La médula ósea, lugar principal de la hematopoyesis, se encuentra en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las cavidades de los LOS Neisseria huesos esponjosos y en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria canales medulares de los LOS Neisseria huesos largos. Existen dos tipos: la médula roja (hematopoyética con abundantes células sanguíneas) y la médula amarilla (con predominio de adipocitos). La composición de la médula humana cambia con la edad. En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria jóvenes, toda la médula ósea es roja, ya que hay una mayor producción de células sanguíneas. A medida que aumenta la edad, se produce un cambio gradual a la variedad de médula amarilla. La médula amarilla puede revertirse en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum médula roja cuando la hematopoyesis es necesaria (e.g., anemia Anemia Anemia is a condition in which individuals have low Hb levels, which can arise from various causes. Anemia is accompanied by a reduced number of RBCs and may manifest with fatigue, shortness of breath, pallor, and weakness. Subtypes are classified by the size of RBCs, chronicity, and etiology. Anemia: Overview and Types). La médula roja, por hematopoyesis, produce unos 6 mil millones de células por kilogramo por día. El proceso se basa en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum que las células hematopoyéticas (células madre y progenitoras) producen células efectoras maduras (linfocitos, plaquetas, granulocitos, eritrocitos) con la ayuda de elementos no hematopoyéticos. La producción está regulada por las citoquinas liberadas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el entorno de la médula ósea y la retroalimentación de los LOS Neisseria tejidos diana. La estructura de la médula permite que la hematopoyesis tenga lugar en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la zona extravascular y, tras una diferenciación por etapas, las células sanguíneas se liberan a la circulación.
Last updated: Mar 27, 2025
La médula ósea es el tejido esponjoso que se encuentra en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria canales medulares de los LOS Neisseria huesos largos y en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las cavidades de los LOS Neisseria huesos esponjosos.
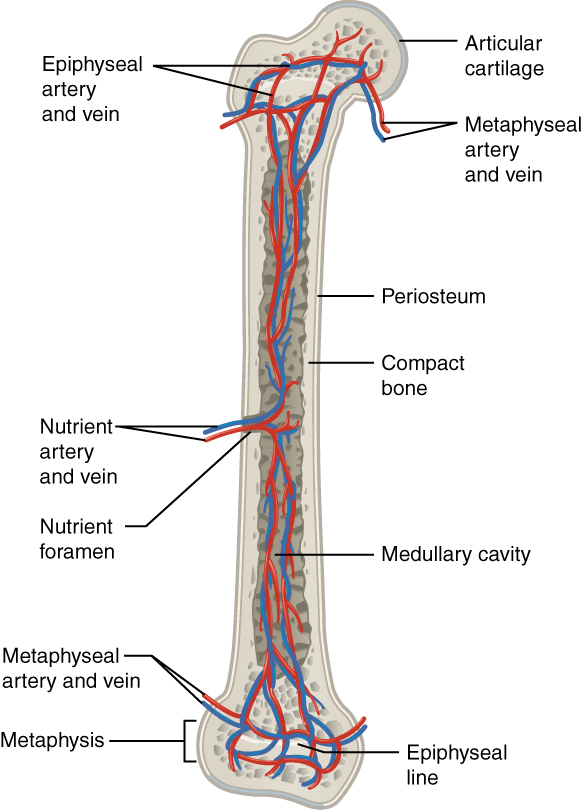
La imagen muestra la irrigación sanguínea (arteria y vena)
Imagen: “609 Body Supply to the Bone” por OpenStax College. Licencia: CC BY 3.0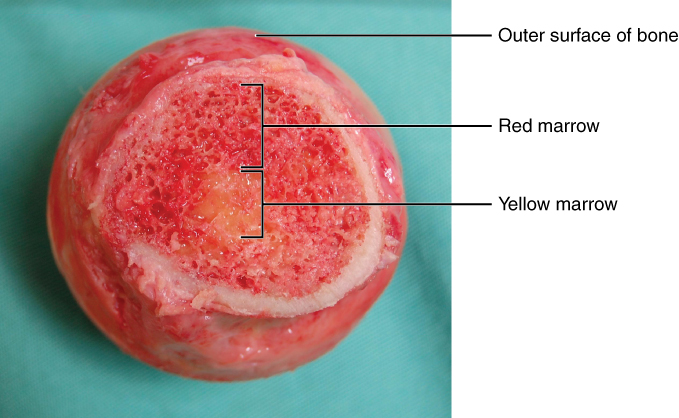
La médula ósea:
Sección transversal que muestra las porciones de médula roja y amarilla del hueso
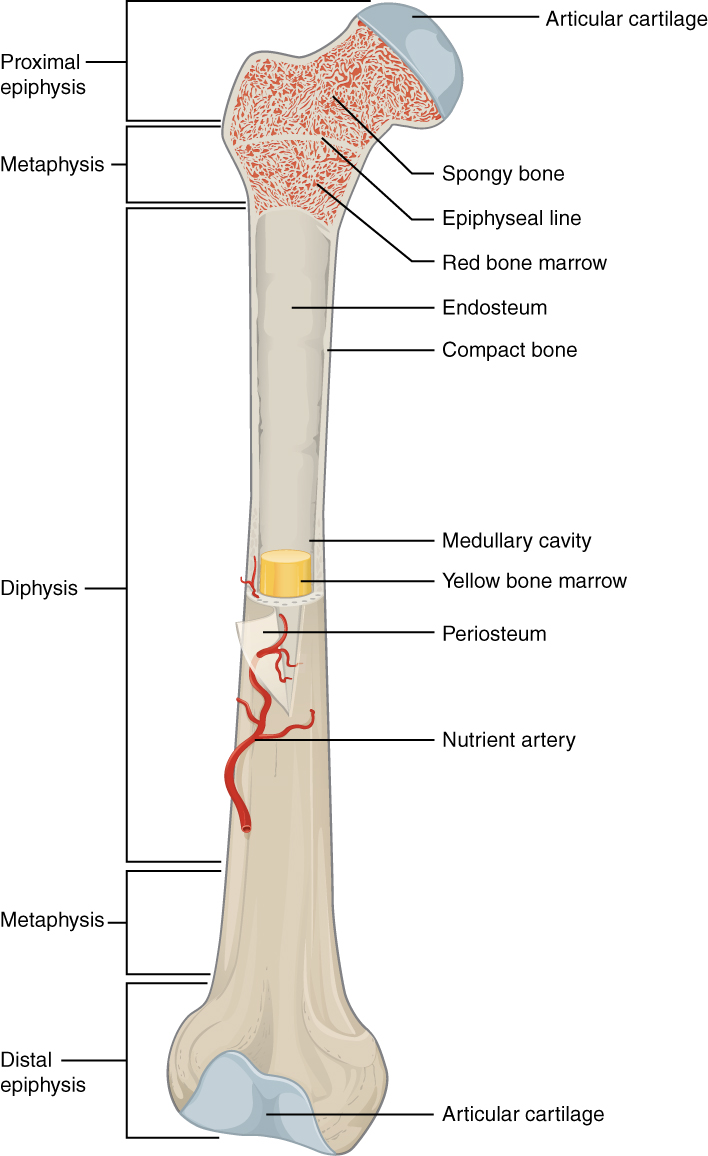
Médula ósea en el interior del fémur
Imagen: “603 Anatomy of Long Bone” por OpenStax College. License: CC BY 3.0Estructuras que proporcionan un microambiente que favorece la diferenciación de las células hematopoyéticas y la proliferación de las células sanguíneas:
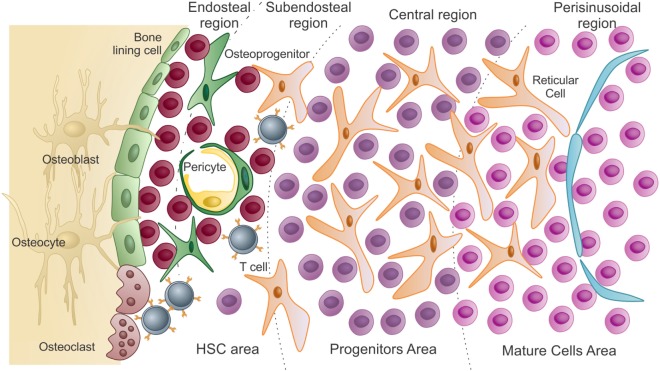
Presentación esquemática del microambiente de la médula ósea:
En la zona de las células madre hematopoyéticas se encuentran las células madre hematopoyéticas y células progenitoras no comprometidas. Están en estrecha asociación con los osteoblastos del endostio y las células de revestimiento óseo. A medida que las células madre hematopoyéticas salen de la quiescencia a los estados proliferativos, migran y colonizan la región subendostial y luego la región central de la médula (progenitores).
Las células diferenciadas llegan a la zona madura, más cerca de los sinusoides. Para ser liberadas a la circulación, estas células maduras atraviesan el endotelio (que recubre los sinusoides) por migración transcelular.
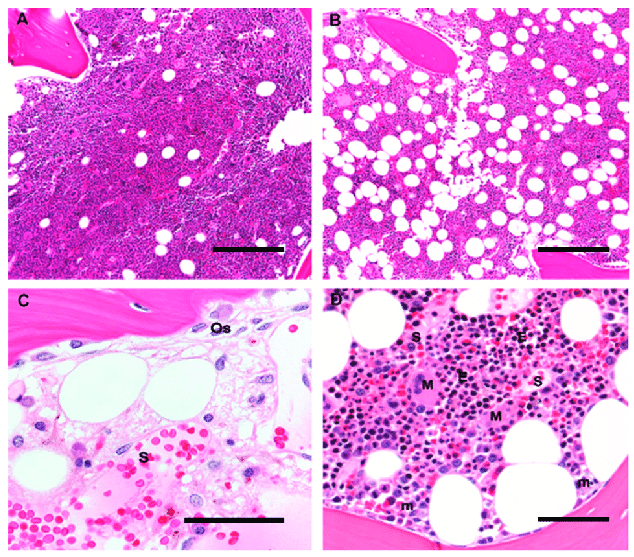
Arquitectura histológica de la médula ósea humana: Las imágenes muestran las diferentes células y estructuras que hay en la médula.
A y B: Aumento original 10×; barra de escala 100 μm
A: Una biopsia de médula ósea de un niño de 5 años es > 90% celular, con un predominio de hematopoyesis de los tres linajes y poco tejido adiposo mezclado.
B: Una biopsia de médula ósea de un adulto de 60 años está compuesta por un 50% de elementos hematopoyéticos y un 50% de tejido adiposo maduro mezclado.
C: Una médula postquimioterapia muestra hueso trabecular con osteoblastos (Os) superpuestos, y una delgada veta osteoide de colágeno no mineralizado. Los sinusoides (S) están llenos de eritrocitos y tienen células estromales con núcleos ovoides. Las células mononucleares dispersas incluyen células plasmáticas, mastocitos y macrófagos; aumento original 60×; barra de escala 25 μm
D: Las colonias eritroides (E) aparecen como colonias de células redondas con núcleos oscuros y se localizan lejos del hueso trabecular, cerca de los vasos sinusoidales de paredes finas (S); los megacariocitos (M) se localizan igualmente en estrecho contacto con los sinusoides, mientras que los precursores mieloides inmaduros (m) se localizan cerca del hueso trabecular. Aumento original 20×; barra de escala 50 μm
La hematopoyesis se inicia con una célula madre hematopoyética, a la que se incita a dividirse y diferenciarse con los LOS Neisseria estímulos químicos adecuados (factores de crecimiento hemopoyético).
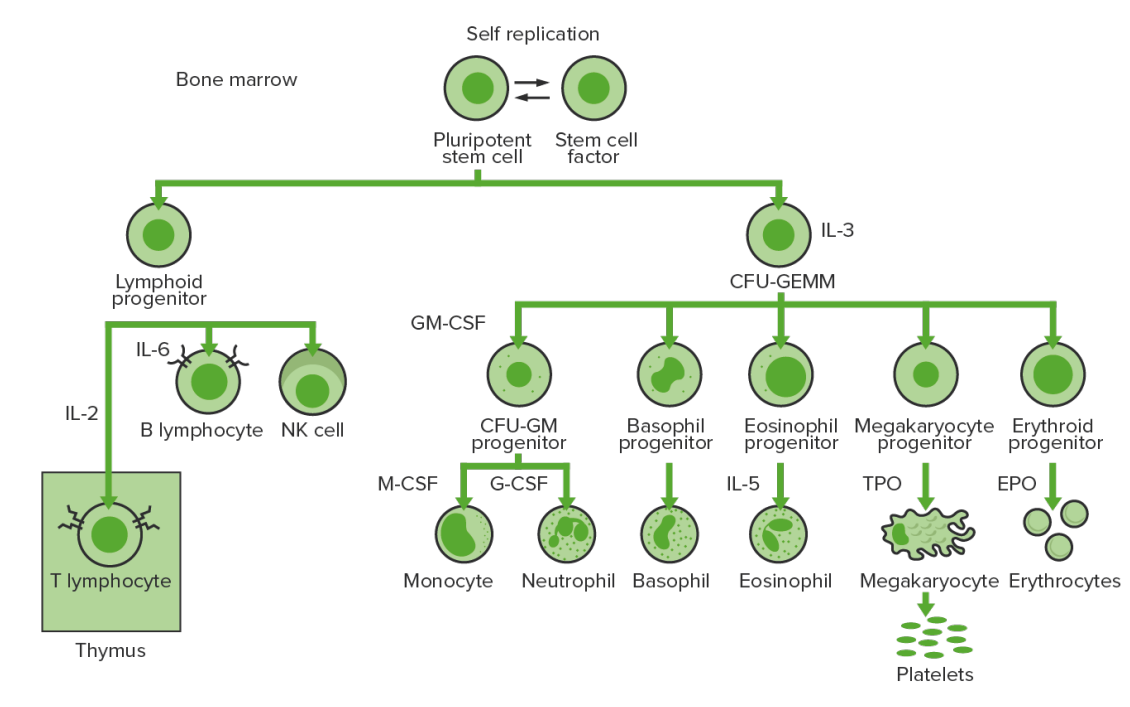
Hematopoyesis de la médula ósea: proliferación y diferenciación de los elementos formes de la sangre
CFU-GEMM: unidad formadora de colonias: granulocitos, eritrocitos, monocitos, megacariocitos
CFU-GM: unidad formadora de colonias: granulocitos-macrófagos
GM-CSF: factor estimulante de colonias de granulocitos y macrófagos
M-CSF: factor estimulante de colonias de macrófagos
G-CSF: factor estimulante de colonias de granulocitos
NK: asesino natural
TPO: trombopoyetina
| Citoquinas/factores de crecimiento | Actividades | Fuente |
|---|---|---|
| Eritropoyetina | Estimula la eritropoyesis, incluida la diferenciación |
|
| Trombopoyetina | Estimula la trombopoyesis |
|
| Factor de células madre | Estimula todas las células progenitoras hematopoyéticas | Células estromales de la médula ósea |
| Factor estimulante de colonias de granulocitos y macrófagos | Estimula las células progenitoras mieloides |
|
| Factor estimulante de colonias de granulocitos | Estimula las células precursoras de neutrófilos |
|
| Factor estimulante de colonias de monocitos | Estimula las células precursoras de monocitos |
|
| Interleuquina (IL) | Actividades | Fuente |
|---|---|---|
| IL-1 | Regulación de la secreción de citoquinas de muchos leucocitos |
|
| IL-2 | Linfocitos T colaboradores | |
| IL-3 | Mitógeno para todas las células progenitoras de granulocitos y megacariocitos/eritrocitos | Linfocitos T colaboradores |
| IL-4 | Linfocitos T colaboradores | |
| IL-5 | Desarrollo y activación de los LOS Neisseria eosinófilos | Linfocitos T colaboradores |
| IL-6 |
|
|
| IL-7 IL-7 A proinflammatory cytokine produced primarily by T-lymphocytes or their precursors. Several subtypes of interleukin-17 have been identified, each of which is a product of a unique gene. Severe Combined Immunodeficiency (SCID) | Estimulación de todas las células madre linfoides | Células estromales de la médula ósea |
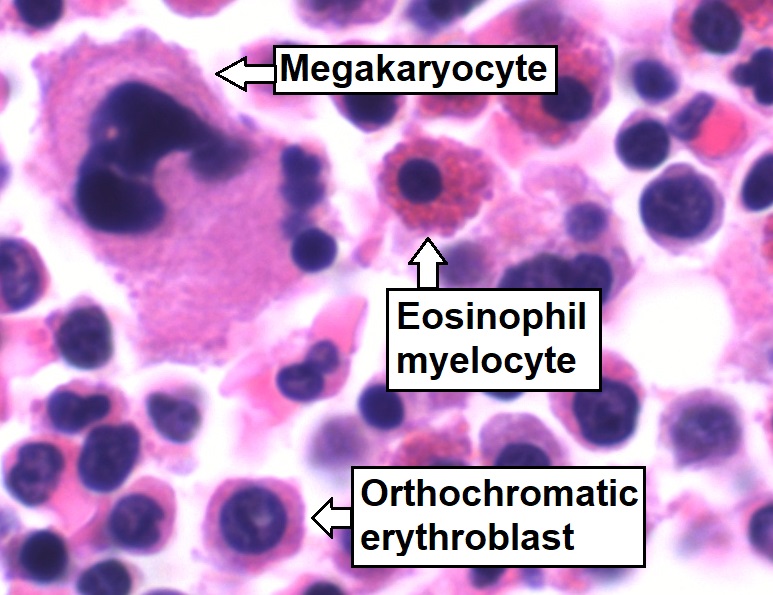
Aspirado de médula ósea que muestra una hematopoyesis de tres linajes normal: células mielomonocíticas (mielocito eosinófilo marcado), células eritroides (eritroblasto ortocromático marcado) y células megacariocíticas
Imagen: “Trilineage hematopoiesis” por Mikael Häggström. Licencia: CC0 1.0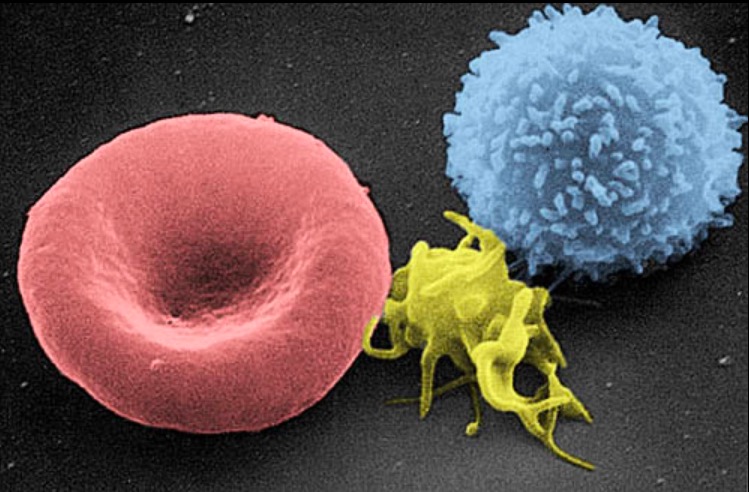
Imagen de micrografía electrónica de barrido de una célula sanguínea: de izquierda a derecha, un eritrocito humano, un trombocito (plaqueta) y un leucocito
Imagen: “Electron micrograph of blood cells” por Electron Microscopy Facility at The National Cancer Institute at Frederick. Licencia: Dominio Público