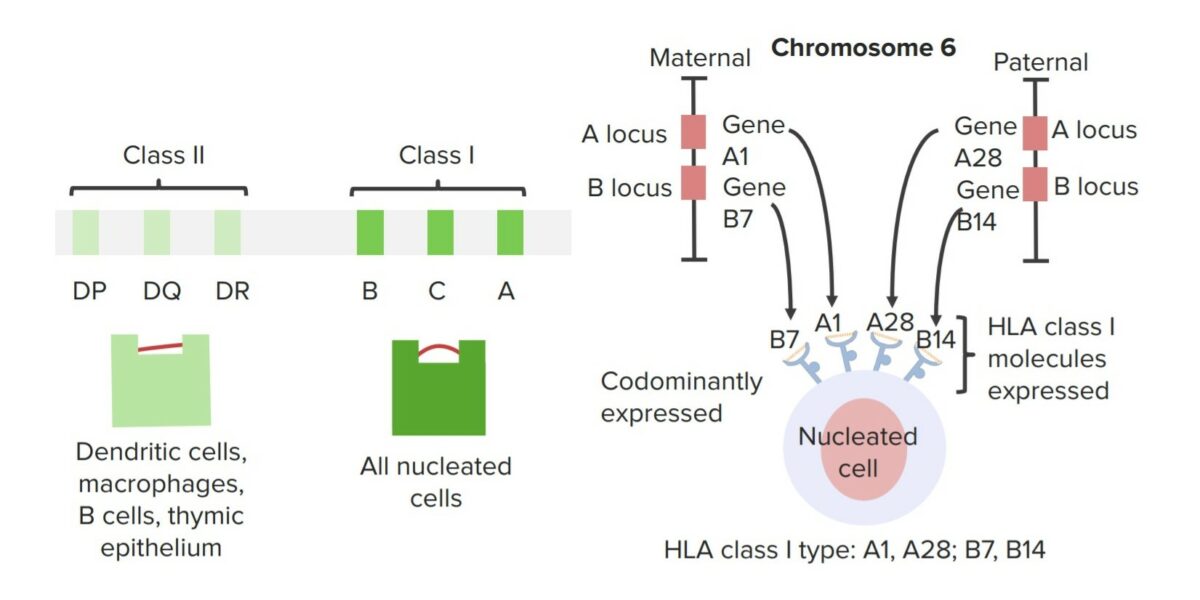
Complejo mayor de histocompatibilidad
Imagen por Lecturio.El rechazo puede ser agudo o crónico, y los LOS Neisseria síntomas varían según el sistema.
| Rechazo | Tiempo después del trasplante | Características del rechazo |
|---|---|---|
| Hiperagudo | Dentro de 48 horas |
|
| Acelerado | 3–5 días |
|
| Agudo | > 5 días |
|
| Crónica | Meses a años |
|
Los LOS Neisseria receptores de trasplantes de órganos sólidos deben tomar medicamentos inmunosupresores para evitar el rechazo del injerto. Los LOS Neisseria medicamentos inmunosupresores actuales tienen como objetivo la activación de los LOS Neisseria linfocitos T y la producción de citoquinas, la expansión clonal de los LOS Neisseria linfocitos T o ambas.
La escasez de órganos de donantes es un factor importante en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el trasplante hepático; muchas personas fallecen mientras esperan un órgano. Ahora se utilizan trasplantes de donantes vivos, en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria que solo se extrae una parte del hígado de un donante sano.
Complicaciones:
Complicaciones de la inmunosupresión:
Inmunización para personas postrasplantadas/inmunosuprimidas:
Rechazo:
Otras complicaciones:
Se puede ofrecer un trasplante cardíaco a personas que tienen síntomas intolerables a pesar de la terapia médica óptima y que corren el riesgo de morir debido a una enfermedad cardíaca.