Los LOS Neisseria linfocitos T, también llamados células T, son componentes importantes del sistema inmunitario adaptativo. Su producción inicia en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las células madre hematopoyéticas de la médula ósea, de las que surgen las células progenitoras de linfocitos T. Estas células migran al AL Amyloidosis timo para seguir madurando. Un linfocito T maduro funcional se desarrolla a partir de un proceso pautado que crea un complejo de receptores de linfocitos T, seleccionando linfocitos T con la afinidad adecuada a los LOS Neisseria autoantígenos asociados a las principales moléculas de histocompatibilidad (selección positiva) y expresando CD4 o CD8. En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum este proceso, las células predispuestas a la autoinmunidad sufren apoptosis Apoptosis A regulated cell death mechanism characterized by distinctive morphologic changes in the nucleus and cytoplasm, including the endonucleolytic cleavage of genomic DNA, at regularly spaced, internucleosomal sites, I.e., DNA fragmentation. It is genetically-programmed and serves as a balance to mitosis in regulating the size of animal tissues and in mediating pathologic processes associated with tumor growth. Ischemic Cell Damage (selección negativa). Cuando se liberan del timo, los LOS Neisseria linfocitos T maduros vírgenes se desplazan a los LOS Neisseria órganos linfoides secundarios para su activación. Se requieren dos señales, una unión del antígeno específico del receptor Receptor Receptors are proteins located either on the surface of or within a cell that can bind to signaling molecules known as ligands (e.g., hormones) and cause some type of response within the cell. Receptors de linfocitos T y la coestimulación, para que esté activado (listo para organizar una respuesta inmune). En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el caso de los LOS Neisseria linfocitos T CD8+, es necesaria una estimulación adicional con citoquinas. Dependiendo de las citoquinas a las que se exponen durante la estimulación antigénica, los LOS Neisseria linfocitos T maduros indiferenciados (Th0, por sus siglas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés) se convierten en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum células con diferentes funciones: los LOS Neisseria CD4+ se convierten en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum linfocitos T colaboradores (Th, por sus siglas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés) y los LOS Neisseria CD8+ en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum linfocitos citotóxicos o citolíticos. Los LOS Neisseria linfocitos Th tienen otros subtipos; los LOS Neisseria más caracterizados son Th1 Th1 A subset of helper-inducer T-lymphocytes which synthesize and secrete interleukin-2; interferon-gamma; and interleukin-12. Due to their ability to kill antigen-presenting cells and their lymphokine-mediated effector activity, th1 cells are associated with vigorous delayed-type hypersensitivity reactions. T cells: Types and Functions, Th2 Th2 A subset of helper-inducer T-lymphocytes which synthesize and secrete the interleukins il-4; il-5; il-6; and il-10. These cytokines influence b-cell development and antibody production as well as augmenting humoral responses. T cells: Types and Functions, Th17 Th17 A subset of helper-effector T-lymphocytes which synthesize and secrete interleukins il-17; il-17f; and il-22. These cytokines are involved in host defenses and tissue inflammation in autoimmune diseases. T cells: Types and Functions, linfocitos Th foliculares y linfocitos T reguladores. Otros tipos son los LOS Neisseria linfocitos T asesinos naturales y los LOS Neisseria linfocitos T de memoria. Estos linfocitos T maduros y diferenciados garantizan una vigilancia efectiva y una respuesta inmediata a agentes patógenos, células tumorales y tejidos extraños, y proporcionan memoria inmunológica.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
El proceso inicial tiene lugar en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la corteza externa del timo, y las células se desplazan a la corteza más profunda a medida que maduran.
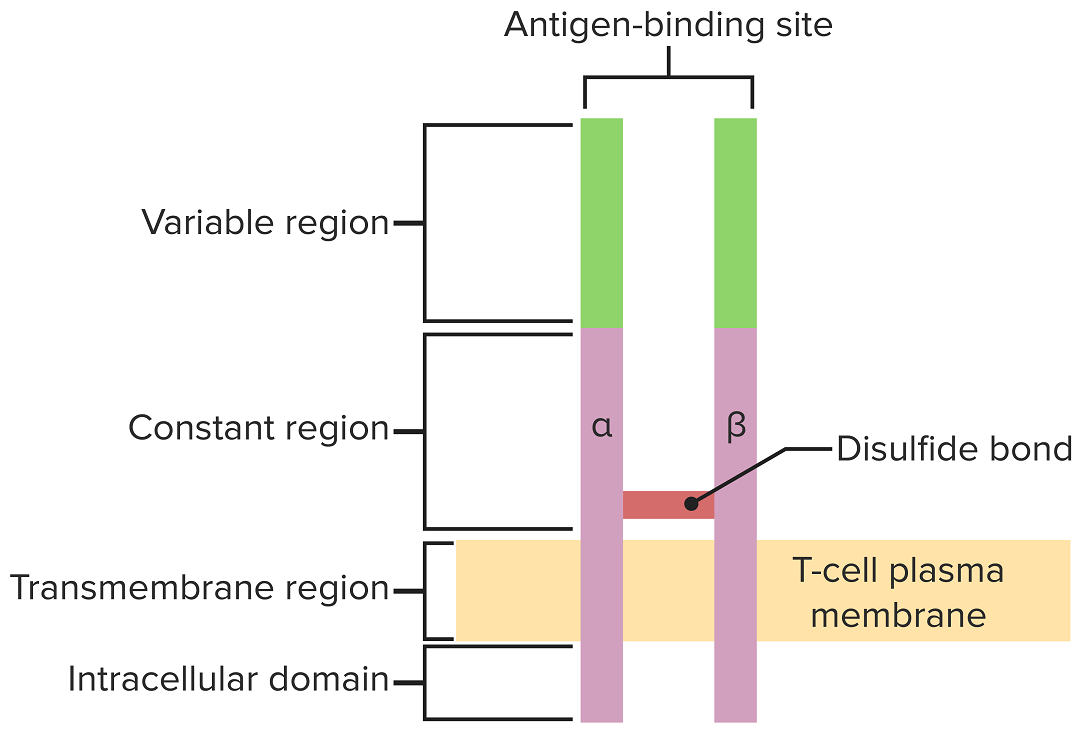
El receptor de linfocitos T se extiende por la membrana citoplasmática y proyecta regiones de unión variables en el espacio extracelular para unirse a antígenos procesados asociados a moléculas CMH I o CMH II.
Imagen por Lecturio.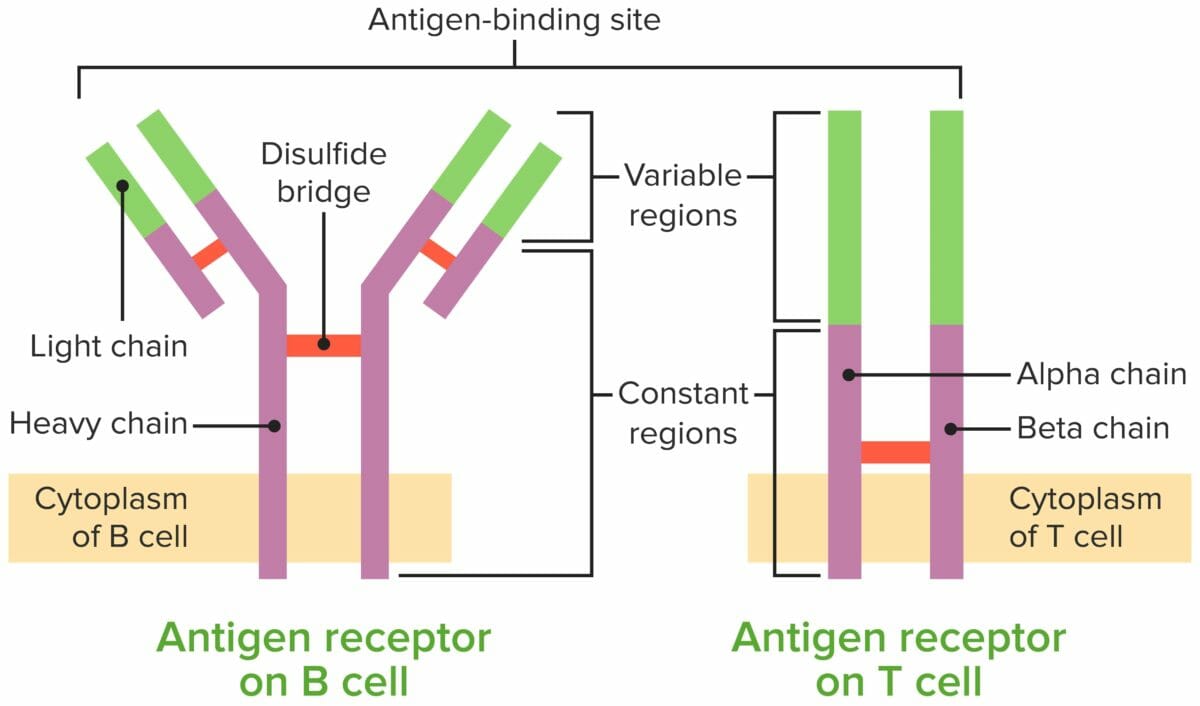
Comparación del receptor de linfocitos B y del receptor de linfocitos T
Imagen por Lecturio.Para alcanzar la funcionalidad, el linfocito T pasa por estadios, liberándose de la médula ósea como células progenitoras para continuar su desarrollo en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el timo. El cuadro resume los LOS Neisseria principales pasos.
| Estadios de maduración | Receptor Receptor Receptors are proteins located either on the surface of or within a cell that can bind to signaling molecules known as ligands (e.g., hormones) and cause some type of response within the cell. Receptors de linfocitos T | Eventos asociados |
|---|---|---|
| Célula progenitora | Ninguno |
|
| Células DN | Reordenamiento de la cadena β (pre-receptor de linfocitos T): la falta de reordenamiento conduce a apoptosis Apoptosis A regulated cell death mechanism characterized by distinctive morphologic changes in the nucleus and cytoplasm, including the endonucleolytic cleavage of genomic DNA, at regularly spaced, internucleosomal sites, I.e., DNA fragmentation. It is genetically-programmed and serves as a balance to mitosis in regulating the size of animal tissues and in mediating pathologic processes associated with tumor growth. Ischemic Cell Damage |
|
| Células DP | Reordenamiento de la cadena ɑ → las cadenas ɑ se ensamblan con las cadenas β → complejo de receptor Receptor Receptors are proteins located either on the surface of or within a cell that can bind to signaling molecules known as ligands (e.g., hormones) and cause some type of response within the cell. Receptors de linfocitos T-CD3 ɑ-β completo (expresado en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la superficie) |
|
| Linfocitos T simple positivos |
|
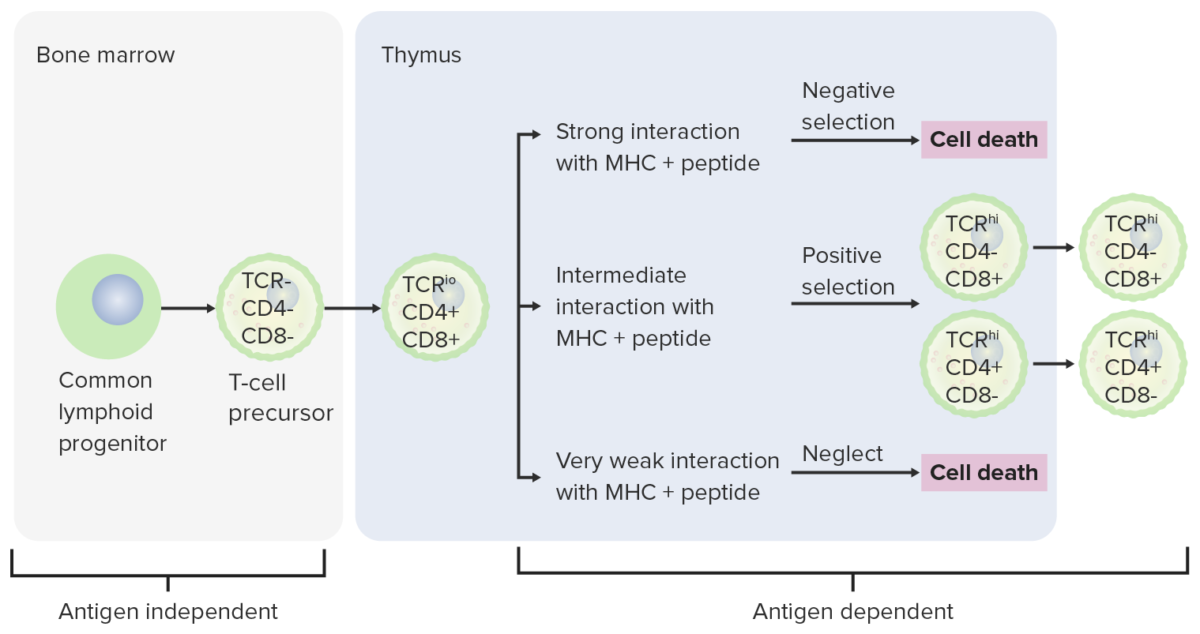
Estadios de diferenciación de los linfocitos T:
Desde la médula ósea, las células progenitoras pasan al timo para su posterior maduración. Las células DN (sin expresión de CD4/CD8 o CD4-/CD8-) no han desarrollado el receptor de linfocitos T. Las células DN experimentan un reordenamiento del gen del receptor de linfocitos T y se convierten en prolinfocitos T y luego en prelinfocitos T. A través del proceso, se expresan CD4 y CD8, y el receptor de linfocitos T se ensambla a través de reordenamientos genéticos (células DP). El timo presenta entonces moléculas CMH a los linfocitos T en desarrollo. Algunas células experimentan selección positiva (se produce una interacción intermedia entre el CMH y el receptor de linfocitos T) y producen células funcionales. Algunas células experimentan selección negativa (fuerte interacción entre el CMH y el receptor de linfocitos T), lo que provoca la muerte celular. Se evita la liberación de linfocitos T disfuncionales, que pueden activar la autoinmunidad. Algunos linfocitos T no logran interactuar, lo que conduce a la apoptosis. Los linfocitos T maduros expresan CD4 (linfocitos T colaboradores) o CD8 (linfocitos T citotóxicos), pero no ambos.
Recuerde la “regla del 8”:
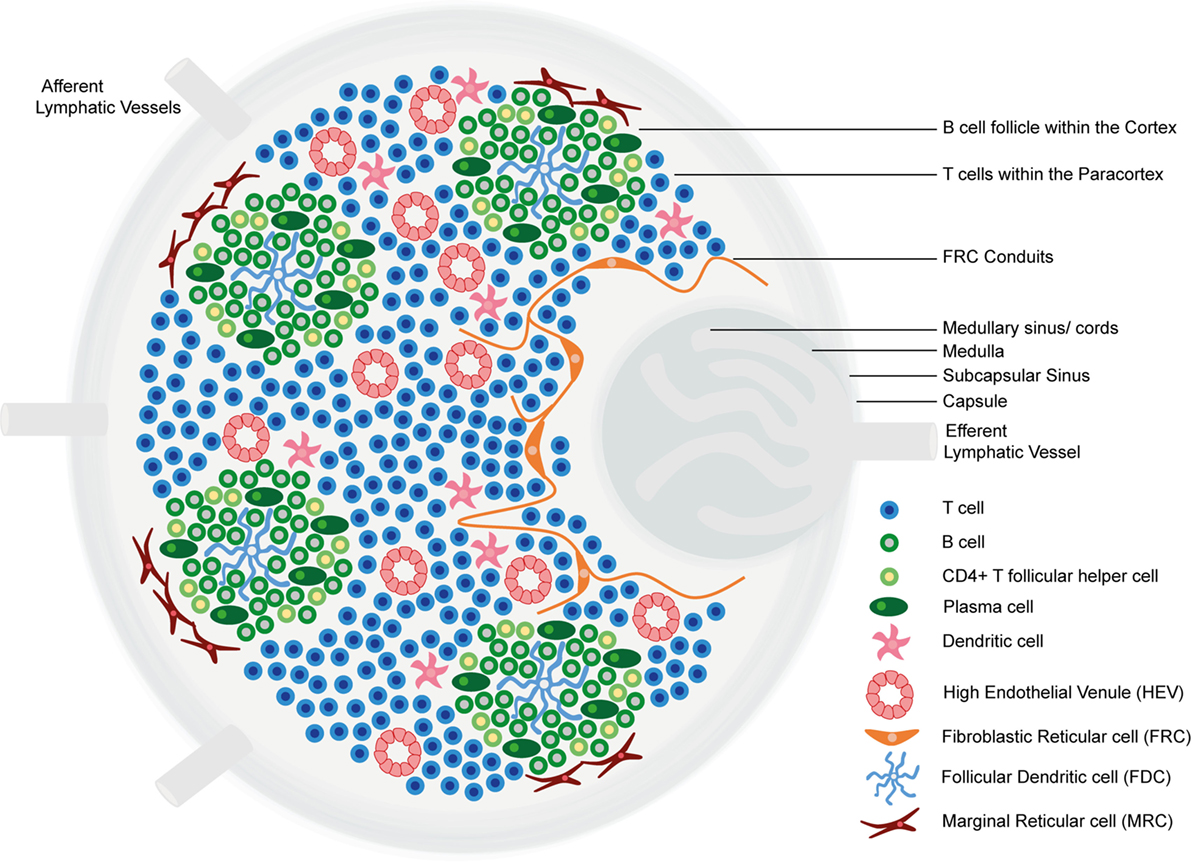
Estructura y regiones funcionales de un ganglio linfático que consta de una cápsula fibrosa rica en colágeno y un seno subcapsular subyacente.
Las células se segregan en (1) la corteza (que consiste en linfocitos B, linfocitos T colaboradores foliculares y células dendríticas foliculares dispuestas en folículos primarios, en los que los linfocitos B examinan los antígenos presentados en la red estromal de células dendríticas foliculares); y en (2) la paracorteza (que aloja a linfocitos T, células dendríticas y células reticulares fibroblásticas, que forman redes de células estromales y fibras reticulares).
La médula interna está compuesta por tejidos linfáticos (cordones medulares) separados por senos medulares compuestos por linfa.
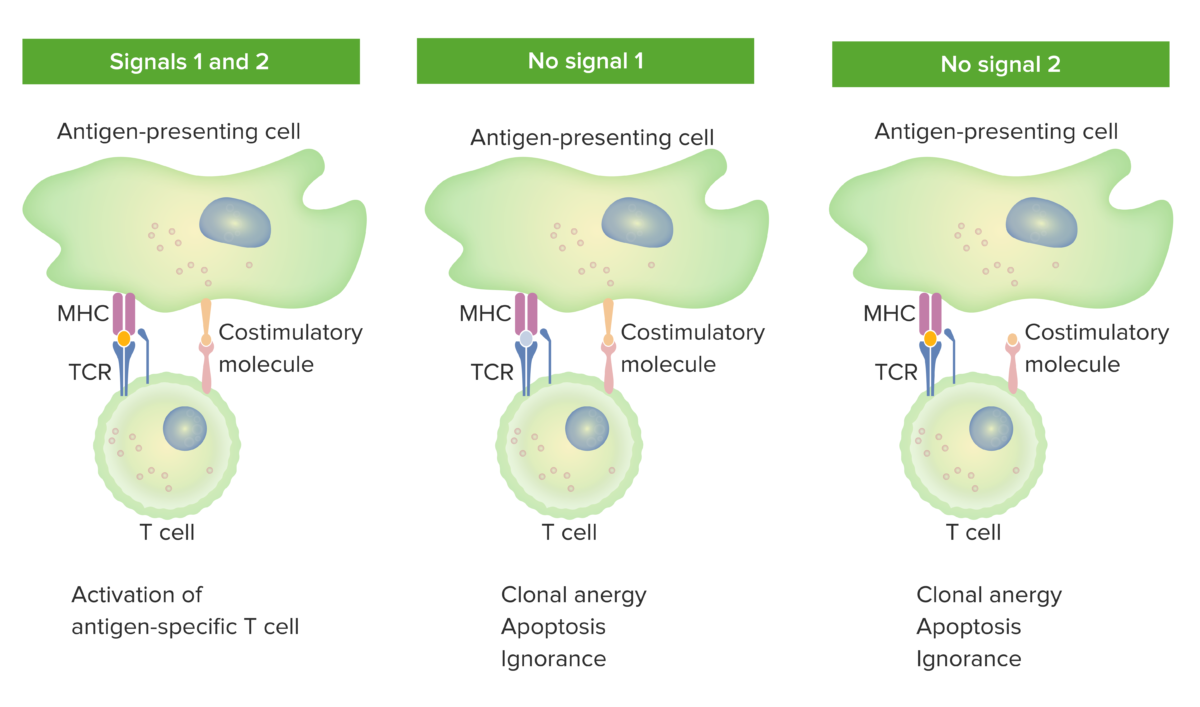
Modelo de 2 señales de la dependencia de los linfocitos T de la coestimulación:
Cuando están presentes tanto la señal 1 (unión del receptor de linfocitos T con el antígeno afín presentado por la molécula del CMH en la célula presentadora del antígeno) como la señal 2 (interacción de la molécula coestimuladora entre la célula presentadora del antígeno y el linfocito T), el linfocito T maduro está totalmente activado.
El punto naranja en el panel de la izquierda indica la unión adecuada entre el antígeno y el receptor de linfocitos T. Sin embargo, cuando falta la señal 1 (la imagen del medio muestra la ausencia de la unión entre el antígeno y el receptor de linfocitos T) o la señal 2 (la imagen de la derecha muestra la ausencia de coestimulación), el linfocito T no se activará completamente.
Los resultados serían anergia (falta de respuesta), apoptosis (muerte celular) o ignorancia (el linfocito T no se da cuenta o no se ve afectado por el antígeno).
Los LOS Neisseria linfocitos T colaboradores tienen diferentes perfiles de citoquinas y funciones en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la respuesta inmune.
| Linfocitos T CD4+ | Diferenciación estimulada por | Funciones | Citoquinas producidas |
|---|---|---|---|
| Th1 Th1 A subset of helper-inducer T-lymphocytes which synthesize and secrete interleukin-2; interferon-gamma; and interleukin-12. Due to their ability to kill antigen-presenting cells and their lymphokine-mediated effector activity, th1 cells are associated with vigorous delayed-type hypersensitivity reactions. T cells: Types and Functions |
|
|
|
| Th2 Th2 A subset of helper-inducer T-lymphocytes which synthesize and secrete the interleukins il-4; il-5; il-6; and il-10. These cytokines influence b-cell development and antibody production as well as augmenting humoral responses. T cells: Types and Functions |
|
|
|
| Th17 Th17 A subset of helper-effector T-lymphocytes which synthesize and secrete interleukins il-17; il-17f; and il-22. These cytokines are involved in host defenses and tissue inflammation in autoimmune diseases. T cells: Types and Functions |
|
Promover la inflamación neutrofílica |
|
| Tfh | IL-6 | Facilitar la activación y maduración de linfocitos B |
|
| Treg |
|
|
|
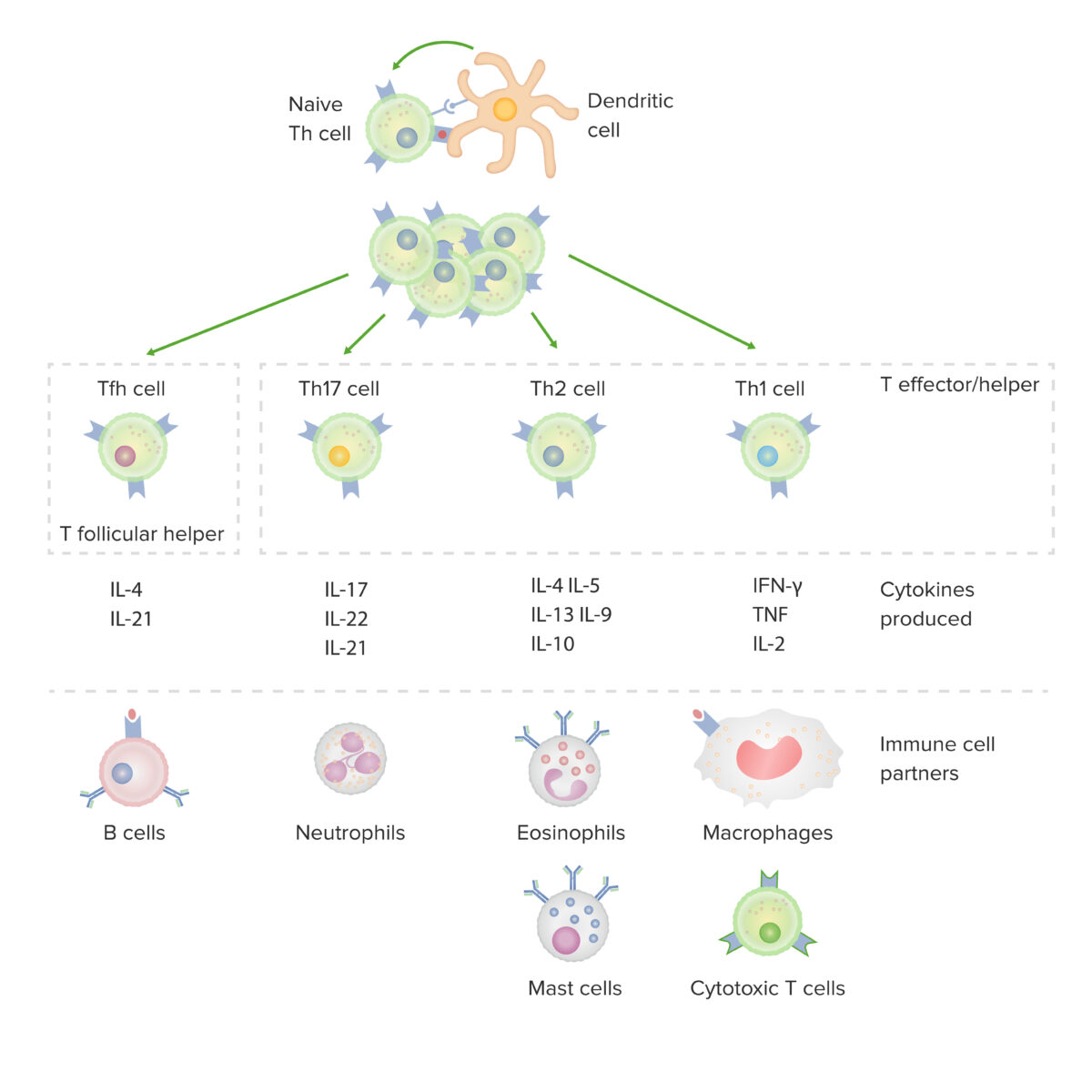
Subconjuntos de linfocitos T colaboradores CD4-positivos:
Tras la activación por parte de una célula dendrítica, en presencia de determinadas citoquinas, un linfocito T CD4-positivo virgen se divide y se diferencia en subconjuntos efector/colaborador (Th1, Th2 o Th17) o colaborador folicular (Tfh). Cada tipo de célula produce citoquinas que facilitan la activación de otras células inmunitarias.
IFN: interferón
TNF: factor de necrosis tumoral (en inglés)
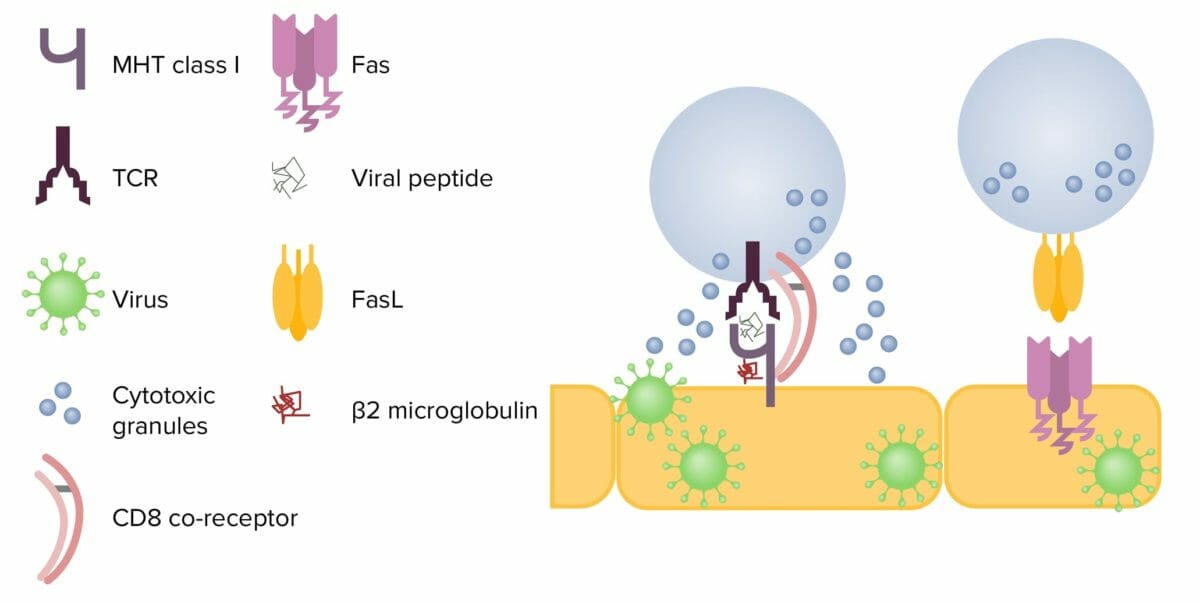
Mecanismos de citotoxicidad de las células T CD8+:
Izquierda: Tras entrar en contacto con una célula infectada, la célula T libera gránulos citotóxicos, perforina y granzimas. La perforina crea un poro en la membrana de la célula objetivo, permitiendo que las granzimas entren en la célula. Éstas escinden las proteínas dentro de la célula, lo que finalmente provoca la apoptosis.
A la derecha: Cuando FasL interactúa con Fas en una célula diana, se activa la cascada de caspasas y se produce la apoptosis.
FasL: ligando de Fas
TCR: receptor de células T
MHC: complejo mayor de histocompatibilidad
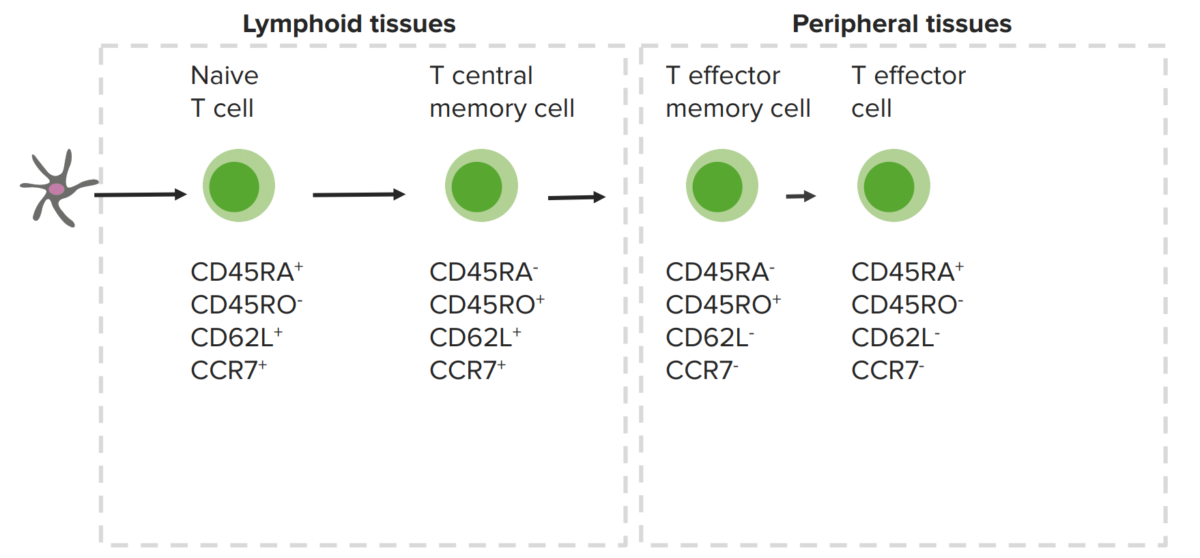
Linfocitos T de memoria y marcadores celulares expresados:
Los linfocitos T de memoria centrales están en los órganos linfoides, mientras que los linfocitos T de memoria periféricos están en los tejidos periféricos.