Listeria Listeria Listeria spp. are motile, flagellated, gram-positive, facultative intracellular bacilli. The major pathogenic species is Listeria monocytogenes. Listeria are part of the normal gastrointestinal flora of domestic mammals and poultry and are transmitted to humans through the ingestion of contaminated food, especially unpasteurized dairy products. Listeria Monocytogenes/Listeriosis spp. son bacilos móviles, flagelados, gram-positivos e intracelulares facultativos. La principal especie patógena es Listeria Listeria Listeria spp. are motile, flagellated, gram-positive, facultative intracellular bacilli. The major pathogenic species is Listeria monocytogenes. Listeria are part of the normal gastrointestinal flora of domestic mammals and poultry and are transmitted to humans through the ingestion of contaminated food, especially unpasteurized dairy products. Listeria Monocytogenes/Listeriosis monocytogenes. Listeria Listeria Listeria spp. are motile, flagellated, gram-positive, facultative intracellular bacilli. The major pathogenic species is Listeria monocytogenes. Listeria are part of the normal gastrointestinal flora of domestic mammals and poultry and are transmitted to humans through the ingestion of contaminated food, especially unpasteurized dairy products. Listeria Monocytogenes/Listeriosis forma parte de la flora gastrointestinal normal de los LOS Neisseria mamíferos domésticos y las aves de corral, y se transmite a los LOS Neisseria humanos a través de la ingestión de alimentos contaminados, especialmente productos lácteos no pasteurizados. Listeria Listeria Listeria spp. are motile, flagellated, gram-positive, facultative intracellular bacilli. The major pathogenic species is Listeria monocytogenes. Listeria are part of the normal gastrointestinal flora of domestic mammals and poultry and are transmitted to humans through the ingestion of contaminated food, especially unpasteurized dairy products. Listeria Monocytogenes/Listeriosis también puede infectar al AL Amyloidosis feto in utero o a los LOS Neisseria neonatos durante el parto vaginal. Las personas sanas expuestas a L. monocytogenes L. monocytogenes A species of gram-positive, rod-shaped bacteria widely distributed in nature. It has been isolated from sewage, soil, silage, and from feces of healthy animals and man. Infection with this bacterium leads to encephalitis, meningitis, endocarditis, and abortion. Listeria Monocytogenes/Listeriosis generalmente no se enferman si el inóculo es pequeño o pueden desarrollar solamente una gastroenteritis Gastroenteritis Gastroenteritis is inflammation of the stomach and intestines, commonly caused by infections from bacteria, viruses, or parasites. Transmission may be foodborne, fecal-oral, or through animal contact. Common clinical features include abdominal pain, diarrhea, vomiting, fever, and dehydration. Gastroenteritis autolimitada. Las personas inmunocomprometidas o de edad avanzada, los LOS Neisseria neonatos y las mujeres embarazadas pueden desarrollar una enfermedad invasiva, como meningitis Meningitis Meningitis is inflammation of the meninges, the protective membranes of the brain, and spinal cord. The causes of meningitis are varied, with the most common being bacterial or viral infection. The classic presentation of meningitis is a triad of fever, altered mental status, and nuchal rigidity. Meningitis y bacteriemia. El tratamiento de la listeriosis invasiva incluye ampicilina y gentamicina.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
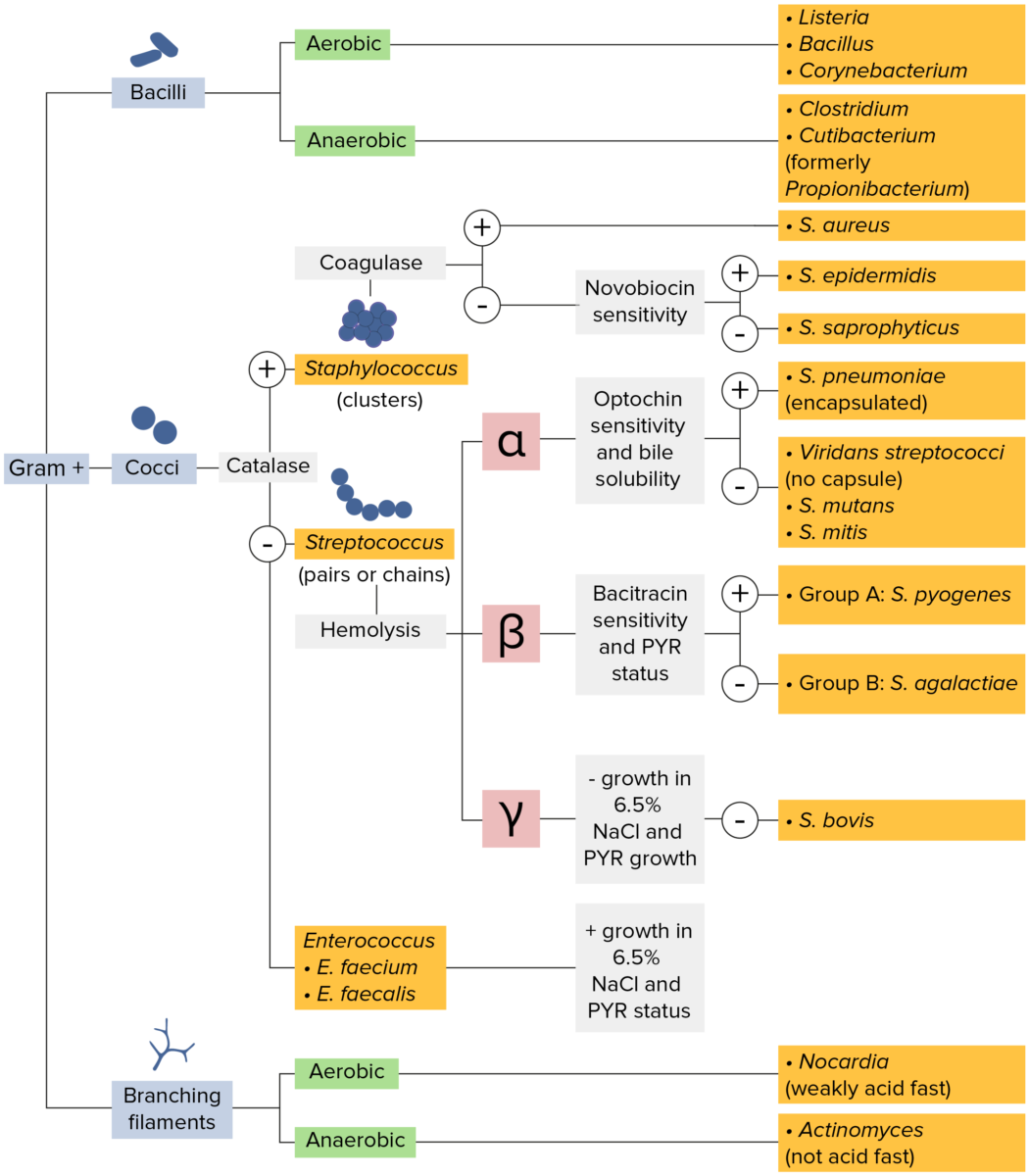
Bacterias gram-positivas:
La mayoría de las bacterias se pueden clasificar de acuerdo con un procedimiento de laboratorio llamado tinción de Gram.
Las bacterias con paredes celulares que tienen una capa gruesa de peptidoglicano retienen la tinción cristal violeta utilizada en la tinción de Gram, pero no se ven afectadas por la contratinción de safranina. Estas bacterias aparecen como azul púrpura en la tinción, lo que indica que son gram-positivas. Las bacterias pueden clasificarse además según su morfología (filamentos ramificados, bacilos y cocos en grupos o cadenas) y su capacidad para crecer en presencia de oxígeno (aeróbicos versus anaeróbicos). Los cocos también pueden identificarse con mayor profundidad. Los estafilococos pueden reducirse en función de la presencia de la enzima coagulasa y de su sensibilidad al antibiótico novobiocina. Los estreptococos se cultivan en agar sangre y se clasifican según la forma de hemólisis que emplean (α, β o γ). Los estreptococos se reducen aún más en función de su respuesta a la prueba de pirrolidonil-β-naftilamida, su sensibilidad a antimicrobianos específicos (optoquina y bacitracina) y su capacidad para crecer en medios de cloruro de sodio (NaCl).
Las características generales de las especies de Listeria Listeria Listeria spp. are motile, flagellated, gram-positive, facultative intracellular bacilli. The major pathogenic species is Listeria monocytogenes. Listeria are part of the normal gastrointestinal flora of domestic mammals and poultry and are transmitted to humans through the ingestion of contaminated food, especially unpasteurized dairy products. Listeria Monocytogenes/Listeriosis incluyen:
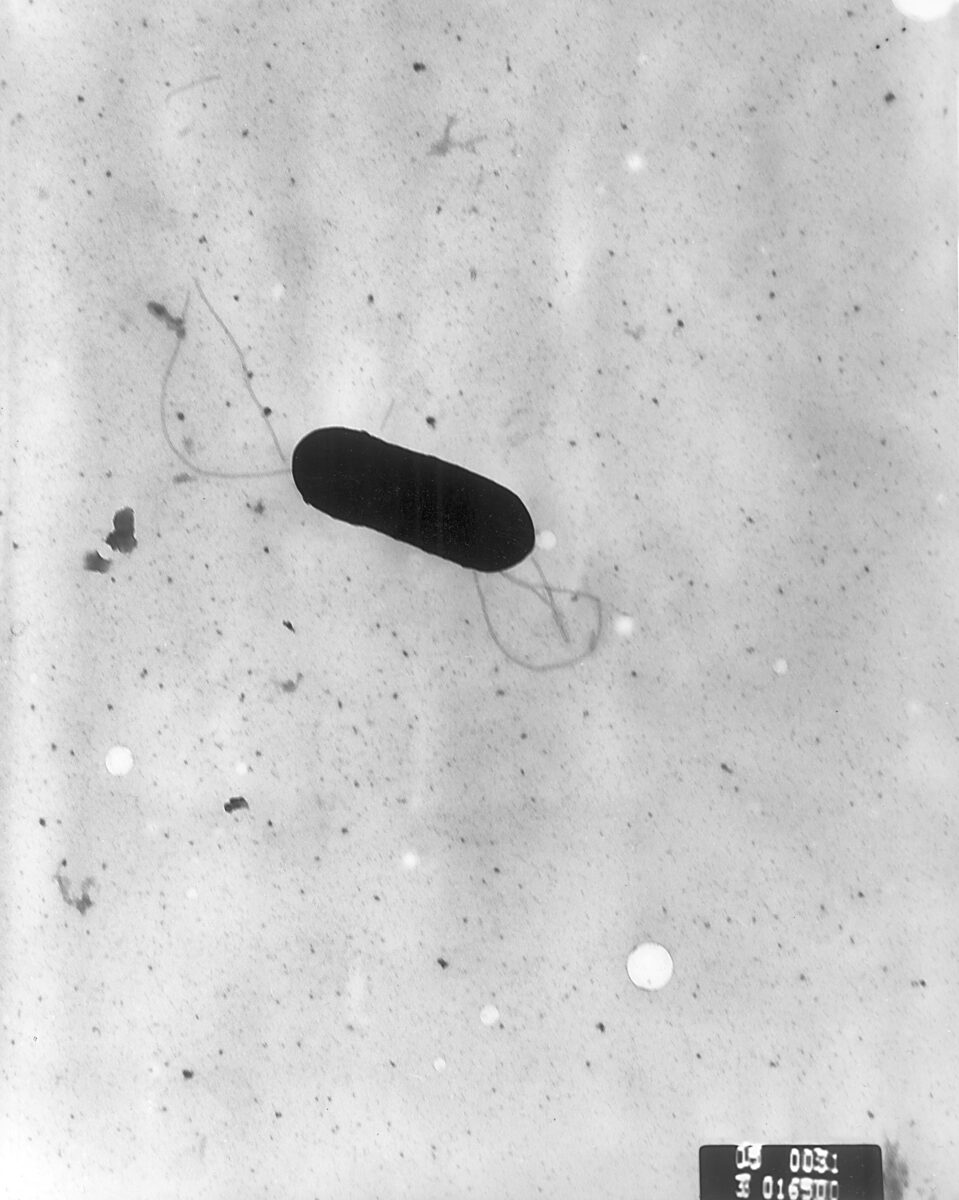
Micrografía electrónica de barrido de la bacteria Listeria monocytogenes
Imagen: “2287” por Elizabeth White. Licencia: Dominio Público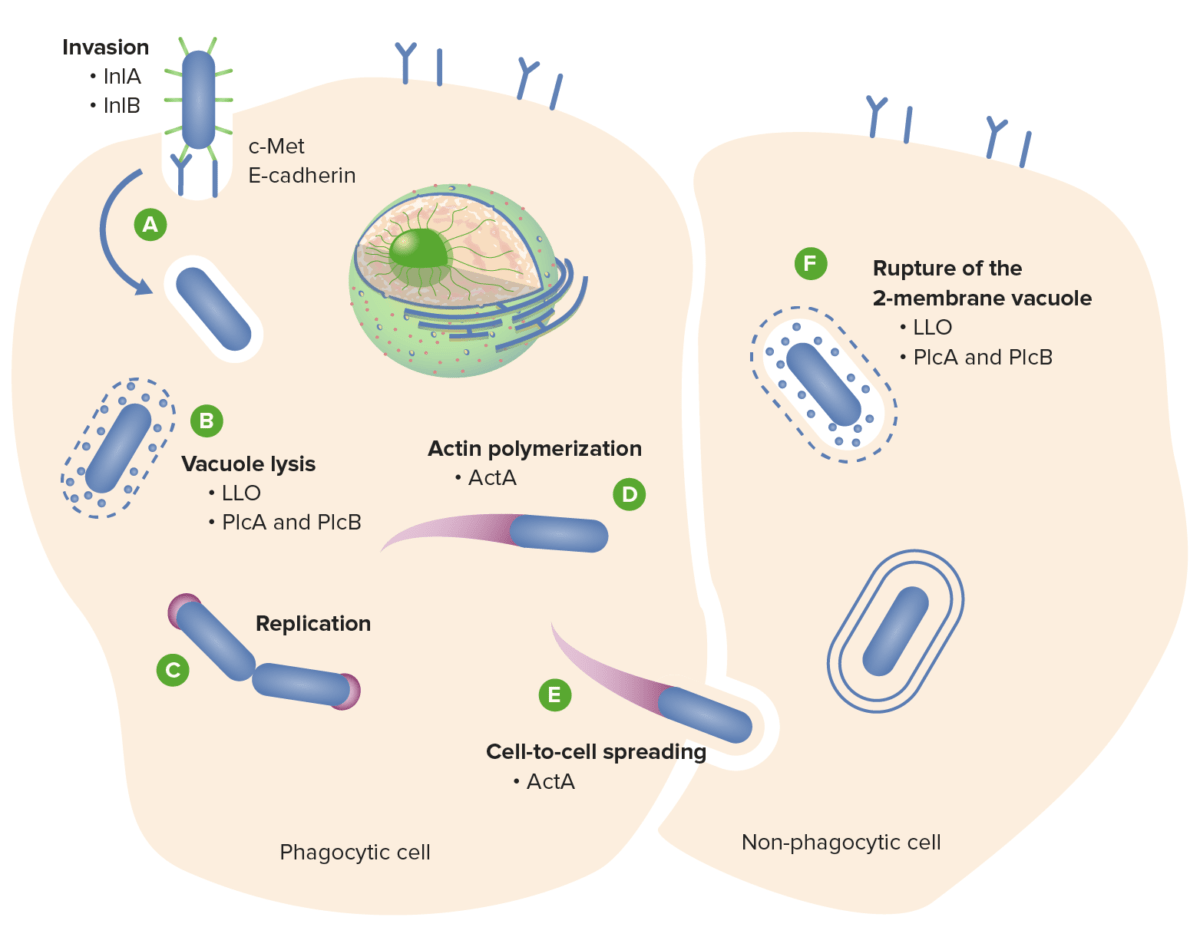
Ciclo de infección de Listeria monocytogenes:
(A) L. monocytogenes invade la célula huésped a través de la interacción de las internalinas de superficie A y B (InlA e InlB) con los receptores de superficie de la célula huésped E-cadherina y c-Met, respectivamente.
(B) Listeria escapa del fagosoma mediante la acción de las toxinas LLO, PlcA y PlcB.
(D) La Listeria se replica en el citosol y se propulsa a la superficie celular mediante la polimerización de la actina, (E) promoviendo la propagación de célula a célula.
(F) La ruptura de la vacuola de dos membranas también está mediada por las toxinas LLO y fosfolipasa.
InIA: internalina A
InlB: internalina B
LLO: listeriolisina O
PlcA: fosfolipasa A
PlcB: fosfolipasa B
ActA: proteína A inductora del ensamblaje de actina
Una forma invasiva de la enfermedad puede desarrollarse en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum ciertas poblaciones:
Según el tamaño del inóculo y el estado del sistema inmunitario del individuo, la infección por L. monocytogenes L. monocytogenes A species of gram-positive, rod-shaped bacteria widely distributed in nature. It has been isolated from sewage, soil, silage, and from feces of healthy animals and man. Infection with this bacterium leads to encephalitis, meningitis, endocarditis, and abortion. Listeria Monocytogenes/Listeriosis puede presentarse de diversas formas.
| Tipo de presentación clínica | Características clínicas |
|---|---|
| Gastroenteritis Gastroenteritis Gastroenteritis is inflammation of the stomach and intestines, commonly caused by infections from bacteria, viruses, or parasites. Transmission may be foodborne, fecal-oral, or through animal contact. Common clinical features include abdominal pain, diarrhea, vomiting, fever, and dehydration. Gastroenteritis autolimitada |
Se presenta
en
EN
Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins.
Erythema Nodosum individuos sanos < 48 horas después de ingerir un inóculo grande
en
EN
Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins.
Erythema Nodosum alimentos contaminados:
|
| Bacteriemia/septicemia | Se presenta
en
EN
Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins.
Erythema Nodosum individuos inmunocomprometidos o ancianos:
|
| Infecciones del SNC | Se presenta
en
EN
Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins.
Erythema Nodosum individuos inmunocomprometidos o ancianos:
|
| Infección en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum mujeres embarazadas |
|
| Infección en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum fetos/neonatos (listeriosis congénita) |
|
El diagnóstico diferencial de la listeriosis incluye todas las causas de meningitis Meningitis Meningitis is inflammation of the meninges, the protective membranes of the brain, and spinal cord. The causes of meningitis are varied, with the most common being bacterial or viral infection. The classic presentation of meningitis is a triad of fever, altered mental status, and nuchal rigidity. Meningitis o septicemia.
| Meningitis Meningitis Meningitis is inflammation of the meninges, the protective membranes of the brain, and spinal cord. The causes of meningitis are varied, with the most common being bacterial or viral infection. The classic presentation of meningitis is a triad of fever, altered mental status, and nuchal rigidity. Meningitis bacteriana | Meningitis Meningitis Meningitis is inflammation of the meninges, the protective membranes of the brain, and spinal cord. The causes of meningitis are varied, with the most common being bacterial or viral infection. The classic presentation of meningitis is a triad of fever, altered mental status, and nuchal rigidity. Meningitis viral | Meningitis Meningitis Meningitis is inflammation of the meninges, the protective membranes of the brain, and spinal cord. The causes of meningitis are varied, with the most common being bacterial or viral infection. The classic presentation of meningitis is a triad of fever, altered mental status, and nuchal rigidity. Meningitis fúngica/tuberculosa ( TB TB Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex bacteria. The bacteria usually attack the lungs but can also damage other parts of the body. Approximately 30% of people around the world are infected with this pathogen, with the majority harboring a latent infection. Tuberculosis spreads through the air when a person with active pulmonary infection coughs or sneezes. Tuberculosis) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Glucosa | ↓ | Normal | ↓ |
| Proteínas | ↑ | Normal | ↑ |
| Leucocitos | ↑ Leucocitos polimorfonucleares | ↑ Linfocitos | ↑↑ Linfocitos |
| Presión de apertura | ↑ | Normal | ↑↑ |
| Color | Turbio | Claro o sanguinolento | Claro u opaco |