Rinovirus es un virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology de ácido ribonucleico (ARN) de sentido positivo, lábil en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum medio ácido, de la familia Picornavirus. El virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology, que causa el resfriado común, se adquiere con mayor frecuencia a través de las vías respiratorias mediante la inhalación de aerosoles, que contienen rinovirus, y fómites. Debido a que el ácido gástrico inactiva el rinovirus, el virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology solo puede afectar la mucosa nasal y la conjuntiva, causando edema Edema Edema is a condition in which excess serous fluid accumulates in the body cavity or interstitial space of connective tissues. Edema is a symptom observed in several medical conditions. It can be categorized into 2 types, namely, peripheral (in the extremities) and internal (in an organ or body cavity). Edema de los LOS Neisseria tejidos subepiteliales y provocando el resfriado común 1–3 días después de la transmisión. El diagnóstico es clínico y la enfermedad suele ser leve y autolimitada. El tratamiento es de soporte y puede incluir una mayor ingesta de líquidos, antiinflamatorios no esteroideos (AINE) y descongestionantes nasales.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025

Identificación de los virus ARN:
Los virus pueden clasificarse de muchas maneras. La mayoría de los virus tienen un genoma formado por ácido desoxirribonucleico (ADN) o ARN. Los virus del genoma de ARN se pueden caracterizar además por un ARN de cadena simple o doble. Los virus “envueltos” están cubiertos por una fina capa de membrana celular (normalmente tomada de la célula huésped). Si la envoltura está ausente, los virus se denominan “desnudos”. Los virus con genomas monocatenarios son virus de “sentido positivo” si el genoma se emplea directamente como ARN mensajero (ARNm), que se traduce en proteínas. Los virus monocatenarios de “sentido negativo” emplean ARN polimerasa dependiente de ARN, una enzima viral, para transcribir el genoma en ARNm.
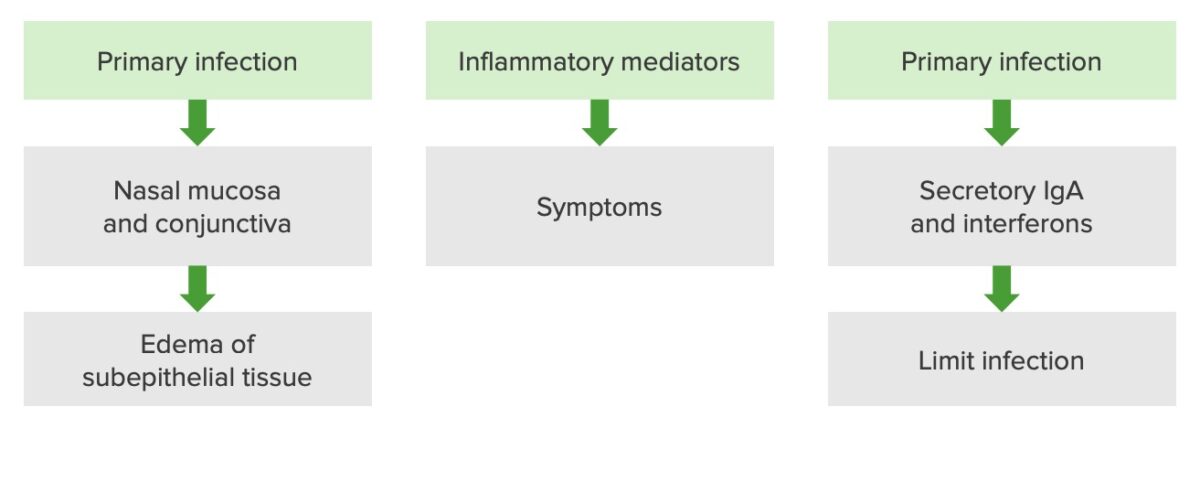
Fisiopatología de una infección por rinovirus
Imagen por Lecturio. Licencia: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0| Síntoma | Coronavirus Coronavirus Coronaviruses are a group of related viruses that contain positive-sense, single-stranded RNA. Coronavirus derives its name from “κορώνη korṓnē” in Greek, which translates as “crown,” after the small club-shaped proteins visible as a ring around the viral envelope in electron micrographs. Coronavirus ( COVID-19 COVID-19 Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is an infectious disease caused by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) that mainly affects the respiratory system but can also cause damage to other body systems (cardiovascular, gastrointestinal, renal, and central nervous systems). ) | Virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology de la influenza Influenza Influenza viruses are members of the Orthomyxoviridae family and the causative organisms of influenza, a highly contagious febrile respiratory disease. There are 3 primary influenza viruses (A, B, and C) and various subtypes, which are classified based on their virulent surface antigens, hemagglutinin (HA) and neuraminidase (NA). Influenza typically presents with a fever, myalgia, headache, and symptoms of an upper respiratory infection. Influenza Viruses/Influenza (gripe) | Rinovirus (resfriado común) | Alergias estacionales |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fiebre | A menudo | A menudo | Raro | Raro |
| Fatiga | A menudo | A menudo | Algunas veces | A menudo |
| Tos TOS Thoracic outlet syndrome (TOS) is a broad term used for a spectrum of syndromes related to the general region of the thoracic outlet, which involves the compression or irritation of elements of the brachial plexus, subclavian artery, or subclavian vein. Thoracic Outlet Syndrome | A menudo | A menudo | Algunas veces | A menudo |
| Estornudos | Raro | No | A menudo | A menudo |
| Mialgias | Algunas veces | A menudo | Algunas veces | No |
| Rinorrea o congestión nasal | Raro | Algunas veces | A menudo | A menudo |
| Dolor Dolor Inflammation de garganta | Algunas veces | Algunas veces | A menudo | No |
| Diarrea | Raro | Algunas veces | No | No |
| Cefalea | Algunas veces | A menudo | A menudo | Algunas veces |
| Disnea | A menudo | Raro | Raro | Raro |
| Pérdida del gusto y el olfato | A menudo | Raro | Algunas veces | Raro |