Los LOS Neisseria meningiomas son tumores de crecimiento lento que surgen de las meninges Meninges The brain and the spinal cord are enveloped by 3 overlapping layers of connective tissue called the meninges. The layers are, from the most external layer to the most internal layer, the dura mater, arachnoid mater, and pia mater. Between these layers are 3 potential spaces called the epidural, subdural, and subarachnoid spaces. Meninges: Anatomy del cerebro y la médula espinal. La gran mayoría son benignos. Estos tumores suelen aparecer en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum individuos con antecedentes de dosis altas de radiación craneal, traumatismos craneales y neurofibromatosis tipo 2. Los LOS Neisseria síntomas clínicos del meningioma Meningioma Meningiomas are slow-growing tumors that arise from the meninges of the brain and spinal cord. The vast majority are benign. These tumors commonly occur in individuals with a history of high doses of skull radiation, head trauma, and neurofibromatosis 2. Meningioma dependen de la localización y la progresión del tumor Tumor Inflammation y una gran proporción de los LOS Neisseria meningiomas son asintomáticos. Cuando los LOS Neisseria síntomas se desarrollan, lo más común es que incluyan cefalea, convulsiones, alteraciones visuales y otros déficits neurológicos focales. El diagnóstico se realiza a partir de la neuroimagenología (la resonancia magnética es el estándar de oro) y la biopsia. El tratamiento consiste en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la vigilancia de los LOS Neisseria pacientes asintomáticos y en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el caso de los LOS Neisseria sintomáticos, es la resección quirúrgica. En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum algunos casos también se utiliza la radiación.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Un meningioma Meningioma Meningiomas are slow-growing tumors that arise from the meninges of the brain and spinal cord. The vast majority are benign. These tumors commonly occur in individuals with a history of high doses of skull radiation, head trauma, and neurofibromatosis 2. Meningioma es un tumor Tumor Inflammation de crecimiento lento que surge de las meninges Meninges The brain and the spinal cord are enveloped by 3 overlapping layers of connective tissue called the meninges. The layers are, from the most external layer to the most internal layer, the dura mater, arachnoid mater, and pia mater. Between these layers are 3 potential spaces called the epidural, subdural, and subarachnoid spaces. Meninges: Anatomy del cerebro y la médula espinal.
| Categorías | Tumores específicos |
|---|---|
| Tumores neuroepiteliales en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el SNC |
|
| Tumores meníngeos |
|
| Tumores de la región selar |
|
| Otros tumores primarios del SNC | Linfoma primario del SNC |
| Metástasis al AL Amyloidosis cerebro (5 veces más común que los LOS Neisseria tumores cerebrales primarios) | Más comúnmente surgen de: |
| Tumores periféricos |
|
Los LOS Neisseria meningiomas son clasificados morfológicamente por la OMS en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum 3 grados:
No se han establecido las causas del meningioma Meningioma Meningiomas are slow-growing tumors that arise from the meninges of the brain and spinal cord. The vast majority are benign. These tumors commonly occur in individuals with a history of high doses of skull radiation, head trauma, and neurofibromatosis 2. Meningioma. Sin embargo, se han identificado ciertos factores de alto riesgo para causar meningiomas:
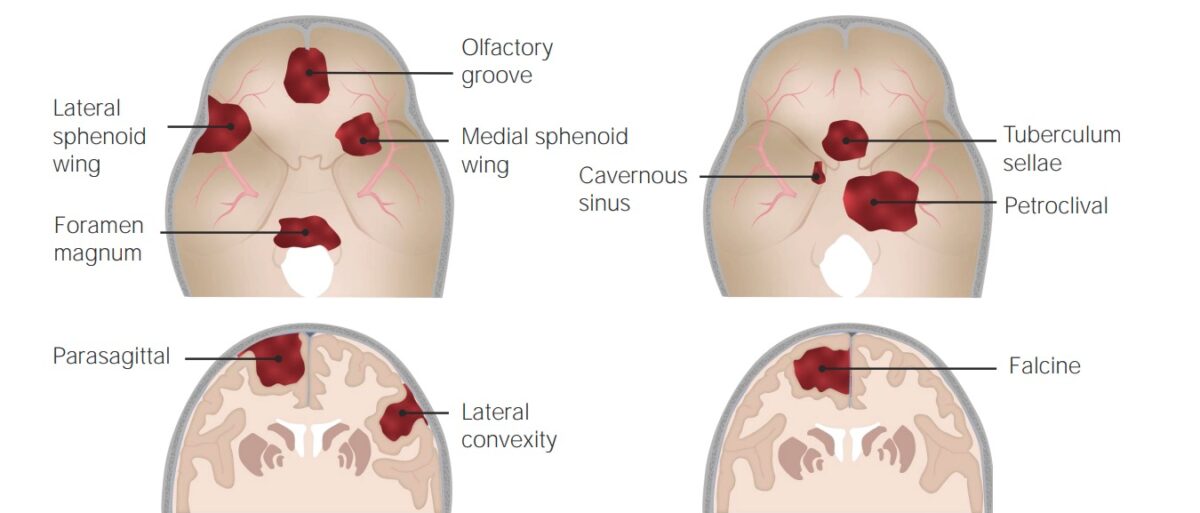
Localizaciones habituales de aparición de los meningiomas
Imagen por Lecturio. Licencia: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0Los LOS Neisseria meningiomas suelen surgir de las células aracnoideas cercanas a los LOS Neisseria senos venosos. A medida que el tumor Tumor Inflammation se agranda, puede causar síntomas debido a:
Algunos pacientes son asintomáticos. Para los LOS Neisseria pacientes sintomáticos, la presentación clínica de los LOS Neisseria meningiomas depende de la localización del tumor Tumor Inflammation.
Los LOS Neisseria estudios de laboratorio son de poca utilidad en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el diagnóstico de los LOS Neisseria meningiomas; la imagenología es una herramienta diagnóstica más útil. Se requiere una biopsia para confirmar el diagnóstico.
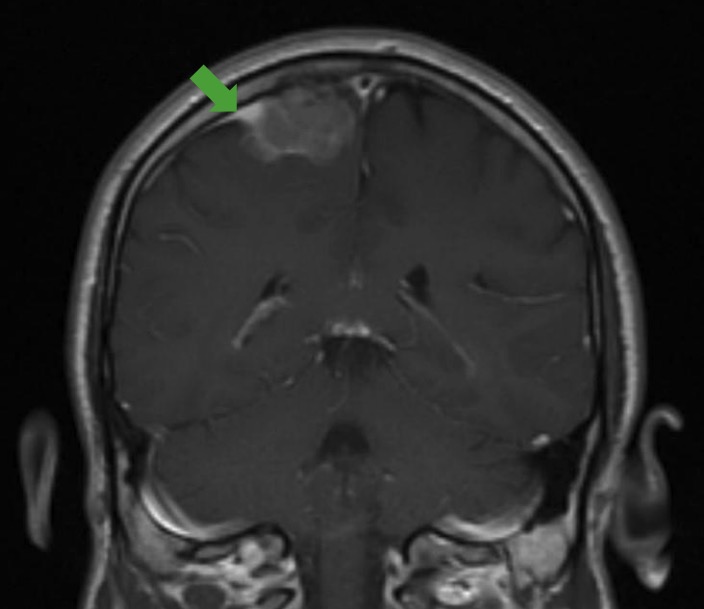
Signo de la cola dural:
RM que muestra el signo clásico de la cola dural (flecha verde), que puede verse en los estudios de imagen de un meningioma.
La biopsia proporciona un diagnóstico definitivo. Los LOS Neisseria hallazgos histológicos incluyen:
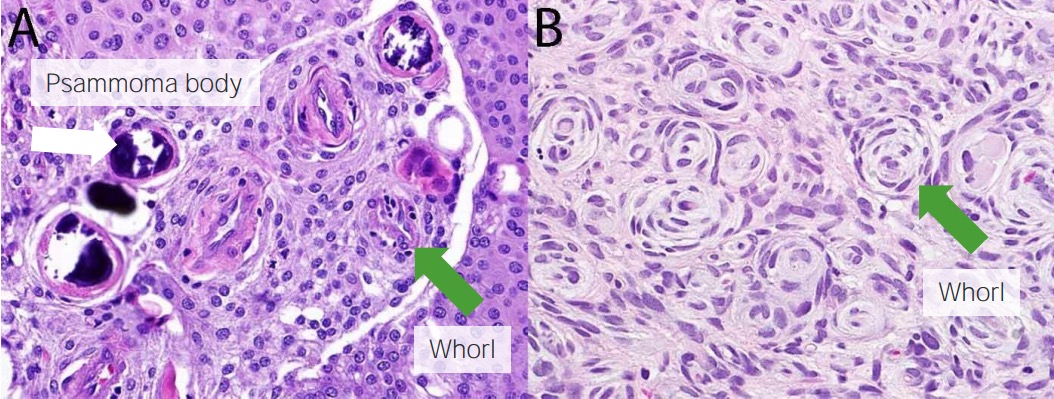
Histología del meningioma:
Se observan cuerpos de psamoma (flecha blanca) y verticilos (flechas verdes).
La mayoría de los LOS Neisseria meningiomas pueden estar bajo observación, al AL Amyloidosis menos de manera inicial.
| Grado | Extensión de la resección | Riesgo de recurrencia (intervalo de 10 años) |
|---|---|---|
| I | Extirpación macroscópica completa del tumor Tumor Inflammation, de los LOS Neisseria huesos implicados, de los LOS Neisseria senos venosos y de la cola dural | 9% |
| II | Extirpación macroscópica completa del tumor Tumor Inflammation, coagulación de la cola dural | 19% |
| III | Extirpación macroscópica completa del tumor Tumor Inflammation, resección de la cola dural | 29% |
| IV | Extirpación parcial del tumor Tumor Inflammation, sin resección de la cola dural | 44% |
| V | Descompresión simple, sin resección de la cola dural | 100% |
| Grado | Tipo de cirugía | Necesidad de radioterapia |
|---|---|---|
| OMS grado I | Resección total macroscópica | Observación |
| Resección subtotal | Observación contra radioterapia | |
| No hay cirugía | Radioterapia | |
| Grado II de la OMS | Resección total macroscópica | Observación contra radioterapia |
| Resección subtotal | Radioterapia | |
| Grado III de la OMS | Cualquier cirugía | Radioterapia |