La leucemia eosinofílica crónica es una neoplasia mieloproliferativa crónica causada por la proliferación clonal autónoma de los LOS Neisseria eosinófilos con apariencia normal, lo que da como resultado un aumento de eosinófilos en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la sangre periférica y la médula ósea. El trastorno es una variante mieloide del síndrome hipereosinofílico y está asociado con la infiltración tisular que conduce al AL Amyloidosis daño de los LOS Neisseria órganos diana. Los LOS Neisseria pacientes presentan síntomas constitucionales junto con signos y síntomas de anemia Anemia Anemia is a condition in which individuals have low Hb levels, which can arise from various causes. Anemia is accompanied by a reduced number of RBCs and may manifest with fatigue, shortness of breath, pallor, and weakness. Subtypes are classified by the size of RBCs, chronicity, and etiology. Anemia: Overview and Types y trombocitopenia. Los LOS Neisseria estudios muestran un recuento absoluto de eosinófilos ≥ 1,5 x 10⁹/L, con blastos en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la médula ósea (5%–19%). Se necesita evidencia de anormalidad clonal o blastos elevados; sin ninguno de los LOS Neisseria dos, el síndrome hipereosinofílico idiopático es el diagnóstico apropiado. Sin embargo, ambos tienen un enfoque de tratamiento similar. El tratamiento tiene como objetivo reducir la carga de la hipercelularidad para prevenir el daño de los LOS Neisseria órganos diana. Las opciones de tratamiento incluyen corticosteroides, agentes quimioterapéuticos e interferón- α.
Last updated: Aug 2, 2022
La leucemia eosinofílica crónica, no especificada de otra manera es una neoplasia mieloproliferativa crónica poco frecuente tipificada por la expansión clonal eosinofílica en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la médula ósea con aumento de blastos (< 20%).
Basada en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la eosinofilia:
La leucemia eosinofílica crónica, no especificada de otra manera, se clasifica en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum neoplasias mieloproliferativas crónicas (clasificación de la OMS):
La hematopoyesis comienza con una célula madre hematopoyética, que se incita a dividirse y diferenciarse con estímulos químicos apropiados (factores de crecimiento hematopoyéticos).
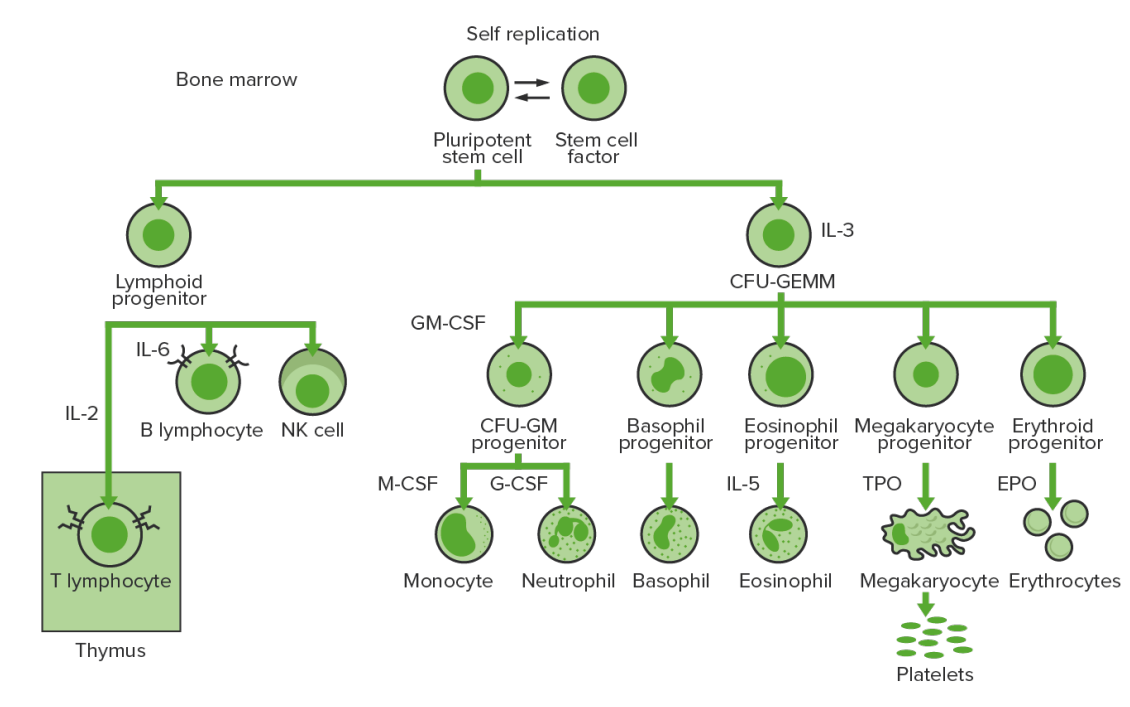
Hematopoyesis de la médula ósea: proliferación y diferenciación de los elementos formes de la sangre.
CFU-GEMM: unidad formadora de colonias de granulocitos, eritrocitos, monocitos, megacariocitos
CFU-GM: unidad formadora de colonias de granulocitos y macrófagos
GM-CSF: factor estimulante de colonias de granulocitos y macrófagos
M-CSF: factor estimulante de colonias de macrófagos
G-CSF: factor estimulante de colonias de granulocitos
NK: células asesinas naturales
TPO: trombopoyetina
La leucemia eosinofílica crónica, no especificada de otra manera, es un diagnóstico de exclusión (requiere descartar otras afecciones eosinofílicas) y se define de acuerdo con los LOS Neisseria criterios de diagnóstico de la OMS:
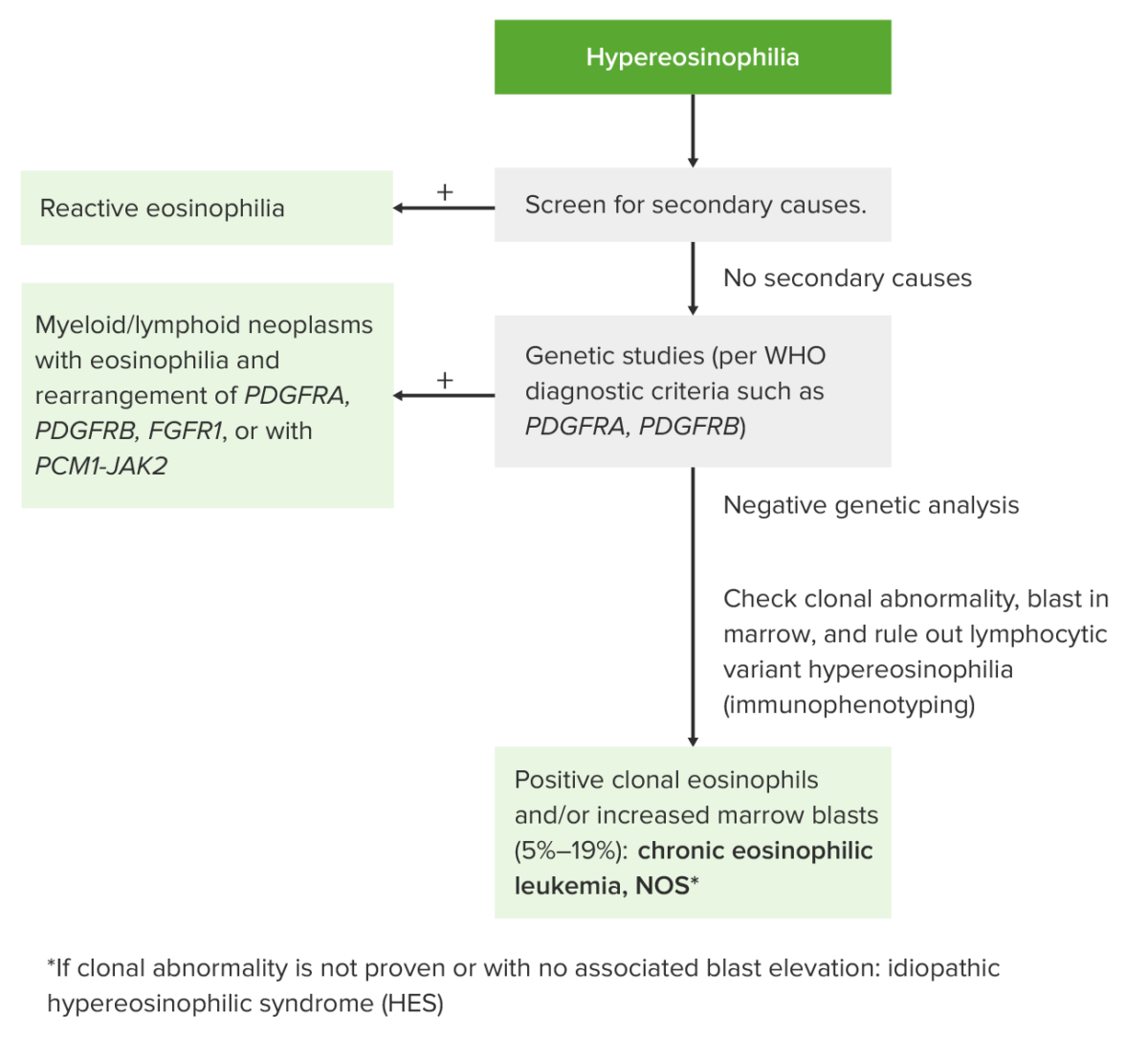
Abordaje de la hipereosinofilia
Imagen por Lecturio.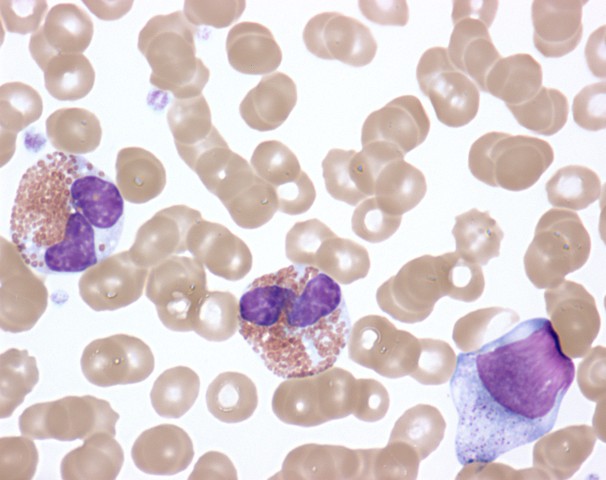
Eosinófilos activados en sangre periférica de un paciente con síndrome hipereosinofílico que muestra aclaramiento citoplasmático, displasia nuclear y presencia de formas inmaduras
Imagen: “Activated Eosinophils in Idiopathic Hypereosinophilic Syndrome (9125007255)” por NIAID. Licencia: CC BY 2.0