Los LOS Neisseria ortopoxvirus son un género de virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology grandes de ácido desoxirribonucleico (ADN) de doble cadena con forma de ladrillo. Existen varias especies clínicamente relevantes, como el virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology variola (causante de la viruela), virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology de la viruela símica (causante de la mpox), virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology vaccinia Vaccinia The cutaneous and occasional systemic reactions associated with vaccination using smallpox (variola) vaccine. Orthopoxvirus y el virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology de la viruela bovina. La transmisión varía en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum función de la especie, pero puede producirse por contacto con secreciones corporales infectadas, lesiones cutáneas o fómites. La viruela es la enfermedad más grave, que se presenta con síntomas constitucionales y una erupción maculopapular Maculopapular Dermatologic Examination difusa y bien circunscrita que progresa a través de un proceso evolutivo que da lugar a cicatrices. La viruela está asociada a una alta tasa de mortalidad. La mpox se presenta de forma similar, pero tiene una menor mortalidad y se asocia a linfadenopatías. El virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology vaccinia Vaccinia The cutaneous and occasional systemic reactions associated with vaccination using smallpox (variola) vaccine. Orthopoxvirus y la viruela bovina producen una enfermedad más leve con lesiones localizadas que se adquieren por contacto directo con la piel. Estas infecciones se diagnostican con la ayuda de la reacción en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum cadena de polimerasa ( PCR PCR Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a technique that amplifies DNA fragments exponentially for analysis. The process is highly specific, allowing for the targeting of specific genomic sequences, even with minuscule sample amounts. The PCR cycles multiple times through 3 phases: denaturation of the template DNA, annealing of a specific primer to the individual DNA strands, and synthesis/elongation of new DNA molecules. Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR), por sus siglas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés), serología, cultivo viral y/o microscopía electrónica. No se conocen tratamientos para estas enfermedades, y el tratamiento es generalmente de soporte. La vacunación ha HA Hemolytic anemia (HA) is the term given to a large group of anemias that are caused by the premature destruction/hemolysis of circulating red blood cells (RBCs). Hemolysis can occur within (intravascular hemolysis) or outside the blood vessels (extravascular hemolysis). Hemolytic Anemia permitido erradicar la viruela.
Last updated: Feb 11, 2025
Identificación de virus de ADN:
Los virus pueden clasificarse de muchas maneras. Sin embargo, la mayoría de los virus tienen un genoma formado por ADN o ácido ribonucleico (ARN). Los virus con un genoma de ADN pueden caracterizarse además como de cadena simple o doble. Los virus “envueltos” están cubiertos por una fina capa de membrana celular, que suele tomarse de la célula huésped. Sin embargo, si la capa está ausente, los virus se denominan “desnudos”. Algunos virus con envoltura traducen el ADN en ARN antes de incorporarse al genoma de la célula huésped.
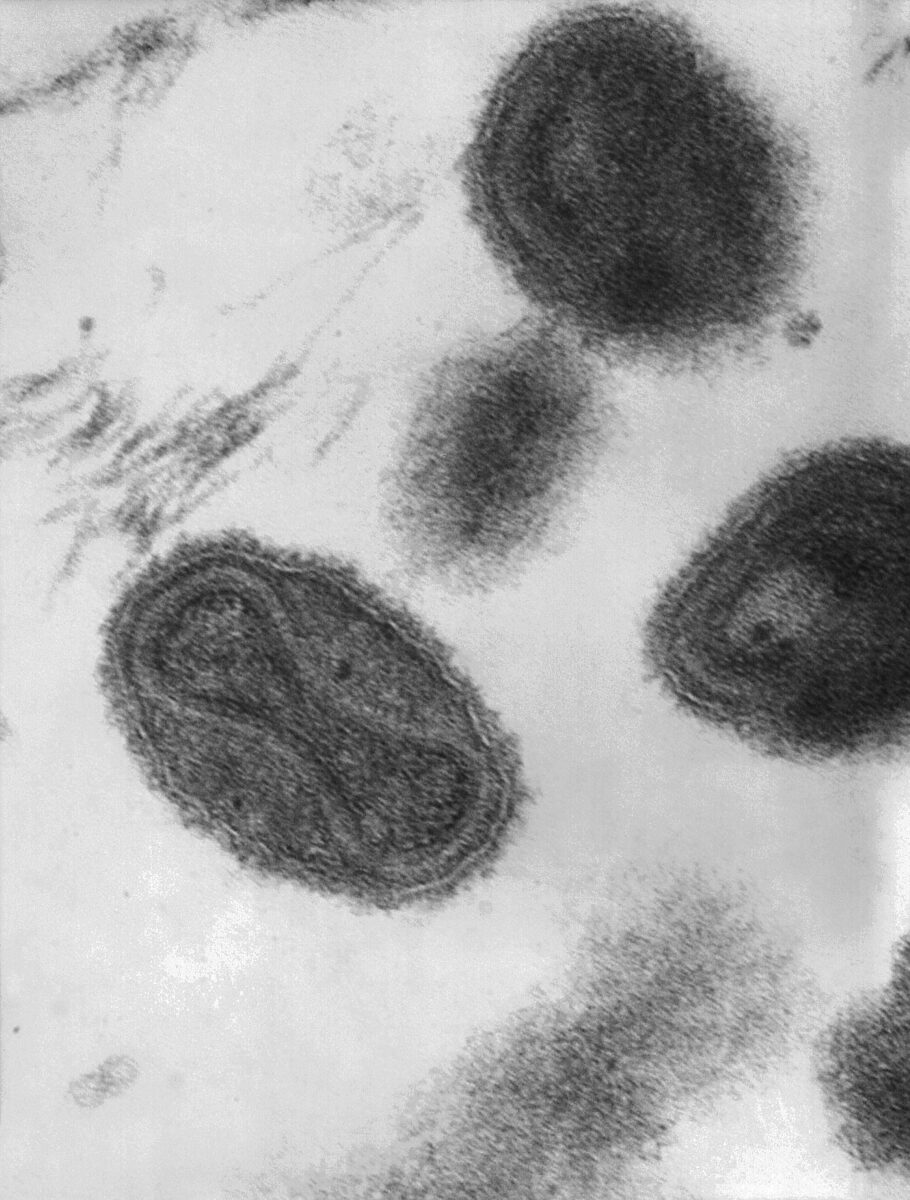
Esta micrografía electrónica de transmisión muestra un número de viriones de viruela:
La estructura en forma de campana dentro del virión es el núcleo viral, que contiene el ADN viral.
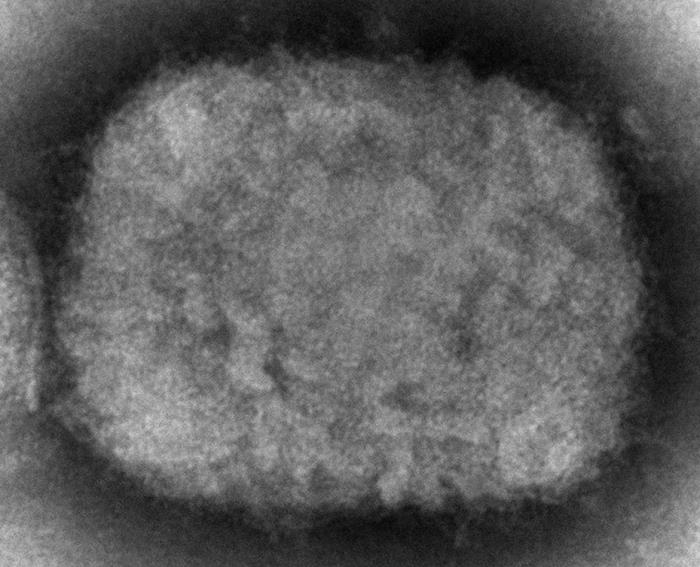
Imagen de microscopía electrónica de transmisión que muestra un virión de viruela símica:
Esta imagen de tinción negativa muestra una única partícula con forma de ladrillo cubierta de filamentos verticales.
Entre los LOS Neisseria ortopoxvirus más destacados que infectan a los LOS Neisseria seres humanos se encuentran:
| Virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology | Reservorio | Transmisión |
|---|---|---|
| Viruela | Humanos |
|
| Viruela símica | Desconocido (quizás pequeños roedores) |
|
| Vaccinia Vaccinia The cutaneous and occasional systemic reactions associated with vaccination using smallpox (variola) vaccine. Orthopoxvirus | Desconocido | Contacto piel con piel (a menudo de los LOS Neisseria recién vacunados) |
| Viruela bovina | Roedores | Contacto directo con animales infectados (a menudo vacas, gatos) |
La enfermedad más severa tiende a ocurrir en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum:
La siguiente tabla resume las enfermedades clínicas más destacadas causadas por ortopoxvirus:
| Enfermedad | Incubación | Síntomas constitucionales | Erupción |
|---|---|---|---|
| Viruela | 7–19 días |
|
|
| Mpox | 5–21 días |
|
|
| Vaccinia Vaccinia The cutaneous and occasional systemic reactions associated with vaccination using smallpox (variola) vaccine. Orthopoxvirus | 2–4 días |
|
|
| Viruela bovina | 2–4 días |
|
|
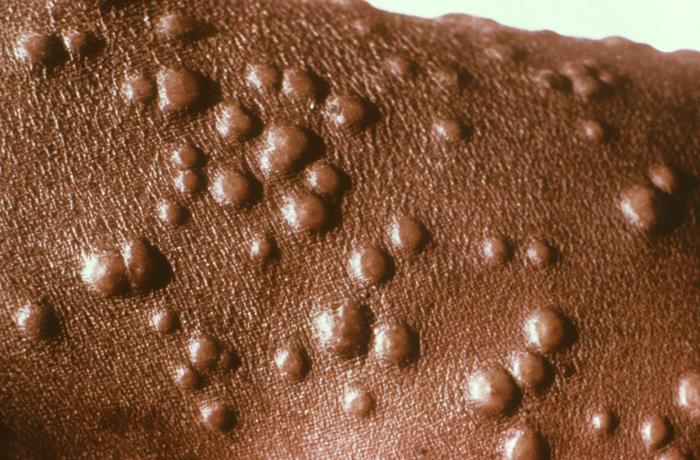
Erupción papular característica que se extiende por la piel del cuello y la parte superior de la espalda en un paciente con viruela
Imagen: “Young patient had been infected with the smallpox virus” por CDC/ Dr. Paul B. Dean. Licencia: Dominio Público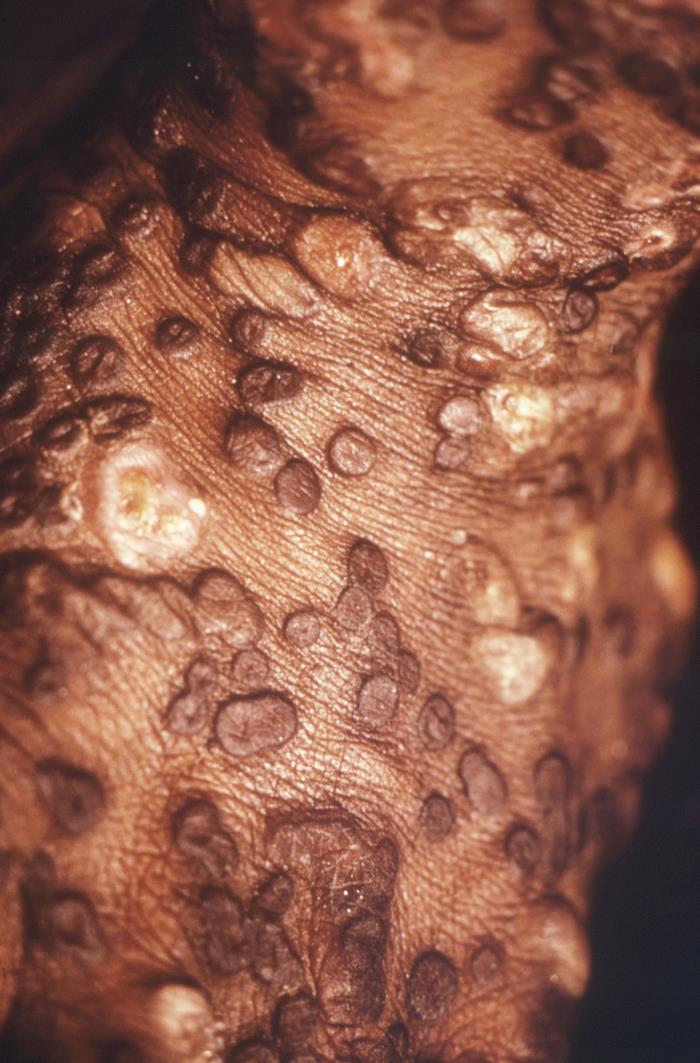
En este punto de la evolución de la enfermedad, las lesiones habían entrado en sus últimas fases de desarrollo, comenzando a formar costras.
Las costras se desprenden y dejan cicatrices cutáneas (en forma de numerosas marcas de viruela).
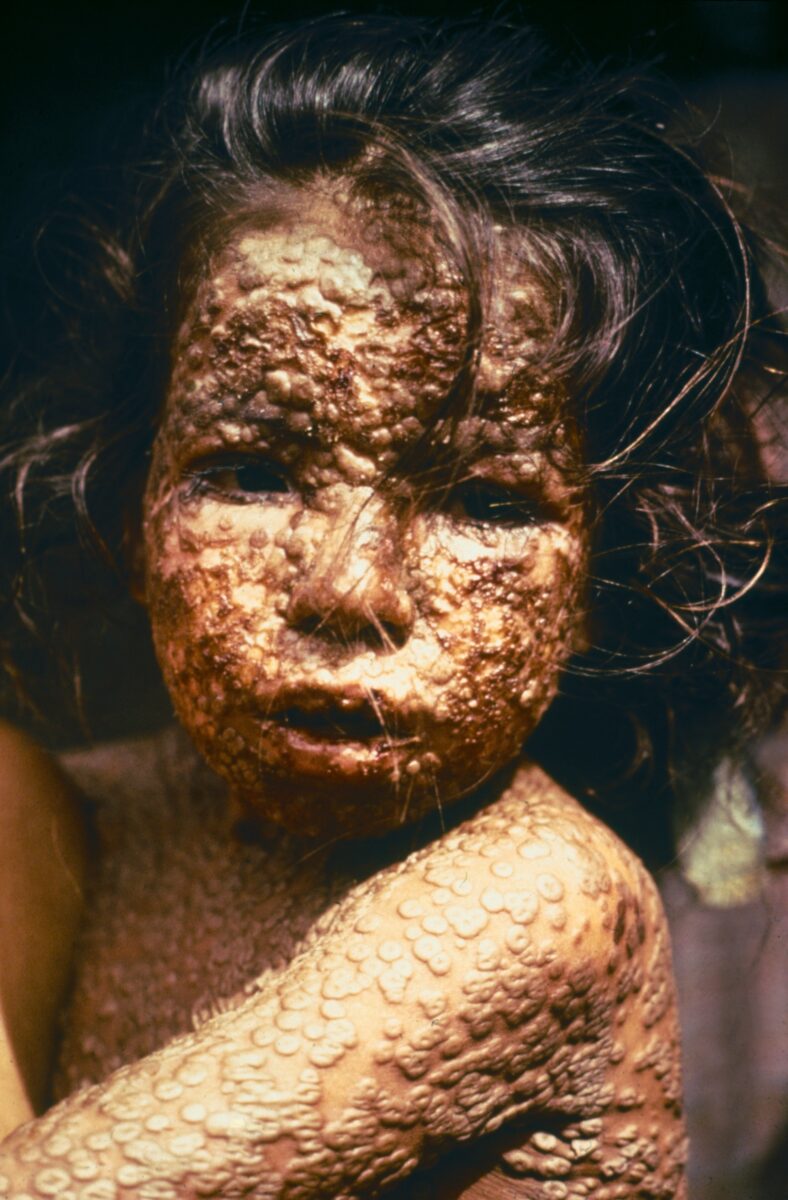
Niña infectada de viruela
Imagen: “This young girl in Bangladesh was infected with smallpox in 1973” por CDC/ James Hicks. Licencia: Dominio Público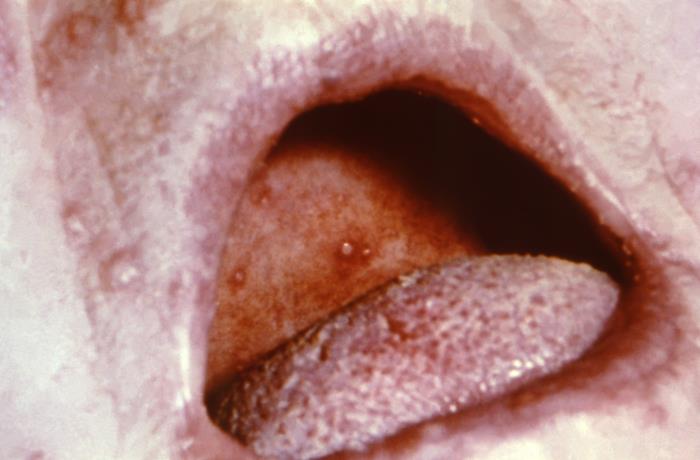
Vista intraoral de un cultivo semiconfluyente de vesículas maculopapulares que apareció durante las primeras etapas de la viruela
Imagen: “This intraoral view depicted the palatal mucosa of a 53-year-old female” por CDC/ Dr. R. Robinson. Licencia: Dominio Público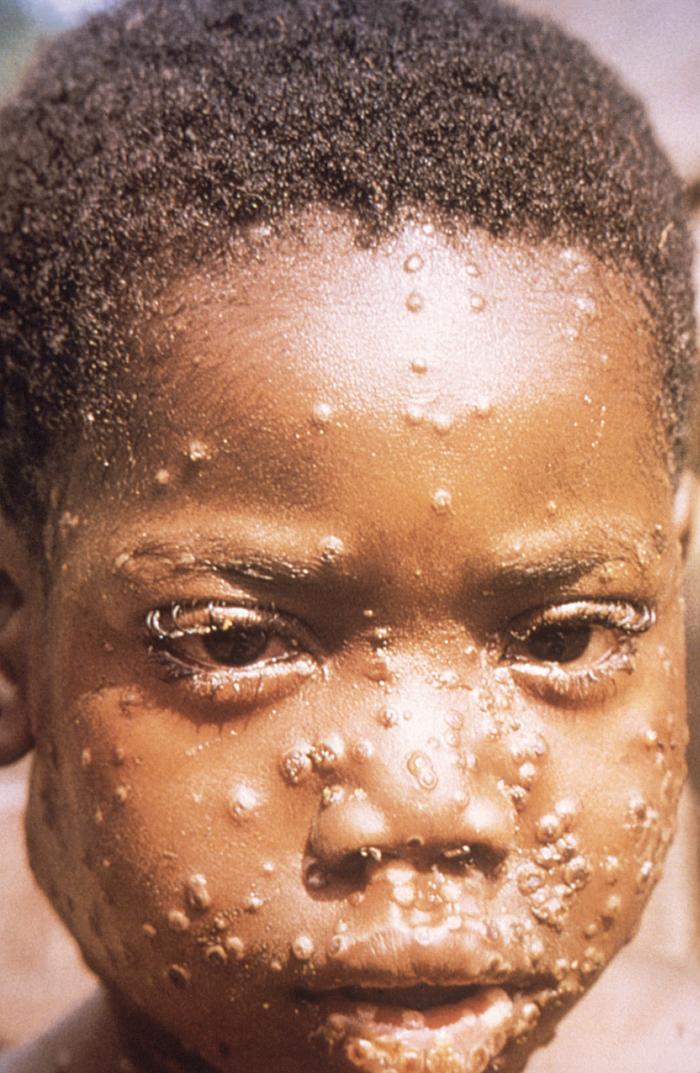
Niño con la característica erupción cutánea maculopapular de la viruela símica, que se asemeja a la erupción causada por el virus de la viruela
Imagen: “This 1997 image was created during an investigation into an outbreak of monkeypox, which took place in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), formerly Zaire” por la Organización Mundial de la Salud (OMS)/ Brian W.J. Mahy. Licencia: Dominio Público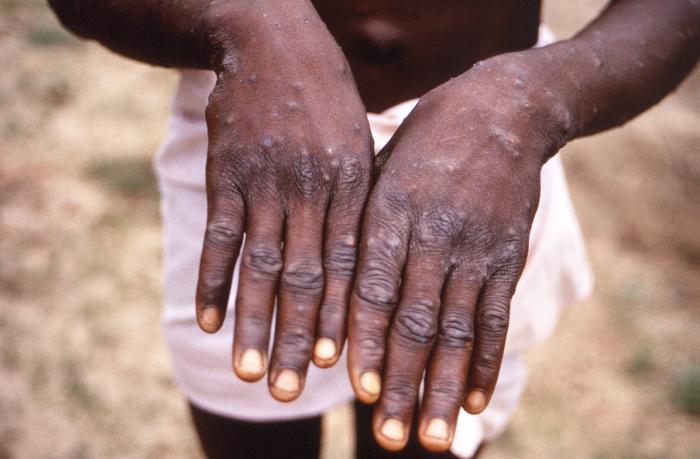
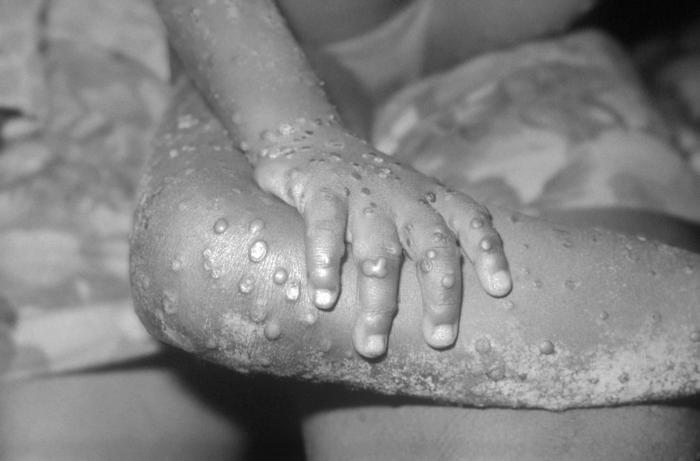
Numerosas lesiones maculopapulares de viruela símica en una paciente joven.
Imagen: “This image from 1971, depicts a view of the right hand and leg, of a 4-year-old female in Bondua, Grand Gedeh County, Liberia” por CDC. Licencia: Dominio Público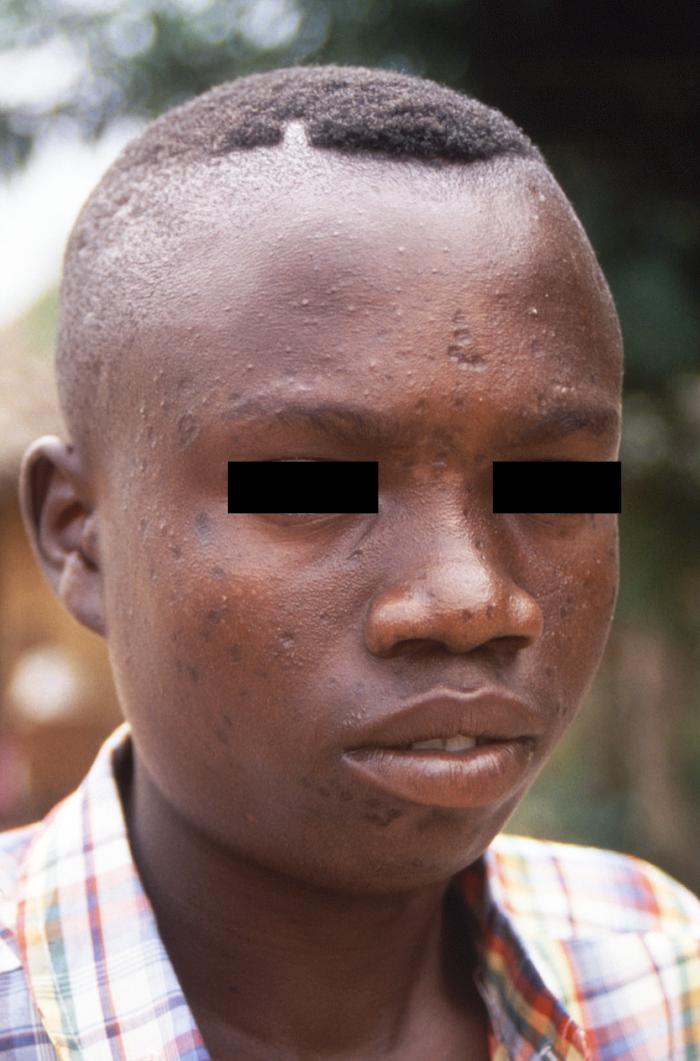
El rostro de un joven que se ha recuperado de un caso de viruela símica, con las cicatrices permanentes de las viruelas en su piel
Imagen: “This 1997 image was created during an investigation into an outbreak of monkeypox, which took place in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), formerly Zaire” por la Organización Mundial de la Salud (OMS)/ Brian W.J. Mahy. Licencia: Dominio Público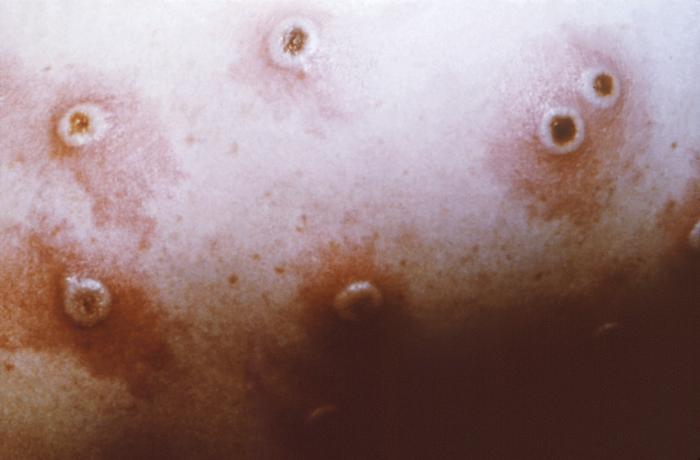
Varón de 20 años que fue inoculado accidentalmente y de forma heterogénea con vaccinia tras haber llevado un jersey que había sido usado por un amigo recién vacunado.
Imagen: “This 1962 photograph depicted a close view of the skin of a 20-year-old male who was accidentally, heterogeneously inoculated with vaccinia, after having worn a jersey that had been worn by a newly vaccinated friend” por CDC/ Dr. R. Robinson. Licencia: Dominio Público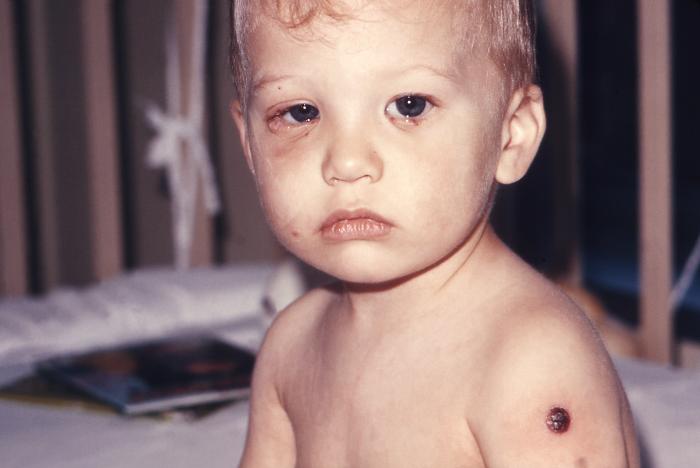
Un niño de 21 meses que desarrolló una infección facial secundaria por vaccinia (tras la vacunación contra la viruela) que afectaba a ambos ojos y a las zonas periorbitales bilaterales
Imagen: “A post-smallpox vaccination complication, this 21-month-old male infant developed a secondary facial vaccinial infection involving both eyes, and bilateral periorbital areas” por CDC. Licencia: Dominio Público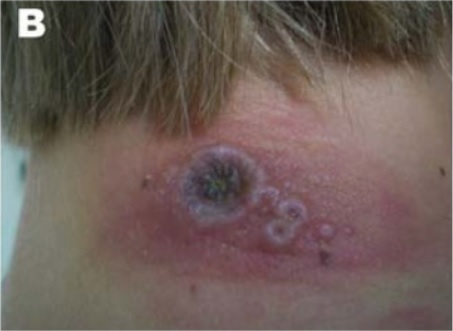
Lesiones en el cuello de una niña que contrajo la viruela bovina
Imagen: “Clinical presentation of cowpox lesions on rats and humans during an outbreak in Germany, 2009” por Reynolds MG et al. Licencia: CC CY 3.0, recortado por LecturioEl diagnóstico puede apoyarse con las siguientes pruebas:
La vacuna contra la viruela no solo es responsable de la erradicación de la viruela, sino también: