Aunque la fidelidad del ácido desoxirribonucleico (ADN) está muy protegida, este puede resultar dañado por una serie de factores ambientales, especies reactivas de oxígeno y errores en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la replicación del ADN. La reparación del ADN es un proceso continuo en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el que la célula corrige los LOS Neisseria daños. La célula tiene múltiples mecanismos que puede utilizar para reparar el ADN. Durante la replicación, la célula dispone de una maquinaria de revisión dentro de la propia ADN polimerasa. Para los LOS Neisseria daños de una sola cadena de ADN, la célula puede usar técnicas de reparación por escisión y fotorreparación. Para las roturas de ambas cadenas del ADN, la célula puede emplear la recombinación homóloga o la unión de extremos no homólogos. Cuando los LOS Neisseria procesos normales de reparación del ADN fallan debido a la edad, a una disfunción o a una sobrecarga del sistema, los LOS Neisseria daños en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el ADN no reparados pueden provocar apoptosis Apoptosis A regulated cell death mechanism characterized by distinctive morphologic changes in the nucleus and cytoplasm, including the endonucleolytic cleavage of genomic DNA, at regularly spaced, internucleosomal sites, I.e., DNA fragmentation. It is genetically-programmed and serves as a balance to mitosis in regulating the size of animal tissues and in mediating pathologic processes associated with tumor growth. Ischemic Cell Damage, senescencia celular o tumores malignos.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
El daño al AL Amyloidosis ADN puede ser causado por:
La revisión de errores se realiza durante la replicación del ADN. La ADN polimerasa (el complejo enzimático que replica el ADN):
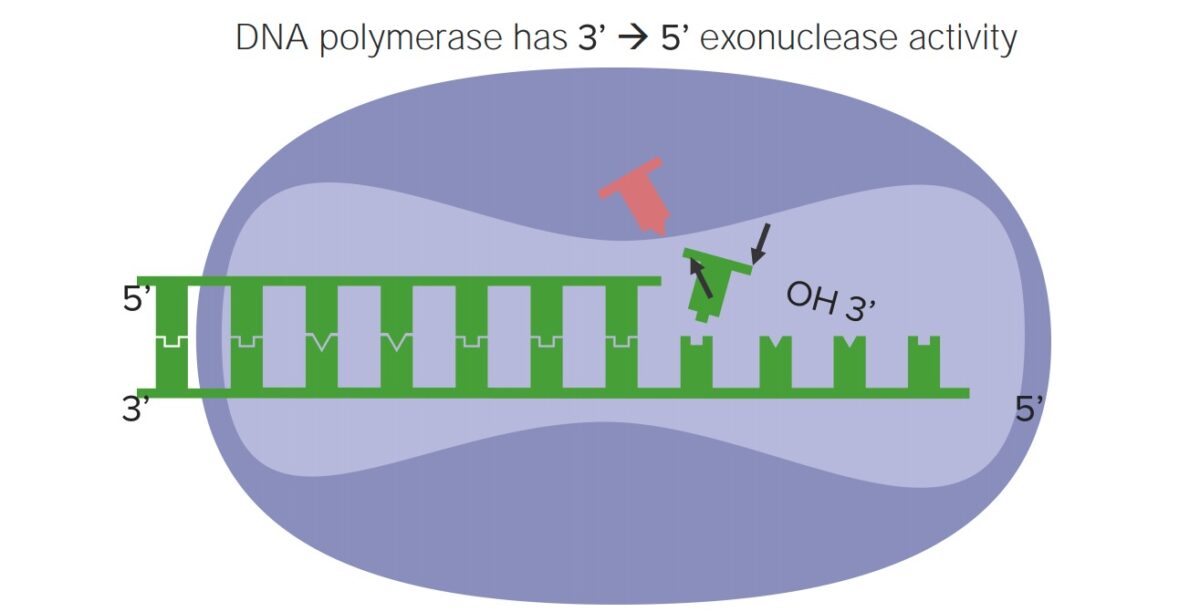
Actividad de revisión de errores de la ADN polimerasa
Imagen por Lecturio.La radiación de la luz UV hace HACE Altitude Sickness que se formen dímeros de pirimidina (T o C) a través de enlaces covalentes entre bases Bases Usually a hydroxide of lithium, sodium, potassium, rubidium or cesium, but also the carbonates of these metals, ammonia, and the amines. Acid-Base Balance adyacentes, creando un cambio conformacional (“abultamiento”) en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el ADN. Estos defectos pueden repararse mediante un proceso denominado fotoreparación o fotoreactivación.
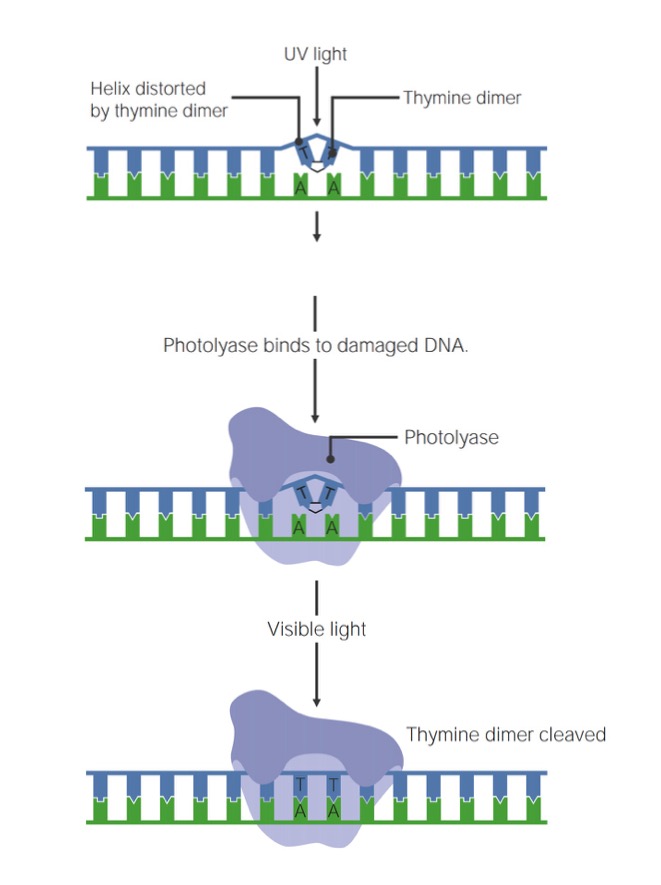
Pasos de la fotoreparación
Imagen por Lecturio.La célula dispone de 3 mecanismos principales para reparar los LOS Neisseria daños en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum una sola cadena de ADN:
Los LOS Neisseria 3 mecanismos siguen el mismo proceso general:
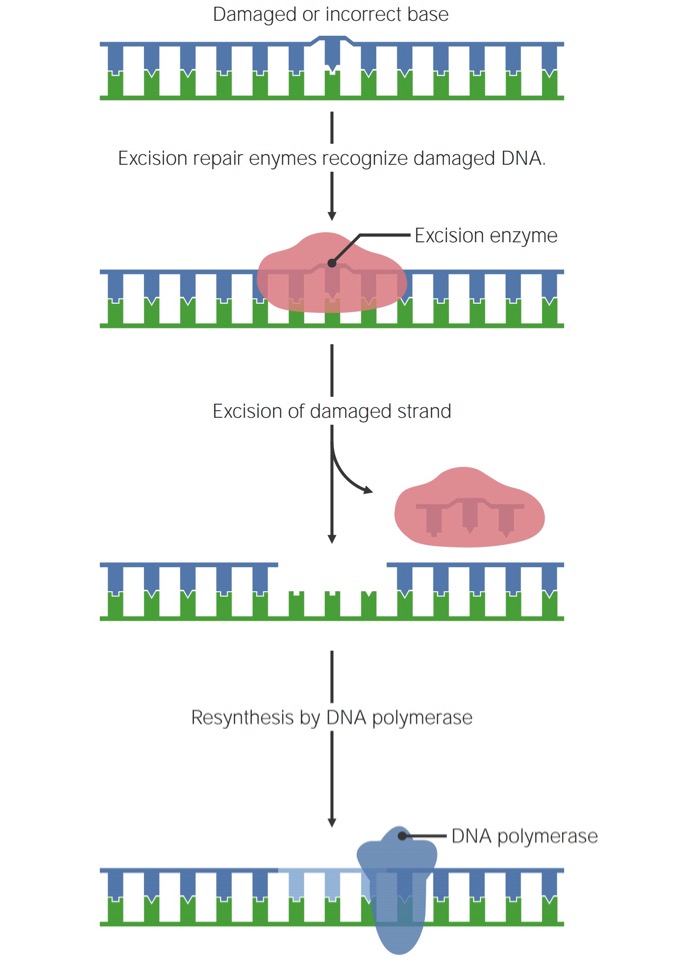
Mecanismo general de reparación de una sola cadena de ADN
Imagen por Lecturio.En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la reparación por escisión de bases Bases Usually a hydroxide of lithium, sodium, potassium, rubidium or cesium, but also the carbonates of these metals, ammonia, and the amines. Acid-Base Balance, se extirpa una única base dañada y se sustituye.
En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum general, los LOS Neisseria daños en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum dos cadenas de ADN son más difíciles de reparar porque no hay una cadena molde con la que trabajar. Los LOS Neisseria dos mecanismos principales para fijar las roturas de dos cadenas de ADN son la recombinación homóloga y la unión de extremos no homólogos.
En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la recombinación homóloga, la cromátida hermana casi idéntica o el cromosoma homólogo se utiliza como plantilla:
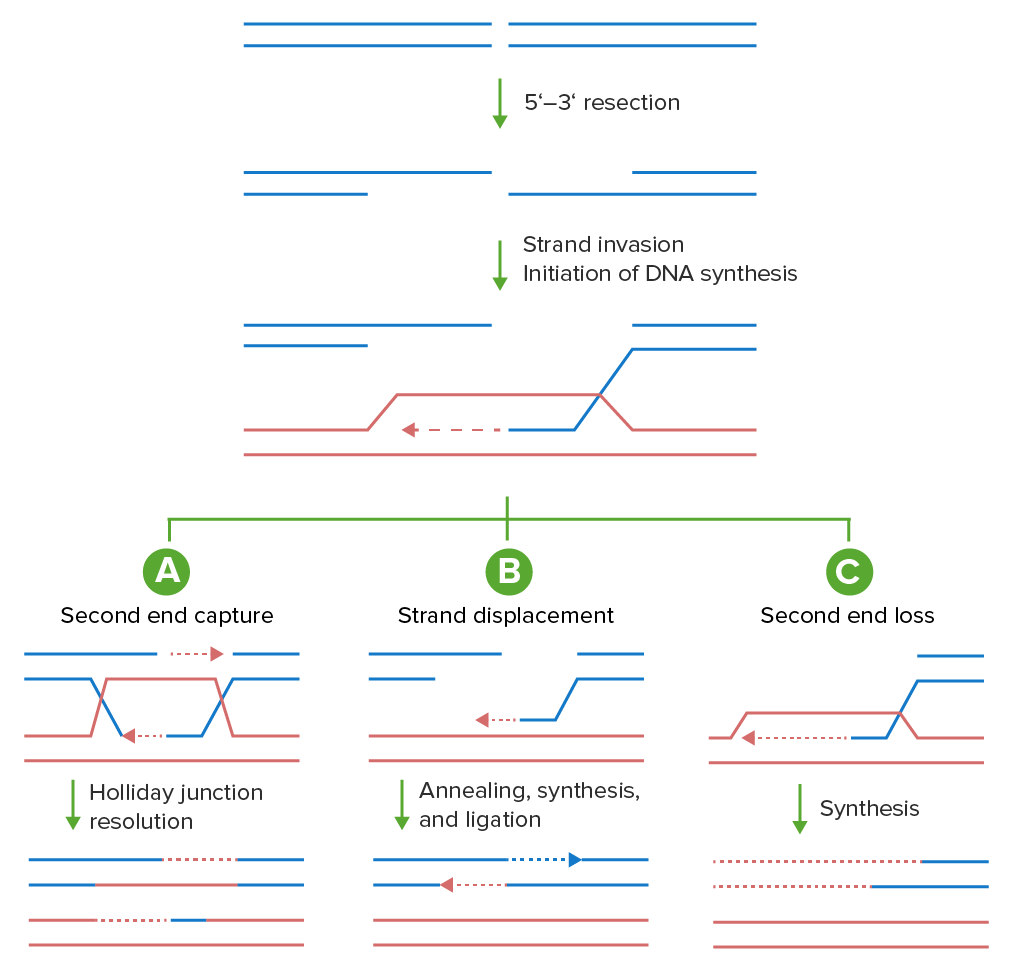
Modelos de recombinación homóloga:
Las roturas de doble cadena pueden repararse mediante la maquinaria de recombinación homóloga de diversas maneras. Los extremos del ADN se procesan primero en colas de ADN de una sola cadena 3’. Estas colas invaden una plantilla homóloga (rojo), iniciando una nueva síntesis de ADN (línea discontinua). Se muestran 3 posibles resultados de esta invasión.
A: En la reparación canónica de la rotura de doble cadena, tanto la cadena invasora inicial como el segundo extremo capturado se unen a la plantilla homóloga y preparan la nueva síntesis de ADN, dando lugar a una doble unión Holliday que puede ser resuelta por las nucleasas en un producto cruzado o no cruzado (se muestra el producto no cruzado).
B: Alternativamente, después de que la cola de ADN de una sola cadena invada la plantilla homóloga, se prepara una ronda de síntesis de ADN a partir del extremo 3′ (línea roja discontinua). El alineamiento de la cadena dependiente de la síntesis se produce cuando la cadena invasora, junto con el segmento recién sintetizado, es desenrollada por una helicasa y es alineada con el otro extremo resecado.
C: En la replicación inducida por rotura, 1 extremo de la rotura de doble cadena se pierde y el extremo restante invade la plantilla homóloga, iniciando la síntesis de ADN hasta el final del cromosoma.